|
#1
| |||
| |||
|
I want to give the exam of Central Teacher Eligibility Test and I want to get the previous year question papers so can you provide me that as it is very urgent for me? Here I am giving you Syllabus and Previous Years Question Paper of Central Teacher Eligibility Test (CTET). Central Teacher Eligibility Test Syllabus: Child Development and Pedagogy: • Child Development (Primary School Child) Concept of development and its relationship with learning • Principles of the development of children • Influence of Heredity & Environment • Socialization processes: Social world & children (Teacher, Parents, Peers) • Piaget, Kohlberg and Vygotsky: constructs and critical perspectives • Concepts of child-centered and progressive education • Critical perspective of the construct of Intelligence • Multi Dimensional Intelligence • Language & Thought • Gender as a social construct; gender roles, gender-bias and educational practice • Individual differences among learners, understanding differences based on diversity of language, caste, gender, community, religion etc. • Distinction between Assessment for learning and assessment of learning; School-Based Assessment, Continuous & Comprehensive Evaluation: perspective and practice • Formulating appropriate questions for assessing readiness levelsof learners; for enhancing learning and critical thinking in the classroom and for assessing learner achievement. • Concept of Inclusive education and understanding children with special need • Addressing learners from diverse backgrounds including disadvantaged and deprived • Addressing the needs of children with learning difficulties, ‘impairment’ etc. • Addressing the Talented, Creative, Specially abled Learners Learning and Pedagogy: • How children think and learn; how and why children ‘fail’ to achieve success in school performance. • Basic processes of teaching and learning; children’s strategies of; learning as a social activity; social context of learning. • Child as a problem solver and a ‘scientific investigator’ • Alternative conceptions of learning in children, understanding children’s ‘errors’ as significant steps in the learning process. • Cognition & Emotions • Motivation and learning • Factors contributing to learning– personal & environmental Language I Language Comprehension • Reading unseen passages – two passages one prose or drama and one poem with questions on comprehension, inference, grammar and verbal ability (Prose passage may be literary, scientific, narrative or discursive) • Pedagogy of Language Development Learning and acquisition • Principles of language Teaching • Role of listening and speaking; function of language and how children use it as a tool • Critical perspective on the role of grammar in learning a language for communicating ideas verbally and in written form • Challenges of teaching language in a diverse classroom; language difficulties, errors and disorders Language Skills • Evaluating language comprehension and proficiency: speaking, listening, reading and writing • Teaching- learning materials: Textbook, multi-media materials, multilingual resource of the classroom • Remedial Teaching Language – II Comprehension • Two unseen prose passages (discursive or literary or narrative or scientific) with question on comprehension, grammar and verbal ability • Pedagogy of Language Development Learning and acquisition • Principles of language Teaching • Role of listening and speaking; function of language and how children use it as a tool • Critical perspective on the role of grammar in learning a language for communicating ideas verbally and in written form; • Challenges of teaching language in a diverse classroom; language difficulties, errors and disorders Language Skills • Evaluating language comprehension and proficiency: speaking,listening, reading and writing • Teaching – learning materials: Textbook, multi-media materials, multilingual resource of the classroom • Remedial Teaching Mathematics: • Geometry • Shapes & Spatial Understanding • Solids around Us • Numbers • Addition and Subtraction • Multiplication • Division • Measurement • Weight • Time • Volume • Data Handling • Patterns • Money Family and Friends: 1.Relationships 2.Work and Play 3.Animals 4.Plants Food Shelter Water Travel Things We Make and Do CTET Syllabus of Paper 2: 1. Number System Knowing our Numbers Playing with Numbers Whole Numbers Negative Numbers and Integers Fractions 2. Algebra Introduction to Algebra Ratio and Proportion 3. Geometry Basic geometrical ideas (2-D) Understanding Elementary Shapes (2-D and 3-D) Symmetry: (reflection) Construction (using Straight edge Scale, protractor,compasses) 4. Mensuration 5.Data handling Nature of Mathematics/Logical thinking Place of Mathematics in Curriculum Language of Mathematics Community Mathematics Evaluation Remedial Teaching Problem of Teaching Science: 1. Food Sources of food Components of food Cleaning food 2. Materials Materials of daily use 3. The World of the Living 4. Moving Things People and Ideas 5. How things work Electric current and circuits Magnets 6. Natural Phenomena 7. Natural Resources Nature & Structure of Sciences Natural Science/Aims & objectives Understanding & Appreciating Science Approaches/Integrated Approach Observation/ Experiment/ Discovery (Method of Science) Innovation Text Material/Aids Evaluation– cognitive/ psychomotor/ affective Problems Remedial Teaching Social Studies/Social Sciences 1. History When, Where and How The Earliest Societies The First Farmers and Herders The First Cities Early States New Ideas The First Empire Contacts with Distant lands Political Developments Culture and Science New Kings and Kingdoms Sultans of Delhi Architecture Creation of an Empire Social Change Regional Cultures The Establishment of Company Power Rural Life and Society Colonialism and Tribal Societies The Revolt of 1857-58 Women and reform Challenging the Caste System The Nationalist Movement India After Independence 2. Geography Geography as a social study and as a science Planet: Earth in the solar system Globe Environment in its totality: natural and human environment Air Water Human Environment: settlement, transport and communication Resources: Types-Natural and Human Agriculture 3. Social and Political Life Diversity Government Local Government Making a Living Democracy State Government Understanding Media Unpacking Gender The Constitution Parliamentary Government The Judiciary Social Justice and the Marginalised Previous Years Question Paper of CTET: CTET Question Paper 1     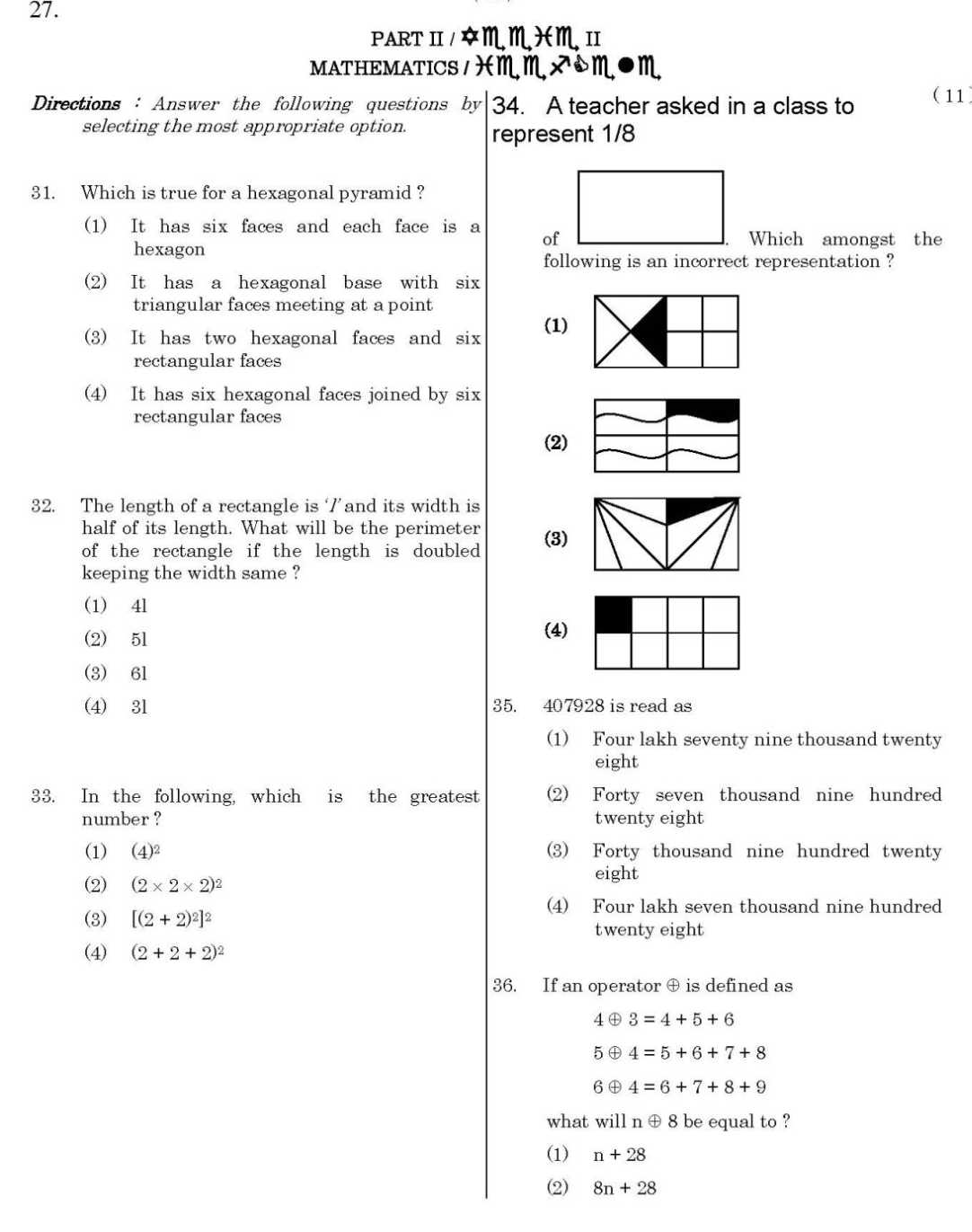 Last edited by Aakashd; June 8th, 2019 at 10:10 AM. |
|
#2
| ||||
| ||||
|
As you want to get the previous year question papers of Central Teacher Eligibility Test so here is the information of the same for you: Previous year question papers of Central Teacher Eligibility Test Directions : Answer the following questions by selecting the most appropriate option. 1. ‘‘Development is a never ending process.’’ This idea is associated with (1) Principle of integration (2) Principle of interaction (3) Principle of interrelation (4) Principle of continuity 2. Four distinct stages of children’s intellectual development are identified by (1) Skinner (2) Piaget (3) Kohlberg (4) Erikson 3. Parents should play a ___________ role in the learning process of young children. (1) sympathetic (2) neutral (3) negative (4) proactive 4. The ‘insight theory of learning’ is promoted by (1) Jean Piaget (2) Vygotsky (3) ‘Gestalt’ theorists (4) Pavlov 5. Motivation, in the process of learning, (1) makes learners think unidirectionally (2) creates interest for learning among young learners (3) sharpens the memory of learners (4) differentiates new learning from old Learning 6. Which of the following is not a sign of an intelligent young child ? (1) One who carries on thinking in an abstract manner (2) One who can adjust oneself in a new environment (3) One who has the ability to cram long essays very quickly (4) One who has the ability to communicate fluently and appropriately 7. Which is the place where the child’s ‘cognitive’ development is defined in the best way ? (1) Auditorium (2) Home (3) Playground (4) School and classroom environment 8. The stage in which a child begins to think logically about objects and events is known as (1) Pre-operational stage (2) Concrete operational stage (3) Sensori-motor stage (4) Formal operational stage 9. Which of the following is not related to the socio-psychological needs of the child ? (1) Regular elimination of waste products from the body (2) Need for company (3) Need for appreciation or social approval (4) Need for emotional security 10. Which of the following will foster creativity among learners ? (1) Emphasizing achievement goals from the beginning of school life (2) Coaching students for good marks in examination (3) Teaching the students the practical value of good education (4) Providing opportunities to question and to nurture the innate talents of every learner 11. ‘Mind mapping’ refers to (1) drawing the picture of a mind (2) researching the functioning of the mind (3) a technique to enhance comprehension (4) a plan of action for an adventure 12. ‘‘A yung child responds to a new situation on the basis of the response made by him/her in a similar situation as in the past.’’ This is related to (1) ‘Law of Attitude’ of learning process (2) ‘Law of Readiness’ of learning (3) ‘Law of Analogy’ of learning (4) ‘Law of Effect’ of learning 13. The best way, specially at primary level, to address the learning difficulties of students is to use (1) easy and interesting textbooks (2) story-telling method (3) a variety of teaching methods suited to the disability (4) expensive and glossy support material 14. Education of children with special needs should be provided (1) in special schools (2) by special teachers in special schools (3) along with other normal children (4) by methods developed for special children in special schools 15. ‘Dyslexia’ is associated with (1) Reading disorder (2) Behavioural disorder (3) Mental disorder (4) Mathematical disorder 16. ___________ is not considered a sign of ‘being gifted’. (1) Novelty in expression (2) Curiosity (3) Creative ideas (4) Fighting with others 17. A student of V-grade with ‘visual deficiency’ should be (1) treated normally in the classroom and provided support through Audio CDs (2) given special treatment in the classroom (3) excused to do a lower level of work (4) helped with his/her routine-work by parents and friends ( 4 ) ( 5 ) 18. Which of the following statements cannot be considered as a feature of the process of learning ? (1) Learning is goal-oriented (2) Unlearning is also a learning process (3) Educational institutions are the only place where learning takes place (4) Learning is a comprehensive process 19. Learning can be enriched if (1) teachers use different types of lectures and explanation (2) due attention is paid to periodic tests in the class (3) situations from the real world are brought into the class in which students interact with each other and the teacher facilitates (4) more and more teaching aids are used in the class 20. To make assessment a ‘useful and interesting’ process, one should be careful about (1) using a variety of ways to collect information about the student’s learning across the scholastic and coscholastic boundaries (2) using technical language to give feedback (3) making comparisons between different students (4) labelling students as intelligent or average learners 21. A teacher, because of his/her democratic nature, allows students to sit all over the class. Some sit together and discuss or do group reading. Some sit quietly and read themselves. A parent does not like it. Which of the following may be the best way to handle the situation ? (1) Parents should show trust in the teacher and discuss the problem with the teacher (2) Parents should take away the child from that school (3) Parents should complain against the teacher to the principal (4) Parents should request the principal to change the section of their ward 22. Which of the following should be considered the most important quality of a teacher at primary level ? (1) Competence in methods of teaching and knowledge of subjects (2) Competence to teach in highly standardised language (3) Eagerness to teach (4) Patience and perseverance 23. ___________ is considered a sign of motivated teaching. (1) Questioning by students (2) Pin drop silence in the class (3) Maximum attendance in the class (4) Remedial work given by the teacher ( 6 ) ( 7 ) 24. At lower classes, play-way method of teaching is based on (1) psychological principles of development and growth (2) sociological principles of teaching (3) theory of physical education programmes (4) principles of methods of teaching 25. The term ‘curriculum’ in the field of education refers to (1) evaluation process (2) text-material to be used in the class (3) methods of teaching and the content to be taught (4) overall programme of the school which students experience on a day-to-day basis 26. According to Piaget, at which of the following stages does a child begin to think logically about abstract propositions ? (1) Sensori-motor stage (Birth – 02 years) (2) Pre-operational stage (02 – 07 years) (3) Concrete operational stage (07 – 11 years) (4) Formal operational stage (11 years and up) 27. A teacher should make an attempt to understand the potentialities of her/his students. Which of the following fields is related to this objective ? (1) Media – Psychology (2) Educational Psychology (3) Educational Sociology (4) Social Philosophy 28. Kritika who does not talk much at home, talks a lot at school. It shows that (1) she does not like her home at all (2) her thoughts get acknowledged at school (3) the school provides opportunities to children to talk a lot (4) teachers demand that children should talk a lot at school 29. ‘‘Children actively construct their understanding of the world’’ is a statement attributed to (1) Kohlberg (2) Skinner (3) Piaget (4) Pavlov 30. In which of the following stages do children become active members of their peer group ? (1) Early childhood (2) Childhood (3) Adolescence (4) Adulthood PART II Directions : Answer the following questions by selecting the most appropriate option. 31. Which is true for a hexagonal pyramid ? (1) It has six faces and each face is a hexagon (2) It has a hexagonal base with six triangular faces meeting at a point (3) It has two hexagonal faces and six rectangular faces (4) It has six hexagonal faces joined by six rectangular faces 32. The length of a rectangle is ‘ l’ and its width is half of its length. What will be the perimeter of the rectangle if the length is doubled keeping the width same ? (1) 4l (2) 5l (3) 6l (4) 3l 33. In the following, which is the greatest number ? (1) (4)2 (2) (2 2 2)2 (3) [(2 + 2)2]2 (4) (2 + 2 + 2)2 34. A teacher asked in a class to represent 1/8 of . Which amongst the following is an incorrect representation ? 35. 407928 is read as (1) Four lakh seventy nine thousand twenty eight (2) Forty seven thousand nine hundred twenty eight (3) Forty thousand nine hundred twenty eight (4) Four lakh seven thousand nine hundred twenty eight 36. If an operator is defined as 4 3 = 4 + 5 + 6 5 4 = 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 6 4 = 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 what will n 8 be equal to ? (1) n + 28 (2) 8n + 28 ( 10 ) ( 11 ) A (3) 8n + 36 ‘‘These days prices have started rising.’’ Which amongst the following graphs represents this situation ? 38. The weight of some mangoes is 2 kg 600 g and that of some apples is 1 kg 450 g. The weight of the mangoes is greater than that of the apples by (1) 4 kg 50 g (2) 1 kg 150 g (3) 1 kg 200 g (4) 150 g ( 12 ) 39. Examine the following matchstick patterns : If the pattern continues, how many matchsticks are needed in the 15th stage ? (1) 105 (2) 65 (3) 61 (4) 62 40. Look at the following table : Station Bus 1 Bus 2 Bus 3 New Delhi Departure 19:15 12:30 16:45 Faridabad Arrival 20:22 13:25 19:10 Departure 20:37 13:35 19:22 Mathura Arrival 00:40 18:10 21:55 Which bus takes the least time to reach Mathura from New Delhi ? (1) Bus 1 (2) Bus 2 (3) Bus 3 (4) Both Bus 2 and Bus 3 take equal time In a dice, the numbers on the opposite faces add up to 7. Which amongst the following will fold into a dice ? ( 13 ) ( 14 ) 42. The number 49532 rounded off to the nearest thousand is (1) 49000 (2) 49500 (3) 41000 (4) 50000 43. How many 4-digit numbers are there in the Hindu-Arabic Numeration System ? (1) 99 (2) 8999 (3) 9999 (4) 9000 44. is ¾ of a `unit’. What will be 1½ ? 45. A rhombus has diagonals of length 8 cm and 6 cm. Find its perimeter. (1) 18 cm (2) 20 cm (3) 24 cm (4) 28 cm 46. When faced with word problems, Rajan usually asks ‘‘Should I add or subtract ?’’ ‘‘Should I multiply or divide ?’’. Such questions suggest (1) Rajan seeks opportunities to disturb the class (2) Rajan has problems in comprehending language (3) Rajan lacks understanding of number operations (4) Rajan cannot add and multiply 47. When teaching ‘shapes’, a teacher can plan a trip of historical places as (1) she has completed most of the syllabus well in time and needs to provide leisure (2) it would be a good break from the routine mathematics class and an opportunity to improve communicative skills (3) field trips have been recommended by CBSE, so they are a must (4) shapes are an integral part of any architecture and such trips encourage connections across disciplines ( 15 ) ( 16 ) 48. The NCF (2005) considers that Mathematics involves ‘a certain way of thinking and reasoning’. From the statements given below, pick out one which does not reflect the above principle : (1) The way the material presented in the textbooks is written (2) The activities and exercises chosen for the class (3) The method by which it is taught (4) Giving students set formulae to solve the numerical questions 49. Sequence the following tasks as they are taken up while developing the concept of measurement : a. Learners use standard units to measure length. b. Learners use non-standard units to measure length. c. Learners verify objects using simple observation. d. Learners understand the relationship between metric units. (1) a, b, d, c (2) b, a, c, d (3) c, b, a, d (4) d, a, c, b 50. Sequence the following tasks as they would be taken up while developing the understanding of shapes and space across primary classes : a. Matches the properties of 2-D shapes by observing their sides and corners b. Describes intuitively the properties of 2- D shapes c. Sorts 2-D shapes d. Describes the various 2-D shapes by counting their sides, corners and diagonals (1) d, b, a, c (2) c, b, d, a (3) a, d, b, c (4) c, a, d, b 51. ‘‘Problem solving’’ as a strategy of doing mathematics involves (1) extensive practice (2) using clues to arrive at a solution (3) activity based approach (4) estimation 52. The purpose of a diagnostic test in mathematics is (1) to know the gaps in children’s understanding (2) to give feedback to the parents (3) to fill the progress report (4) to plan the question paper for the endterm examination ( 17 ) ( 18 ) 53. Vikas teaches mathematics to a class of 56 students. He believes that conducting a test is effective if the feedback is given immediately. He conducted a short class test of 10 marks. What is the best possible way of giving the feedback effectively ? (1) He can let the students check each other’s answer (2) He can explain the solution of each problem on the board and ask the students to check their answer on their own (3) He can have a whole class discussion on ways in which they have got their solutions and which is the effective strategy to arrive at the correct answer (4) Pick out any copy at random and discuss the method followed in the copy on the board 54. To introduce the concept of area, a teacher can start with (1) comparing area of any figure with the help of different objects like palm, leaf, pencil, notebook, etc. (2) calculating area of a rectangle by finding length and breadth of a rectangle and using the formula for area of a rectangle (i.e. length ´ breadth) (3) calculating area of figures with the help of counting unit square (4) explaining of formulae for finding area of figures of different shapes 55. To introduce the concept of fractions, a teacher can begin with (1) identifying numerators and denominators of different fractions (2) finding fractions on a number line (3) writing fractions in the form a b of where b 0 (4) identifying fractional parts of things around them 56. While teaching comparison of fractions in which the numerators are same e.g. 3 5 and 3 7 Rohit’s response was ‘‘since the numerators are same and since 7 is larger than 5, therefore 3 7 is bigger than 3 5 .’’ This suggests that (1) Rohit does not understand the magnitude of fractions (2) Rohit does not know the concept of numerator and denominator (3) Rohit does not know the concept of equivalent fractions (4) Rohit has not practised well 57. When teaching addition of fractions, a teacher came across the following error : 1 2 1 3 2 5 What remedial action can the teacher take in such a situation ? (1) Ask the child to practise as much as she can (2) No intervention is needed because she will understand as she grows (3) Help the child to understand the magnitude of each fraction (4) Help the child to understand the concept of LCM ( 19 ) ( 20 ) 58. The chapters in the NCERT textbook of mathematics of Class-IV have titles like ‘‘The Junk Seller’’, ‘‘Trip to Bhopal’’, ‘‘The Way the World Looks’’. This shift has been done to (1) challenge the students to guess the mathematical content in the chapters (2) make them understand differently (3) make it interesting by relating it to everyday life (4) know about selling junk and travelling 59. To be a ‘‘good’’ mathematician one must be able to (1) memorise most of the formulae (2) solve the problem in no time (3) understand, apply and make connections across the concepts (4) master the techniques of answering questions 60. ‘‘Start a discussion in the class on things in the child’s environment which roll and slide. Help children to look at their shapes and see how some things roll and others slide.’’ Source : Math Magic II, NCERT Suggestions like this have been given in the NCERT textbook of Class-II to help a teacher understand that (1) discussion is the best strategy for the mathematics classroom (2) it is imperative for the teachers to draw the children’s attention to the things around them (3) discussions supplemented with demonstration help students to understand concepts better (4) discussions bring multiple perspectives into the classroom PART III ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES Directions : Answer the following questions by selecting the most appropriate option. 61. It has been observed that the process of digestion is faster inside the stomach than outside because (1) the digestive juices inside the stomach are acidic, while outside they are alkaline (2) the amount of digestive juices produced in the stomach in the presence of food is much more (3) the digestive juices when kept outside the stomach become inactive (4) the food is churned in the stomach thereby increasing the surface area for quicker enzyme action 62. Cooked rice can be preserved for a longer time in a refrigerator because (1) microbes become inactive at low temperature (2) microbes are destroyed and killed at low temperature (3) moisture content in the food is reduced at low temperature (4) refrigerators contain certain chemicals which kill the microbes 63. A lemon sinks in normal water but floats in salty water because the density of (1) salt water is more than normal water (2) normal water is more than salt water (3) lemon increases in salt water (4) lemon decreases in salt water 64. Malaria can be detected by testing the blood for the presence of (1) ruptured liver cells in blood (2) larvae of mosquito in blood (3) eggs of mosquito in red blood cells (4) Plasmodium in red blood cells A 65. A Shooting Star is a (1) shining object which moves with a constant speed in the atmosphere (2) star with a tail at the end (3) meteoroid which catches fire as it enters the Earth’s atmosphere (4) star which moves with a constant speed 66. Durga lives in a village and cooks food on a chulha (earthen stove) using wood or cow dung cakes as fuel. She has been suffering from severe cough for the last three months. This may be due to the (1) carbon monoxide produced by burning fuel which may have been deposited in her respiratory tract (2) soot produced by burning the fuels which may have been deposited in her respiratory tract (3) smoke produced by burning fuels which may have caused her allergy (4) old age and pollution inside and outside her hut 67. A man with blood group ‘O’ marries a woman with blood group ‘A’. The chance of their first child having blood group ‘O’ is (1) 50% (2) 100% (3) 25% (4) 75% 68. The difference between boiling and evaporation is that (1) boiling causes a change of state of water while evaporation does not (2) evaporation can take place at any temperature while boiling cannot (3) boiling causes reduction in volume of liquid while evaporation does not (4) changing of boiling liquid into vapour can be seen but evaporation cannot be seen ( 23 ) 69. A farmer wanted to separate the grains from the chaff. This can be achieved by the process called (1) Threshing (2) Winnowing (3) Harvesting (4) Handpicking 70. In rural areas, cow dung is used to coat the floor and walls of huts to (1) make them smooth and clean (2) make them rough to increase friction (3) give a natural colour to the floor (4) keep the insects away 71. Mira and Divya are young girls. Mira likes to eat samosas, cutlets and bread. Divya, on the other hand, takes an iron deficient diet. Which of the following disorders are Mira and Divya likely to suffer from, respectively ? (1) Anaemia and night blindness (2) Obesity and anaemia (3) Obesity and scurvy (4) Scurvy and anaemia 72. Vitamins are substances (1) required as medicines to make us healthy (2) that build muscles to keep us strong (3) required in small quantities to prevent deficiency diseases (4) that increase our metabolic rate leading to loss of weight 73. Chipko Movement was strengthened under the leadership of (1) Amrita Devi Bishnoi (2) Medha Patkar (3) A.K. Banerjee (4) Sunder Lal Bahuguna ( 24 ) 74. Rina separated the garbage from the house into two piles as shown below : Rina has separated the garbage waste into two piles depending on the criteria (1) can be decomposed/cannot be decomposed (2) can be recycled/cannot be recycled (3) are household/industrial waste (4) have odour/are odourless 75. An egret bird is often seen on a buffalo’s back. This is because the egret (1) loves to sing while sitting on the buffalo’s back (2) rests after flying for a while (3) feeds on parasites on the buffalo’s back (4) feeds on insects present in the grass 76. Which of the following statements is not an objective of teaching EVS at the primary level ? (1) Arouse curiosity about the natural and social environment (2) Engage in exploratory and hands-on activities that lead to the development of cognitive and psychomotor skills (3) To load learners with terms and definitions for assessment (4) To internalise the values of concern for life and environment 77. The idea of showing a sample of a railway ticket in the EVS textbook is to (1) give the students an idea of the rail fare (2) provide them the knowledge of various abbreviations used in the ticket (3) enhance the skills of students to arrive at conclusions (4) give them an opportunity to interact with real information and develop the skill of observation ( 25 ) 78. The concept of ‘seed germination’ can be taught best by (1) howing germinated seeds to the class and explaining the process of germination (2) presenting the germination stages through drawings on the board (3) asking the students to perform an activity to sow seeds, observe different stages and draw them (4) showing photographs of seed germination 79. Which one of the following is not an objective of including riddles and puzzles in the EVS textbook ? (1) To develop critical thinking ability in students (2) To develop reasoning ability in students (3) To confuse the mind of the students and let them enjoy the confusion (4) To develop curiosity and ability to think creatively 80. As an EVS teacher, you plan to take the students to the zoo. Which of the following activities would you not allow the students to undertake ? (1) Collect photographs of the animals they expect to see at the zoo (2) Take their drawing books along with them to draw what they see at the zoo (3) Take along lots of eatables for the animals at the zoo (4) Try to find out the food taken up by different animals at the zoo ( 26 ) 81. At the primary stage, assessments should consist of (1) continuous and unstructured teacher observations to be shared with learners and parents (2) formal tests and games done every week and recorded in the Report Card (3) half-yearly and annual examinations at the end of the year (4) home assignments and class assignments every week to rate young learners under the categories of pass or fail 82. Simple experiments and demonstrations can be performed in the EVS class (1) to enable children to learn on their own and sharpen their observation skills (2) to follow what is being done in the senior classes (3) to discuss ideas, record and analyse observations on the basis of questions raised by students (4) to control the students to ensure discipline in the class 83. Which of the following statements about assignments is correct ? (1) Assignments need to be given as classwork followed by homework every day to provide variety and practice (2) Assignments should be the only method of assessment (3) Assignments provide learners an opportunity to search for information, construct their own ideas and articulate them (4) Assignments can be done by parents, brothers or sisters depending on the talent that they possess ( 27 ) 84. The skills required to read a map include (1) excellent drawing and painting skills (2) ability to use calculations and sketch positions on a globe (3) excellent communication skills to draw out the expressive ability (4) ability to understand relative position of places, distances and directions 85. The use of poems and story telling to explain concepts in an EVS class helps to (1) make the lesson enjoyable and interesting (2) promote the ability to imagine and explore the nature of the world at the local and global level (3) take care of the language and cultural diversity among learners (4) channelize the energies of the students in the right direction 86. To make children aware of different kinds of fuel, a teacher can (1) show pictures of fuels on a chart (2) ask children to list different fuels (3) show some samples of fuels in the class (4) discuss with children about possible kinds of fuel that can be used for cooking, along with a short film 87. Giving importance to individual experiences of children in an EVS class will benefit the teacher (1) to know the unique experiences of children (2) to help and improve the language and communication skills of the children (3) to connect the subject to the learners’ experiential world and promote reflection and learning (4) to save her energy as children enjoy talking 88. Which of the following represents one of the objectives of teaching EVS at Primary School ? (1) To make learners aware of technical terms and definitions (2) To assess technical terms related to EVS (3) To inform the learners about the books they should read to expand their knowledge (4) To connect the experiences of the learners in school with the outside world 89. A school planned an educational trip for Class-V students to Rajasthan. What would be your expectation from the children during the visit ? (1) They should enjoy themselves (2) They should observe keenly, make notes and share their observations with other students and the teacher (3) They should note down their questions, if any, and ask the parents after reaching home (4) They should observe everything without asking questions about it 90. After the lunch break, while teaching EVS, you find that students are not taking interest in the lesson. What would you do ? (1) Use audio-visual aids based on multiple intelligences to make the lesson interesting (2) Change the topic immediately (3) Take the children out to play in the ground (4) Ask them to put their heads down on the desk and relax ( 29 ) PART IV LANGUAGE I ENGLISH Directions : Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow (Q. No. 91 to 99) by selecting the most appropriate option. 1 Max Weber laid the foundation for my belief that decent and hard-working people with high aspirations make great nations, no matter what the odds are. This was the first piece of the development puzzle for me. Mahatma Gandhi opened my eyes to the importance of good leadership in raising the aspirations of people, making them accept sacrifices to achieve a grand vision, and most importantly, in converting that vision into reality. He unleashed the most powerful instrument for gaining trust – leadership by example. He ate, dressed, travelled and lived like the poor. Walking the talk was extremely important to the Mahatma who understood the pulse of our people like no other Indian leader. The biggest lesson for me from Gandhi’s book and life is the importance of leading by example. I realized fairly early that this was the second piece of the development puzzle. 2 Frantz Fanon’s book on the colonizer mindset of elites in a post-colonial society opened my eyes to the role of the bureaucracy and the elite in decelerating the progress of the poor and the disenfranchised. The colonial mindset of the ‘dark elite in white masks’ in a post-colonial society – the mindset that the ruled and the rulers have different sets of rights and responsibilities with a huge asymmetry in favour of the rulers — was indeed the third piece of the development puzzle. I see this attitude of the Indian elite every day in how they send their children to English medium schools while forcing the children of the poor into vernacular schools, extol the virtues of poverty while living in luxury, and glorify the rural life while they sit comfortably in cities. Source : ‘A Better India, A Better World’ – N.R. Narayana Murthy (Adapted) 91. The main purpose of the author in the above passage is to (1) discuss the different writers he has read (2) argue why India should not be considered a developed country (3) delineate the lessons he has learnt for the development of a nation (4) prioritise goals for only economic development of India 92. The first piece of the development puzzle, according to the author, is (1) creating a team of industrious people for a national cause (2) the importance of decent, inspired and industrious people for a nation’s development (3) imbuing the citizens of the country with decency and aspirations (4) the need for making people understand the importance of leading an idealistic and simple life 93. Mahatma Gandhi proved that only leadership by example can (1) mobilise the people of a country against colonial rule (2) fully and properly understand the pulse of the people of a country (3) gain the trust of the people so that they are willing to make sacrifices for a larger cause (4) inspire people to eat, dress, travel and live like the poor ( 30 ) ( 31 ) 94. The expression ‘walking the talk’ means (1) addressing public gatherings in an election campaign (2) talking to the common people by mingling with them (3) being diplomatic in one’s behaviour and words (4) practising what one preaches 95. The colonial mindset of ‘dark elite in white masks’ with reference to the passage is (1) discriminating people on the basis of the colour of their skin (2) an assumption that the administrators and politicians have more rights and privileges than the common people (3) looking down upon the poor and the disenfranchised (4) the bureaucratic practice of according topmost priority to confidentiality in official dealings 96. Extolling ‘the virtues of poverty while living in luxury’ is an instance of (1) the hypocrisy of the people of our country (2) practising what you preach (3) the ideal of a good government (4) the need to make people adopt a simple life 97. ‘I realized fairly early that this was the second piece of the development puzzle.’ The underlined part of this sentence is a/an (1) Adjective clause (2) Adverbial phrase (3) Noun clause (4) Verb clause 98. Pick out a word or phrase from the second paragraph of the passage that means the same as ‘to make (something) go slower’. (1) disenfranchised (2) dark elite (3) decelerating (4) vernacular 99. ‘Development’ is a noun with ‘-ment’ as a suffix. Which of the following will become a noun if we add the suffix ‘-ment’ to it ? (1) Extort (2) Enter (3) Enchant (4) Endure Directions : Read the poem given below and answer the questions that follow (Q. No. 100 to 105) by selecting the most appropriate option. On A Tired Housewife Here lies a poor woman who was always tired, She lived in a house where help wasn’t hired: Her last words on earth were: ‘Dear friends, I am going To where there’s no cooking, or washing, or sewing, For everything there is exact to my wishes, For where they don’t eat there’s no washing of dishes. I’ll be where loud anthems will always be ringing, But having no voice I’ll be quit of the singing. Don’t mourn for me now, don’t mourn for me never, I am going to do nothing for ever and ever.’ Anonymous 100. The woman described in the poem (1) was very busy doing chores (2) was no more (3) lived in her own house (4) worked in the house of a rich man ( 32 ) A 101. The woman was always tired because (1) she was physically very weak (2) she was suffering from a serious ailment (3) she did all the household work without any help (4) she had hardly anything to eat 102. The woman wanted to go to a place where (1) people didn’t sing or dance (2) people didn’t cook, wash or sew (3) people would take good care of her (4) people would sincerely mourn for her 103. The woman’s account in the poem shows (1) how overworked a housewife is (2) that there is no work in heaven (3) how a woman can escape from work (4) how we should help each other 104. ‘For everything there is exact to my wishes,’ In this line, the word ‘exact’ can be interpreted to mean (1) contrary (2) contributing (3) according (4) leading 105. The rhyme pattern in the poem is (1) ab, ab, ab, ab, ab (2) aa, ab, cd, cd, ee (3) aa, bb, cc, dd, ee (4) aa, ab, bc, cd, de Directions : Answer the following questions by selecting the most appropriate option. 106. Ria is unable to pronounce the words ‘smile’ and ‘school’ clearly. As her teacher, what will you do ? (1) Make Ria repeat the ‘words’ many times (2) Make Ria understand the meaning and sound pattern and get the class as a whole to listen to these words through an audio-visual medium (3) Humiliate Ria by isolating her and asking her to repeat the words (4) Asking the entire class to repeat the words and appreciating Ria when she repeats them correctly 107. Lalita, a teacher of young learners, provides them with opportunities to play with clay, water and sand so as to (1) build fine motor skills, especially of the fingers and thumb (2) encourage play with no other objective (3) please them and make them happy (4) dirty their hands so that they may learn to wash them 108. The spoken skills in a language teaching classroom can be developed through (1) engaging in small talk as confident agressive learners (2) emotionally connecting with learners (3) enabling activities with a focus on conversation skills leading to communicative competence (4) group activities where learners can talk in whichever language they would like to ( 33 ) A 109. Ritu often makes errors in Subject-Verb concord. The teacher can help her by (1) taking up many examples for the entire class and paying special attention to Ritu (2) explaining to her the rules of grammar (3) asking Ritu to learn the rules and scolding her (4) asking Ritu to write the rules ten times in her notebook 110. How will a teacher best teach ‘writing’ skills to a class ? (1) By brainstorming ideas and asking students to write in their own words (2) By asking students to write neatly (3) Through dictation (4) By asking students to learn articles and rewrite them 111. In a diverse classroom, learners find it difficult to speak and write good English and often lapse into their mother-tongue because (1) they are not motivated to learn (2) they lack enough competence and the structures of the two languages are different (3) they do not have the ability to learn English (4) they are slow learners 112. Read the two sentences given below : The lizard ate the fly. The fly ate the lizard. A teacher can use this example to explain that (1) there is no difference in the two sentences because both have the same words (2) when subject and object change positions, the meaning of the sentence changes (3) they are examples of reported speech (4) they are a collection of words 113. Mary, a young teacher, believes in personalised learning because she thinks that (1) every person must be exposed to learning (2) every learner is unique and needs to be given a chance to develop to the best of their ability (3) all learners must learn on their own (4) children must enjoy their learning 114. Grammar should be taught by (1) asking students to learn rules (2) making learners do written assignments (3) giving clear explanations (4) enabling practice in context ( 34 ) A 115. A child studying in Class-III says : ‘‘I dranked the water.’’ It indicates that the child (1) has not learnt grammar rules properly (2) should memorise the correct sentence (3) has overgeneralized the rule for making past tense verbs, showing that learning is taking place (4) is careless and needs to be told that she should be conscious of such errors 116. Children who are differently abled join a new school. Teachers give different reactions. Which one reflects the concept of inclusive education ? (1) ‘‘Oh ! How can I teach children who cannot even read ?’’ (2) ‘‘I’m worried that my class may not accept these children and some of the mischievous children may even harm the poor kids.’’ (3) ‘‘Good, it will provide a good opportunity for the children to learn to help each other and be supportive.’’ (4) ‘‘Such children should go to special schools where they will learn better.’’ 117. Leena uses Big Reading Books in her language classes to (1) allow students to read at home (2) ensure books carry a lot of information (3) use these illustrated colourful books for reading together (4) use them for big students of different ages 118. A teacher can cater to the learning styles of all the children by (1) teaching every lesson thoroughly and revising the lessons (2) testing the children frequently (3) advising the children to join drawing/dance/music classes (4) employing a variety of teaching methods and modes of assessment which cater to diversity among learners 119. The Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009 stipulates that learning should be (1) restricted to co-scholastic subjects (2) carefully monitored by frequent testing (3) through activities in a child-friendly manner (4) supported by extra coaching 120. As part of a class project, a teacher planned a salad fruit celebration day in which all learners needed to participate. The boys protested as they felt that boys do not cook. The teacher should (1) ignore such protests and tell the boys what she thinks of their bias (2) complain to the head of the school seeking action against the boys (3) make an attempt to counsel the boys, impressing upon them that gender stereotyping is not healthy (4) respect the sentiments of the boys and allow them not to participate in the class project ( 35 ) A PART V LANGUAGE II ENGLISH Directions : Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow (Q. No. 121 to 129) by selecting the most appropriate option. 1 Karuna Verma is bewildered. ‘‘I don’t know how she did it,’’ she says about her mother, Renu Chopra. Karuna’s childhood memories are of her father leaving late for office so that, by then, her mother would be back from work. Of her parents working in sync to make sure the kids were well taken care of. Of her mother handling kitchen and classroom with ease. 2 When her own daughter was born, Karuna too wanted to do the balancing act. But it did not turn out to be as easy as it seemed. For starters, her parents’ era was different from hers. As she was living with her husband in Andheri, Mumbai, away from their families, resuming work would have meant leaving her daughter with a maid while she was away. Her daughter’s formative years would be spent with an outsider, a thought that did not appeal to Karuna. She quit her teaching job in a school. 3 For a woman who was encouraged to be independent throughout her life, the decision to quit and stay at home was a difficult one. Ironically it was her mother who urged her to quit the job and become a full-time mother. For Karuna, being a housewife is one of the tougher jobs she has had. ‘‘I have no time for myself,’’ says Karuna. ‘‘I make sure all my personal work is done when Avni is asleep. Earlier I had a set routine. My husband and I used to wake up at 6 a.m. I would re-heat the food the maid had cooked the day before and pack it for lunch. Then we used to head off to work, and at night, we would go out. I had a lot of time to myself and for my husband then,’’ says Karuna. 4 The routine is quite different now. Karuna has taken to cooking. She wakes up quite early and makes sure all her work is done before the baby is up. The rest of the day flies by, pandering to two-year-old Avni’s needs. Source : The Week, March 13, 2011 (Adapted) 121. Karuna Verma is bewildered at (1) the amount of work that she has to do after becoming a mother (2) the late hours of work that her father followed (3) the responsibility of bringing up a daughter in a big city (4) her mother’s ability to combine her career with household work 122. ‘... parents working in sync’ means (1) parents pooling their resources together to take care of expenses (2) husband and wife sinking their differences to preserve domestic harmony (3) father earning and mother taking care of children (4) parents having staggered office hours and sharing household work 123. ‘... Karuna too wanted to do the balancing act.’ In this sentence, the term ‘balancing act’ implies (1) sharing of responsibilities by both husband and wife (2) a mother’s ability to look after her child without quitting her job (3) managing the time efficiently so that parents can spend quality time with their children (4) making adjustments in order to balance work and leisure properly 124. ‘As she was living with her husband in Andheri, Mumbai, away from their families ............ . In this sentence ‘their families’ refers to (1) Karuna’s mother and father’s families (2) Karuna’s husband’s family (3) Families of friends in Andheri, Mumbai (4) Karuna’s parents and in-laws A 125. Karuna’s parents and her husband’s parents probably lived (1) in Andheri, Mumbai (2) in some other city (3) in Mumbai but not in Andheri (4) with Karuna and her husband 126. Karuna decided to quit her job because (1) she was not interested in her teaching job (2) she did not want her daughter to spend her early years with a maid (3) she wanted to have more time to herself and for her husband (4) she wanted to pay more attention to her cooking 127. It was ironical that Karuna’s mother should advise her to quit her job and stay at home because (1) Karuna herself was keen on quitting her job (2) Karuna’s parents had insisted that household chores should be shared between husband and wife (3) Karuna’s parents had always advised her that home was much more important than career (4) Karuna’s mother herself had not quit her job to take care of children as she encouraged independence of women 128. After Karuna quit her job (1) she had a lot of time to herself and for her husband (2) she occupied herself with cooking to spend her time usefully (3) she sent her maid away as she felt that the maid was a bad influence on Avni (4) she had no time for herself as Avni needed all her attention and care 129. ‘‘I have no time for myself,’’ says Karuna. This sentence can be written in reported speech as (1) Karuna says that she have no time for herself (2) Karuna said that she had no time for myself (3) Karuna said that she had no time for herself (4) Karuna says that she had no time for herself Directions : Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow (Q. No. 130 to 135) by selecting the most appropriate option. 1 This was one of the Old Man’s pet schemes; and one about which he would brook no interference. Each child would review the events of his school week in his own words, in his own way; he was free to comment, to criticize, to agree or disagree, with any person, subject or method, as long as it was in some way associated with the school. No one and nothing was sacred, from the Headmaster down, and the child, moreover, was safe from any form of reprisal. 2 ‘‘Look at it this way,’’ Mr. Florian had said. ‘‘It is of advantage to both pupil and teacher. If a child wants to write about something which matters to him, he will take some pains to set it down as carefully and with as much detail as possible; that must in some way improve his written English in terms of spelling, construction and style. Week by week we are able, through his reviews, to follow and observe his progress in such things. As for the teachers, we soon get a pretty good idea what the children think of us and whether or not we are getting close to them. It may sometimes be rather deflating to discover that a wellprepared lesson did not really excite Johnny Smith’s interest, but, after all, the lesson was intended to benefit Johnny Smith, not his teacher. 130. The scheme, according to the Old Man, was useful because (1) it was meant to humiliate the teacher (2) it was meant to give power to the teacher (3) it was excellent feedback for the teacher, principal and school (4) he was slightly eccentric 131. ‘Pet schemes’ in line 1 refers to (1) a pet animal (2) a method he has advocated (3) a student he is fond of (4) a formula he had discovered 132. The ‘Old Man’ refers to (1) a teacher of the school (2) the headmaster called Mr. Florian (3) a parent of the school (4) a student of the school ( 43 ) A 133. The advantages of the scheme were many. Pick out the disadvantage from the list given below. (1) Effective feedback (2) Enhanced writing skills (3) Sometimes deflating to the teacher’s ego (4) Diagnostic and remedial for the student and the teacher 134. ‘Sacred’ in the context of the Headmaster means (1) that he was a holy man (2) that he was the powerful head of the school (3) that even ‘he’ was not above the ‘scheme’ he advocated for students (4) he believed in the sacred nature of all life 135. ‘Brook’ as a verb means ‘to tolerate’ in para 1. As a noun, it means (1) Suffer (2) Stream (3) Tolerance (4) Allow Directions : Answer the following questions by selecting the most appropriate option. 136. The Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2009 has included ‘all round development of the child’ as one of the aims of education because (1) every child grows rapidly between six to fourteen years (2) proper health care is essential (3) it nurtures the physical, mental and emotional aspects of the child (4) it ensures that every child is a part of a workforce 137. A textbook describes a domestic scene which shows the father cooking in the kitchen, the mother coming home from work and their son sewing. What is the concept conveyed ? (1) Removing gender bias (2) Dignity of labour (3) Division of labour among sexes (4) Work is worship 138. Teachers do not give the meaning of new words to learners directly because (1) learners already know the meaning of the words (2) vocabulary will not be enriched (3) learners do not like to be given the meaning of words (4) it prevents learners from discovering the meaning through puzzling out using clues 139. Reading for comprehension can be best achieved through (1) Helping learners speak words softly while reading (2) Learners reading silently and asking comprehension questions (3) Teaching learners to run a finger or pencil under the line being read (4) Asking the children to read the text aloud 140. Remedial teaching as part of Formative Assessment means (1) extra coaching by parents (2) teaching for gifted students (3) diagnosing and addressing gaps in learning (4) teaching beyond the textbooks 141. What type of questions promote thinking skills in children ? (1) Personal response questions (2) Closed-ended questions (3) Factual questions (4) Questions based purely on the reading text 142. Which of the following is a value associated with an inclusive classroom ? (1) Sympathy (2) Collaboration (3) Competition (4) Envy ( 44 ) A 143. ‘Students need to brainstorm ideas, organise them, draft, edit and revise their work,’ is a ‘process’ which reflects (1) Reading skills (2) Writing skills (3) Listening skills (4) Speaking skills 144. The aim of mechanical drills is to (1) improve the fluency of the learners (2) improve the accuracy of the learners (3) strengthen the role learning capacity of the learners (4) encourage creative use of language among the learners 145. Teachers help learners ‘construct’ their knowledge in English by (1) giving extensive language drills in which learners practice language items mechanically (2) enabling them to see the relationship between their prior knowledge and the new knowledge (3) giving the learners a lot of assignments and projects that will lead to much practice (4) correcting every mistake a learner makes and giving the relevant rule of grammar as immediate feedback 146. Learners are involved in individual activities, pair work, group work and whole-class work because these (1) enable the already over-worked teacher to preserve her energy thereby becoming more effective (2) afford the learners opportunities to use the language in a focused manner for real-life interaction (3) provide the learners enough opportunities to relax in a language classroom (4) have the sole aim of introducing variety in a language classroom 147. Which of the following is an instance of nonformal learning ? (1) Children learning through correspondence lessons (2) Children learning to draw from their art teacher (3) Children learning to cook from their parents (4) Children learning a new game from friends 148. Which of the following statements is true ? (1) While all formative tasks are meant for improving teaching-learning, some are used for assessment too. (2) Formative assessment helps us to grade students into good, average and poor. (3) All formative tasks are meant for assessment. (4) Formative assessment, to be effective, must be conducted only after teaching a lesson 149. Group project work helps in developing (1) competition among learners to excel in academics (2) good memory in the young learners (3) a high level of ambition to achieve (4) collaboration, critical thinking and problem solving 150. When young learners seem to lose interest in a lesson, the teacher should (1) allow them to go out and play (2) ask them to sleep for a while (3) tell a story or conduct an interesting activity (4) ask them to sit quietly for some time
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |
 |
| Tags |
| Eligibility, Previous questions papers |
| |