| Other Discussions related to this topic | ||||
| Thread | ||||
| B.Com previous year question papers of 1st year of University of Kerala | ||||
| need previous year question papers of m.com 1st year, of vinayaka mission university | ||||
| B.A.R.C sample papers and previous year question papers | ||||
| Previous year question papers of B.Com 1st year | ||||
| IIT JAM Previous Year Question Papers | ||||
| Madras University MBA 1st Year Previous year question papers | ||||
| TNOU MBA-Second Year Total Quality Management previous year’s question papers | ||||
| IFS previous year question papers | ||||
| BDS 1st year previous year question papers | ||||
| Previous year question papers of D.Ed CET | ||||
| NEED previous year question papers | ||||
| Previous year question papers of CAT | ||||
| B.Com 3rd year Mumbai University previous year question papers of Business Economics | ||||
| KVS TGT Previous Year Question Papers | ||||
| CSE previous year question papers | ||||
| Previous year question papers of B.Com 1st year of University of Kerala | ||||
| Previous year question papers for GRE | ||||
| B.Com 3rd year previous year question papers of Mumbai University | ||||
| STI previous year question papers | ||||
| KU BE ECE 3rd Year previous year’s question papers of Computer Hardware Design | ||||
|
#2
| ||||
| ||||
|
As you want to get the previous year question papers of Common Proficiency Test so here is the information of the same for you: Some content of the file have been given here: 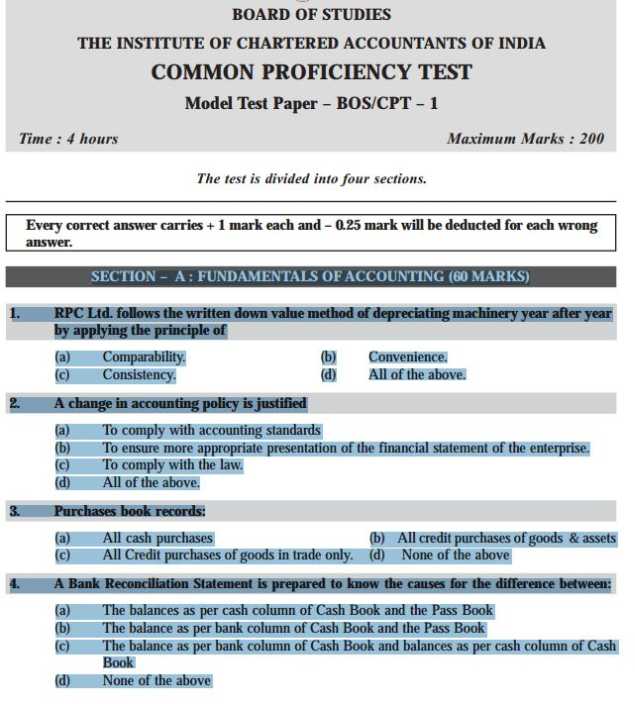  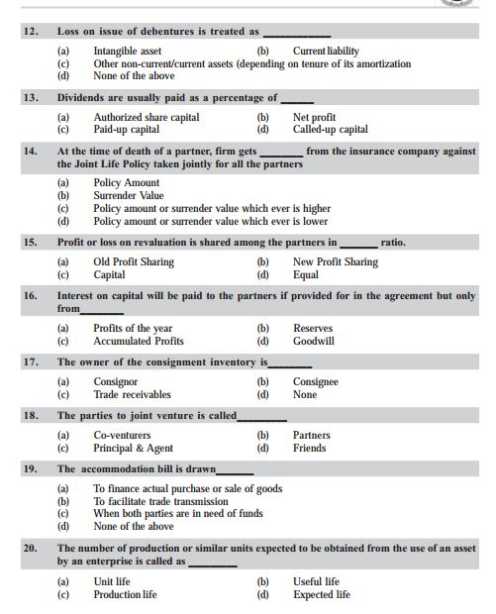 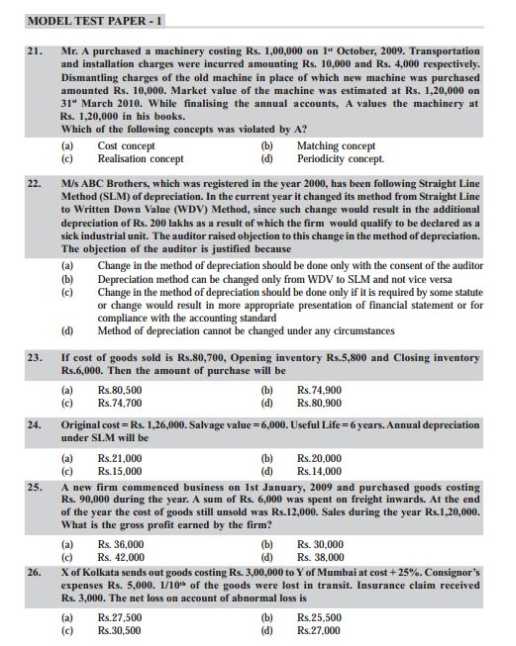 For more detailed information I am uploading a PDF files which are free to download:
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member Last edited by Aakashd; July 30th, 2018 at 08:19 AM. |
|
#5
| |||
| |||
|
As you want to get the previous year question papers of entrance exam of CPT so here is the information of the same for you: Previous year question papers of entrance exam of CPT     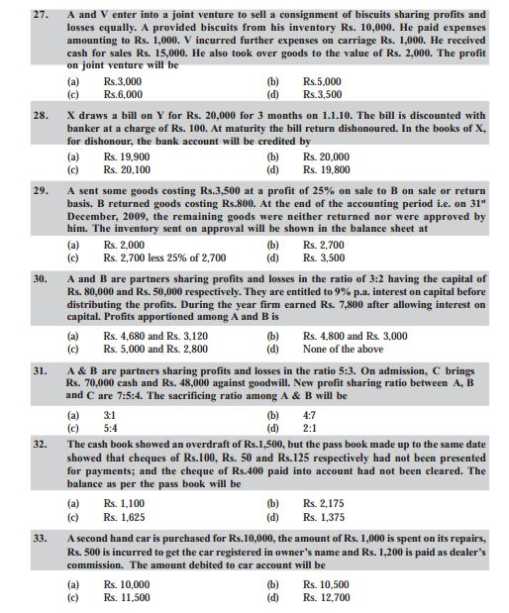 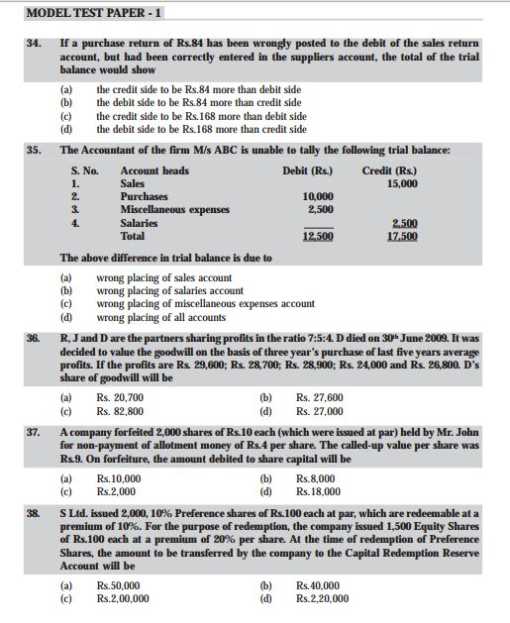
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member Last edited by Aakashd; July 30th, 2018 at 08:19 AM. |
|
#7
| ||||
| ||||
|
As you want to get the previous year question papers of CPT exam so here is the information of the same for you: Some content of the file has been given here: 1. Securities premium will be shown in Balance Sheet under the head of ____ a) Reserves & Surplus b) Miscellaneous exp. c) Loans & advances d) None 2. Which of the following provide frame work and accounting policies so that the financial statements of different enterprises become comparable. a) Business Standards b) Accounting Standards c) Market Standards d) None 3. Which of the following factor is not considered while selecting accounting policies? a) Prudence b) Substance over form c) Accountancy d) Materiality 4. Prorata basis allotted 5000 shares out of 7500 shares were applied, then 600 shares were applied by a person, how many shares allotted and how much amount adjusted to allotment account. If application money is Rs.2 per share ____, ______ a) 400 shares 600/- b) 200 shares 300/- c) 200 shares 600/- d) 300 shares 500/- 5. Debit the receiver & credit the giver is _____ account a) Personal b) Real c) Nominal d) All the above 6. Cash a/c is a ______ a) Real a/c b) Nominal c) Personal d) None 7. Which of the following is a characteristic of a partnership a) Artificial person b) Perpetual succession c) Limited liability of all partners d) None 8. X and Y are partners. Their profit sharing ratio is 5:3. They admitted a partner Z for 5 1 th share and contribute equally by the old partners, then new profit sharing ratio is __ a) 21:11:8 b) 20:8:9 c) 22:5:6 d) 5:3:2 9. Working capital is ______ a) Current Assets – Current liabilities b) Fixed Assets- Current liabilities c) Fixed Assets – liabilities d) Fixed Assets – Current Assets 10. Sub-partner in the partnership is a) a partner & the known person b) a two partners in the same firm c) two partners in the different time d) none of these 11. Securities premium used for the purpose of a) Dividends b) fully paid bonus shares c) capital loss d) none of these 12. Cash Rs. 6750 paid to M but debited to N account. What would be the effect? a) Trial balance b) Balance sheet c) Individual ledgers d) total debtors 13. If there is no agreement in between the partners for sharing profits & losses then they share profits or losses in the ratio of ____ a) capital ratio at the beginning b) equally c) capital ratio at the ending d) none of the above 14. Balance in share forfeiture account is shown under the head of ____ a) share capital b) reserves & surplus c) secured loans d) current liabilities 15. Dissolution of partnership automatically takes place a) if the business becomes unlawful b) if any one at the partners became insolvent c) if all the partners became insolvent d) all of the above 16. Error relating to fundamental aspect of ____ a) error of principle b) error of commission c) error of compensating d) error of omission 17. Liability on bills discounted at the time of final accounts is treated as ____ a) not an liability b) current liability c) differed liability d) contingent liability 18. Profit or loss on revaluation is shared by old partners in _____ ratio a) old profit sharing ratio b) new profit sharing ratio c) sacrificing ratio d) gaining ratio 19. Goods given as charity credited to _ account a) charity b) purchases c) drawings d) sales 20. In sale by description, subject matter can be in the form of a) sample words b) symbols c) numbers d) all of the above 21. Selection of accounting policies appropriation is not based on a) prudence b) amount involved c) substance over form d) materiality 22. As per accrual concept, which of the followings is not true a) revenue – expenditure = profit b) revenue – profit = expenditure c) sales + gross profit = revenue d) revenue = profit + expenditure 23. A company forfeited A’s 1000 shares Rs. 10 each @ 10% discount. But A failed to pay first call of Rs. 2 and final call of Rs. 4 and all the shares were re issued for Rs.8 per share as fully paid up. The loss on re issue is ____ to forfeited account will be _____ a) debited Rs. 1,000 b) debited Rs. 2,000 c) credited Rs. 2,000 d) No affected will be made 24. Mr. X sold goods to Mr. Y ask Mr. X to keep the goods with him for some time a) symbolic delivery b) actual delivery c) constructive delivery d) none of these 25. The credit balance in the ledger account shows a) revenue or an asset b) expense or an asset c) expense or an liability d) revenue or an liability 26. Subsidiary and journal are called a) primary books b) secondary books c) principal books d) cash book 27. Hari, Roy and Prasad are sharing in 3:5:1. The Roy retired then his share was taken by Prasad fully, then Hari & Prasad profit sharing ratio is _____ a) 1 : 2 b) 2 : 1 c) 3 : 2 d) equally 28. The liability of a partner in a firm to outside is _____ a) unlimited b) Unlimited up to their capital sharing ratio c) Unlimited up to their guaranteed amount d) Unlimited up to their profit sharing ratio 29. Cost of goods sold Rs.80,700 ; Opening stock Rs.5,800, Closing stock Rs.6,000 then purchases is Rs. ____ a) 80,500 b) 74,900 c) 74,700 d) 80,900 30. If JLP is taken jointly, on death of a partner ______ is distributed to partners against JLP a) Policy amount b) Surrender value c) Surrender value for dead partner & policy value for other d) none of these 31. Closing stock increased by 5000, gross profit ratio 10% then what will be the profit a) Gross profit will be increased by 5000 b) Gross profit will be decreased by 5000 c) Increase by 500 d) decrease by 500 32. Provision for doubtful debts is Rs.1000 & debtors are Rs.90,000 at end of year, provision for doubtful debt 1% required, then the entry a) P & L A/c Dr 900 To provision for doubtful debts 900 b) Provision for doubtful debts 900 To P & C A/c 900 c) P & L A/c Dr 100 To RDD A/c 100 d) none of these 33. If nothing is written about the accounting assumption to be followed it is presumed that a) They have been followed b) They have not been followed c) They are followed to some extent d) none of these 34. By preparing trail balance the errors can be revealed the following a) Posting an entry twice in the ledger b) Debit of Rs. 1000 is credited twice c) Omission of complete entry d) none 35. The sale __ is completed with reserved price a) sale by sample b) sale by description c) sale by auction d) sale by staple 36. The buyer refused to take delivery and the seller refused to take return then the goods are a) Deemed to be in transit b) Not deemed to be in transit c) both d) none of these 37. Payment made to creditor is with cash discount is ____ a) reduce asset & reduce liability, add to expenses b) reduce asset & reduce liability, add to income c) reduce asset & increase liability, add to expenses d) increase asset & reduce liability, add to income 38. Purchased the asset for Rs. 2,00,000 with available discount 20% then what amount should be credited to debentures A/c, when the purchase consideration is discharged by the issue of debentures. a) Rs.2,00,000 b) Rs.1,80,000 c) Rs. 1,60,000 d) Rs.2,40,000 39. A sold goods to B on credit for Rs. 10,000 but debited to C instead of B. What will be effected a) trail balance b) individual account c) balance sheet d) total debtors 40. On 31-3-09 the balance of the cash book is Rs. 7074 (credit) and balance as per bank statement is Rs. 3159 (debit). On scrutiny it was found that the difference was due to cheque issued but not yet presented for payment. The bank balance as on 31-3-09 will be shown in bank statement as ____ a) as bank overdraft Rs. 3159 b) as cash at bank Rs. 7074 c) as bank overdraft Rs. 7074 d) as cash at bank Rs. 3159 41. A purchased a computer on 1-4-06 for Rs.60,000 and another on 1-10-07 for Rs. 40, 000. He charged depreciation @ 20% p.a under straight line method. What will be the balance as on 31-03-09 a) Rs.40,000 b) Rs.64,000 c) Rs.52,000 d) Rs.48,000 42. A company forfeited 2000 shares of Rs. 10 each held by Mr. John for non payment of allotment money of Rs. 4 per share. The called up value per share was Rs. 9 on forfeiture. The amount debited to share capital will be Rs._____ a) 10,000 b) 8,000 c) 2,000 d) 18,000 43. Cost of goods sold Rs.10,000, Opening stock Rs.2,000 and Closing stock Rs. 3,000. Find the amount of purchases _____ a) Rs.10,000 b) Rs.11,000 c) Rs.15,000 d) Rs.9,000 44. A draws a bill on B. B did not accept the same. Which of the following Journal entries in the books of A a) B/R A/c Dr b) B A/c Dr To B A/c To B/P A/c c) B A/c Dr d) No entry is passed To B/R A/c 45. A owned Rs. 25,000 to B. A is insolvent. B got A’s computer valuing Rs. 11,500 in full settlement. Pass the Journal entry in the books of B. a) Purchases a/c Dr 11,500 To A a/c 11,500 b) Computer a/c Dr 11,500 Bad debts a/c Dr. 13,500 To A a/c 25,000 c) Computer a/c Dr 25,000 To A a/c 25,000 d) Computer A/c Dr 11,500 To A a/c 11,500 46. An amount of Rs. 8765 paid to M was debited to N a) increase in net profit b) Decrease in net profit c) increase in asset d) no effect on net profit 47. At the end of financial year, accounts receivable has a balance of Rs.1 lakh & provision for bad & doubtful debts provided amounting to Rs.7,000. The expected of net realisable value of A/c receivable is Rs.____ a) 7,000 b) 1,07,000 c) 93,000 d) 1,00,000 48. Rosa paid Rs.1,200 on 1-7-09 towards yearly subscription (July 1, 2009 to June 30, 2010) of a newspaper. It means she has to make adjustment of _____ expenses for finalisation of a/c for the year ended 31-3-10 a) Rs.300 as prepaid b) Rs.300 as outstanding c) Rs.200 as prepaid d) Rs.200 as outstanding Part B - M.Law 49. Prima facie risk passes with _____ a) property of ownership b) computed agreement c) verification & delivery of goods d) payment of price 50. Reserve price is considered in ____ a) sale by sample b) sale by description c) sale by auction d) all of the above 51. An unpaid seller’s right of storage of goods in transit can be excised only the buyer is insolvent a) true b) partly true c) false d) none 52. A agrees to sell B smuggled goods for Rs. 1000 per unit. The agreement is void due to a) uncertainty b) illegality c) impossibility d) immortality 53. Which of the following will be account in fiduciary position a) parent and son b) doctor and patient c) all of the above d) none 54. Partnership agreement between persons arise from a) the states of person b) operation of law c) the contract of those person d) none of these 55. The transactions collateral to illegal agreements is ____ a) valid b) voidable at the option of plaintiff c) also illegal & not enforceable by law d) none of these 56. A sleeping partner is ____ a) not take active part in the firm b) take only salary from the firm c) not contribute capital to the firm d) none of these 57. A sells to B 100 Kg. of wheat on the due date B says to A to keep the wheat for some time. This is a _____ a) symbolic delivery b) actual delivery c) constructive delivery d) none 58. Counter offer is a ____ a) change in the original offer b) rejection of original offer c) same as original offer d) not a offer at all 59. Offer can be withdrawn when a) before the acceptance of offers against the oferror b) after the acceptance of offers against the oferror c) at any time d) cannot be withdrawn 60. Future goods are the subject matter of a) sale b) agreement to sale c) neither sale or agreement to sale d) both sale & agreement to sale 61. ______ agreements are created by situation a) written b) oral c) void d) implied 62. Under the Indian contract act 1872, the age of the person to enter into the contract is a) 21 years b) 16 years c) less than one day of 18 years d) 1 day more than 18 years 63. Partnership is dissolved automatically in cases of ____ a) All partners are insolvent b) All partners expect one are insolvent c) The subject matter becomes unlawful d) In any of the above statements 64. A invites B to attend to his son’s Birthday party and arranged everything but B failed then a) Here there is no contract b) There is no intention to create relationship c) both of the above d) none of the above 65. In case of _____ sale, it is subjected to be complete at reserve price a) Sale of sample b) Sale of description c) Sale of auction d) Reissue of shares 66. Which of the following is under implied authority of a partner in a firm a) submit a dispute of firm to arbitration b) acquire a immovable property behalf of firm c) open a bank account on behalf of firm in his own name d) participate in the business, decisions 67. Sharing of profits in a partnership firm is a) Conclusive evidence b) Not a conclusive evidence c) must in firms d) not compulsory 68. A partner in an dangerous situation can act as a person who is in ____ a) ordinary situation b) as an agent of the firm c) as an major in the firm d) all of the above 69. The implied warranty of contract of sale a) The goods should satisfy buyer purpose b) The right of the seller to sell the goods c) Seller can get back his goods at any time d) none of these 70. If the goods are “perishable goods” then seller resales the goods then the buyer gets a) good title b) partied goods c) no title d) none 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. A 5. A 6. A 7. D 8. A 9. A 10. D 11. B 12. C 13. B 14. A 15. D 16. A 17. D 18. A 19. B 20. D 21. B 22. C 23. A 24. A 25. D 26. A 27. A 28. A 29. D 30. A 31. A 32. A 33. B 34. B 35. B 36. A 37. B 38. C 39. B 40. A 41. C 42. D 43. B 44. D 45. B 46. D 47. C 48. A Part – B - 49. A 50. C 51. A 52. B 53. B 54. C 55. C 56. A 57. A 58. A 59. A 60. B 61. D 62. D 63. D 64. B 65. C 66. D 67. C 68. D 69. A 70. A 71. 72. 73. Part A - Economics 1. Allocation of resources is the subject matter of _____ a) Micro economics b) Macro economics c) Development economics d) Welfare economics 2. Micro Economics is connected with ____ a) Consumer’s Behaviour b) Product pricing c) Factor pricing d) all of these 3. Fixed costs are also called ____ a) direct costs b) prime costs c) supplementary costs d) opportunity costs 4. Direct costs are also known as ____ a) traceable costs b) indirect costs c) opportunity costs d) none of these 5. OPEC is an example for a) monopoly b) monopolistic competition c) perfect competition d) oligopoly 6. The firms AFC is Rs.200 for 10 units. What will be the average fixed costs at 20 units? a) 500 b) 100 c) 150 d) 300 7. Long run price is also known as ____ a) administered price b) market price c) normal price d) none 8. Toothpaste industry is an example for ____ a) monopoly b) monopolistic competition c) oligopoly d) perfect competition 9. AR & MR are same in ____ market a) oligopoly b) monopoly c) perfect competition d) none 10. In monopoly when price elasticity is 1, then the MR is___ a) 1 b) 0 c) negative d) positive 11. Amount paid to the outside factors of production are known as ___ a) implicit costs b) explicit costs c) traceable costs d) opportunity costs 12. An increase in demand with unchanged supply leads to ____ a) rise in price b) fall in price c) no change in price d) an increase in supply 13. When supply curve takes a rightward shift, then supply ____ a) decreases b) contracts c) expands d) increases 14. When the income increases, then demand decreases for ____ a) veblen goods b) conspicuous goods c) normal goods d) inferior goods 15. Which of the following are not true? a) Wants are limited b) resources are scarce c) resources have alternative uses d) both (b) & (c) 16. Average revenue curve is also known as ___ a) profit curve b) demand curve c) supply curve d) none of these 17. Which of the following statements is in correct? a) Competitive firms are price takers and not price makers b) Price discrimination is possible in monopoly only c) Duopoly may lead to monopoly d) Competitive firms always try to discriminate prices 18. Find AFC of 2 units by using the table given below: Output 0 1 2 TC 580 690 850 a) 105 b) 135 c) 290 d) 161 19. If the total utility of a commodity is 5 and marginal utility is 1, a person consumes 3 units. What is consumer’s surplus? a) 6 b) 8 c) 2 d) 3 20. The first stage of law of variable proportions is known as _____ a) increasing returns b) diminishing returns c) constant returns d) none 21. Primary sector includes ____ a) Transport and shipping b) banking and financial institutions c) mining and quarrying d) insurance 22. The IRDP was started in ____ plan a) 5th b) 6th c) 7th d) 8th 23. Which is the regulatory authority of telecom in India a) BSNL b) MTNL c) SEBI d) TRAI 24. GNP = ____ + NFIA a) NNP FC b) NNP MP c) GDP d) National Income 25. National Income is measured by _____ a) Ministry of finance b) CSO c) RBI d) SBI 26. The difference between narrow money and broad money is _____ a) Time deposits b) Saving deposits c) Post office saving deposits d) none of these 27. Which of the following related to financial reforms _____ a) Banking b) Insurance c) Capital d) All of these 28. The main reason behind the implementation of economic reforms in the year 1991 is ____ a) Indication from world bank b) Failure of economic policies of present government c) low foreign exchange reserves d) none of these 29. National Bank for agriculture and rural development (NABARD) is _____ a) a commercial bank b) a co-operative bank c) an apex bank set up for rural & agriculture credit d) a subsidiary of SBI 30. In India, most of the unemployment is _____ a) Disguised b) Open c) Cyclical d) Urban 31. Personal disposable income is _______ a) Personal Income – net indirect taxes b) Personal Income – Indirect taxes c) Personal Income – personal taxes d) none of these 32. Fiscal policy refers to ____ a) Public debt b) public revenue c) public expenditure d) all of the above 33. The systematic record of all receipts and payments of international trade is known as _ a) Balance of Trade b) Balance of Payment c) Balance of current account d) Balance of capital account. 34. 1921 is termed as ____ in the history of Indian population a) beginning census b) big divide c) beginning registration system d) beginning of family planning 35. Trade disputes in international trade are settled by ____ a) WTO b) ILO c) IBRD d) UNO 36. The static function of money is____ a) store of value b) medium of exchange c) standard of differed payments d) all of these 37. The apex bank for industrial finance in India is ____ a) IDBI b) RBI c) SBI d) Ministry of Finance 38. The main cause for unemployment in India is ____ a) raising prices b) increase in public expenditure c) defective mandatory policy d) unproper utilization of resources 39. Devaluation of currency stands for _____ a) increase in the value of domestic currency in terms of foreign currency b) decrease in the value of domestic currency in terms of foreign currency c) keeping value of domestic currency as constant in terms of foreign currency d) none of these 40. Purchasing power of a consumer is low when rise in the general price level is a situation relates to ____ a) inflation b) deflation c) stagflation d) none 41. Measurement of value of goods and services is ____ function of money a) medium of exchange b) unit of account c) standard of differed payments d) store of value 42. Important problem in calculating GNI is ____ a) double counting b) smuggling c) black marketing d) unorganized market For more detailed information I am uploading PDF files which are free to download:
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |
|
#8
| |||
| |||
|
I have completed my 12th and want to prepare for the CA CPT exam and for doing CPT exam preparation I am looking for the CPT Previous Year Question Papers. Will you please provide me some last year question papers along with CPT books name?
|
|
#9
| |||
| |||
|
As per your query here I am providing you the CPT Previous Year Question Papers so that you can prepare well for your exams. CPT previous year paper 1. Which of the following is wrong? a) All real and personal accounts are transferred to balance sheet b) Nominal accounts are transferred to P & L account c) Each account is opened separately in ledger d) Rent is a personal account, outstanding rent is nominal account 2. In Journal Entries which pertain to outstanding entries, prepaid entries, depreciation entries are called a) Adjustment Entries b) Rectification Entries c) Transfer Entries d) closing Entries 3. In a three column cash book the discount columns are a) Totalled but not adjusted b) Totalled and adjusted c) Totalled but not balanced d) None of the above 4. Cash Book O.D. Balance Rs. 2,000. It was found that cheques of Rs. 100, Rs. 150, Rs. 175 which are issued but not presented till the date and the cheque of Rs. 600 deposited but have not been cleared, then O.D. Balance as per pass book is : a) Rs. 2150 b) Rs. 2175 c) Rs. 1475 d) Rs. 1925 5. Bank Balance O.D. as per pass book Rs. 26,500. Calculate balance as per cash book is 1) Cheques deposited for Rs. 4700 but not collected 2) Cheques issued for Rs. 11,000 but not presented 3) Bill discounted and dishonoured Rs. 4000, and Bank paid noting charges Rs. 200 a) Rs.28600 O.D b) Rs.16000 O.D c) Rs.24000 O.D d) Rs.28500 O.D 6. Agreement of Trial balance is not a ___ proof of accuracy a) Submissive b) Inclusive c) Exhaustive d) Conclusive 7. Capital- Rs. 2,00,000 Interest paid- Rs. 2310 Debtors- Rs. 15,200 Discount allowed- Rs. 820 Creditors-Rs.12,960 Discount received-Rs. 1030 Purchases- Rs. 92,670 Rent - Rs. 14,670 Sales- Rs. 1,16,850 Loan - Rs. 12,060 Opening stock – Rs. 56,000 Sales returns – Rs. 27,430 Debit Total of Trial Balance will be a) Rs. 2,09,000 b) Rs. 2,09,100 c) Rs. 2,10,000 d) None 8. From the following information find the amount to be debited to P & L A/c for the period ending 31-03-2014. Provision for doubtful debts - Rs. 800 (on 01-04-2013) Debtors on 31-03-2014 - Rs. 40,000 Bad debts - Rs. 2,000 Bad debts to be written off and provision for doubtful debts is to be created @ 5% on debtors a) Rs. 3100 b) Rs. 4000 c) Rs. 3200 d) Rs. 3900 9. Opening Stock Rs.30,000, Cost of goods available for sale Rs. 1,60,000, Sales were Rs. 1,60,000. Gross profit on sales is 30% Calculate closing stock. a) Nil b) Rs. 48,000 c) Rs. 98,000 d) None of the above 10. By products are generally valued at __ when the cost of by products is not directly traceable. a) Cost of main products b) N.R.V. c) Cost of main product or N.R.V. which ever is lower d) None of these 11. The purpose of Accommodation bill a) To facilitate trade transmission b) To finance the actual purchases & sales c) When both parties are in need of funds d) None of these 12. A draws a bill for Rs. 20,000 on ‘B’. ‘B’ Accepts for 2 months. After 1 month ‘B’ paid the bill amount @9%. Journal entry in the Books of ‘B’ will be a) Bank A/c Dr.20,000 To Bills payable A/c 20,000 b) Bank A/c Dr.20,000 To Bills payable A/c 19,850 To Discount A/c 150 c) Bills payable A/c Dr. 20,000 To Bank A/c 20,000 d) Bills payable A/c Dr.20,000 To Discount A/c 150 To Bank A/c 19,850 13. Promissory note features 1) Must be stamped 2) Payee must sign 3) Conditional undertaking 4) Certain amount 5) Not transferable to bearer a) 1,2,3,4 b) 1,4,5 c) All of the above d) None of these 14. In the absence of agreement, the loss of goods in consignee godown is borne by a) Consignor b) Consignee c) Both a & b d) Insurance Company 15. Goods sent on consignment for Rs.50,000. During transit 1/10th of goods were destroyed by fire. Again 1/9th of goods received by consignee were destroyed by fire in godown. Half of the remaining goods were sold for Rs.30,000. Freight & insurance paid by consignor Rs.2,500 and Rs.1500 respectively. Calculate closing Stock. a) Rs.24,000 b) Rs.21,600 c) Rs.20,000 d) None 16. Yogam consigned cost of goods of Rs. 1,00,000 at an invoice price of 20% above cost. Consignee is entitled to 5% commission on sales up to Invoice price, 20% on sales which exceeds invoice price, 2% delcredre commission on credit sales. He sold 25% of goods for cash for Rs. 40,000 and 50% of goods on credit for Rs. 70,000, 10% of goods taken by consignee. Calculate commission? a) Rs. 10,500 b) Rs.9900 c) Rs.10,200 d) none 17. In case of Joint Venture business, method of Accounting to be followed and decided by a) Separate Act for J.V. b) Accounting Standard c) Co-venturer as per their convenience d) ICAI 18. In case of purchase of machinery in joint venture through joint bank A/c, while separate set of books is maintained. Which of the following is the correct entry. a) Debit machinery, credit joint bank A/c b) Debit machinery, credit joint venture A/c c) Debit Joint venture, credit joint bank A/c d) Debit Joint venture A/c, Credit machinery A/c 19. ‘A’ and ‘B’ enter into a joint venture business ‘A’ purchased goods worth Rs. 30,000 and ‘B’ sold for Rs. 40,000. ‘A’ is entitled to 1% commission on purchases and ‘B’ is entitled to 5% commission on sales. The profit on venture to be shared by A & B is (The profit sharing ratio is 2:1) a) Rs. 4000 : Rs. 2000 b) Rs. 5133 : Rs. 2567 c) Rs. 5000 : Rs. 2500 d) Rs. 4200 : Rs. 2100 20. Rohan Ltd is in the business of extracting coal from mines. It should charge depreciation as per _____ method. a) Sinking fund b) Annuity c) Production units d) Depletion method 21. Cost of machine is Rs.1,00,000 Scrap value Rs. 10,000 and life is 4 years. What will be the amount of depreciation in 3rd year according to sum of years digits method a) Rs.40,000 b) Rs.27,000 c) Rs.9,000 d) Rs.18,000 22. A Trader followed WDV method of depreciation, the book value of Asset after 4 years is 24% of original cost. Find rate of depreciation. a) 24% b) 26% c) 32 % d) 30% 23. Loss on sale of machinery is credited to __ account. a) Machinery A/c b) Purchase A/c c) Profit & Loss A/c d) None 24. A machine purchased for Rs. 2,50,000 on 1.1.2010. It can produce 30,000 units during its useful life, its estimated scrap value is Rs. 10,000. The pattern of production over the next 4 years is as follows 2010 – 6250 units, 2011-2275 units, 2012-12,000 units, 2013- 3452 units, the WDV of the machine after 3rd year will be a) Rs. 85,800 b) Rs. 1,54,200 c) Rs. 58,158 d) Rs. 1,91,816. 25. After rectification of the following errors, effect on Net profit will be i) A cheque dishonoured Rs.3,100 debited to discount A/c ii) Sales book (undercast) short by Rs.23,000 iii) A customer returned goods of value of Rs.1,200, included in stock but not recorded a) Increased by Rs. 24,900 b) Decreased by Rs. 24,900 c) Increased by Rs. 23,700 d) No change 26. The following are the errors committed while the entries are posted in ledger. 1) Errors of Principle 2) Errors of commission. 3) Errors of Partial omission 4) Errors of complete omission. a) 1,2,3,4 b) 2,3,4 c) 1,2,4 d) 1,3,4 27. InCase of insufficient profits i.e., profits less than interest on capital then the profits are distributed in : a) Profit sharing ratio b) Capital ratio c) Not distributed d) None 28. The assets which were earlier revalued upward and now revalued downward, to the extent of earlier upward revaluation amount should be. a) Credited to Revaluation Reserve A/c b) Debited to Revaluation Reserve A/c c) Credited to P&L A/c d) Debited to P&L A/c 29. A, B are partners sharing profit & losses in the ratio of 5 : 3. ‘C’ admitted as a new partner for 1/5th share and his capital is Rs. 1,20,000 & goodwill Rs. 60,000 Capitals of A, B & C were Rs/- a) 3,00,000 : 1,20,000 : 1,80,000 b) 3,00,000 : 1,80,000 : 1,20,000 c) 3,00,000 : 1,80,000 : 1,80,000 d) 3,00,000 : 1,20,000 : 1,20,000 30. At the time of admission the unrecorded investments Rs. 30,000 should be treated, the adjustment entry will be a) Unrecorded investment A/c Dr. 30,000 To Revaluation 30,000 b) Revaluation A/c Dr. 30,000 To Unrecorded Investment A/c 30,000 c) Partners capital A/c Dr. 30,000 To unrecorded Investment A/c 30,000 d) Unrecorded Investment A/c Dr.30,000 To Partners capital A/c 30,000 31. Kapur and sharma are partners in partnership firm. Calculate the interest on drawings of kapur and sharma @ 10% p.a. for the year ending on 31st December 2013. Kapur withdrew Rs. 2,000/- per month in the beginning where as sharma withdrew same amount at the end of every month a) Kapur Rs. 2,400, sharma Rs. 2,400 b) Kapur Rs. 1,100, sharma Rs. 1,300 c) Kapur Rs. 1,200, sharma Rs. 1,200 d) Kapur Rs. 1,300, sharma Rs. 1,100 32. Neeraj & Gopi are partners with Rs.5,00,000 capital each. They admitted champak for 1/4th share with Rs.8,00,000 capital. The P & L A/c credit balance is Rs.4,00,000. Find the amount of hidden goodwill a) Rs.10,00,000 b) Rs.12,00,000 c) Rs.8,00,000 d) Rs.16,00,000 33. Angola & Bangola sharing profits 2 : 3, Mangola joined the firm. Angola gave 1/3rd of his share, Bangola gave 1/4th of his share. what is new profit sharing ratio? a) 17:27:37 b) 16:27:17 c) 17:27:17 d) None 34. When goodwill is withdrawn by the partners ___ account is credited. a) Cash b) Partners capital A/c c) Partners loan a/c d) Goodwill A/c 35. A & B are in partnership sharing profits & losses in the proportion of 3:1 respectively. On 1-4-2013, they admitted ‘c’ into partnership on the following terms. i) ‘C’ is to purchase 1/3rd of the goodwill for Rs.2000/- by paying cash ii) future profits & losses are to be shared by A, B & C equally Set out the entry to the above arrangement in the firm journal a) Cash/Bank A/c Dr.2000 To ‘A’ s capital A/c 2000 b) Cash/Bank A/c Dr.2000 ‘B’ s capital A/c Dr. 500 To ‘A’s capital A/c 2500 c) Cash/Bank A/c Dr.2000 To Goodwill A/c 2000 d) Cash/Bank A/c Dr.2000 To ‘A’s capital A/c 1500 To ‘B’s capital A/c 500 36. The maximum number of partners is mentioned in a) Companies Act b) Partnership Act c) Limited Partnership Act d) None 37. As per companies Act 1956 application money more than___ % of nominal value of the share and as per SEBI guidelines application money atleast __ % of issue price a) 5 %, 25% b) 25%, 25% c) 5%, 5% d) 25%, 5% 38. MAR Ltd forfeited 300 shares of Rs. 10/- each fully called up for non payment of final call money of Rs.4/- per share. These shares are subsequently reissued for Rs.12 per share as fully paid up. What amount should be transferred to capital reserve account. a) Rs. 2,400 b) Rs. 3,000 c) Rs. 1,800 d) Rs. 3,600 39. A company has a subscribed capital of Rs. 80,00,000 in shares of Rs. 100 each. There are no calls in arrears till the final call. The payment on final call was received for 77,500 shares. The amount of calls in arrears Rs. 67,500. Then the amount of final call is a) Rs. 25 b) Rs. 27 c) Rs. 20 d) Rs. 65.20 40. Zebra Ltd invites applications for 50,000 shares for which 2/- per share is payable on application. Applications received for 80,000 shares and 70,000 shares are allotted on prorata basis. How much application money will be adjusted to allotment, when Mr.Lion who has allotted 200 shares. a) Rs. 100 b) Rs. 160 c) Rs. 240 d) Rs. 80 41. Ajay Ltd decides to redeem 10,000 preference shares of Rs. 10/- each at 10% premium. Balance in P & L A/c is Rs. 65,000 and securities premium A/c is Rs. 5,000. You are required to calculate the minimum number of equity shares at the rate of Rs. 10/- each at 20% discount a) 3125 b) 5625 c) 5000 d) None 42. Unless otherwise stated preference shares always deemed to a) Cumulative, Participating, Convertible b) Cumulative, Non-Participating, Non- convertible c) Non-Cumulative, Participating, Non- Convertible d) Non-Cumulative, Non-Participating, Convertible. 43. When the debentures are issued as collateral security for a loan then such debenture holders are entitled to a) Interest on the amount of loan b) Interest on the amount of debenture c) No Interest amount d) Either (a) or (b) 44. Which method is exception to non-historical cost methods a) Adjusted selling price b) Latest purchase price c) Standard Cost d) Weighted average 45. Cost of physical inventory on 15-04-2014 was Rs.3,00,000. Sales amounting to Rs.1,00,000 and purchases worth Rs.50,000 were made between 31-03-2014 to 15-4-2014. Goods are sold at 20% profit on sales. Value of Inventory as on 31-3-2014 is a) Rs. 3,50,000 b) Rs. 2,70,000 c) Rs. 3,00,000 d) Rs. 3,30,000 46. Average stock Rs. 14,000, closing stock is Rs. 3,000 more than the opening stock, then closing stock is ___ a) Rs. 15,500 b) Rs. 15,000 c) Rs. 12,200 d) Rs. 12,000 47. Which method of valuation is adopted in above table a) FIFO b) LIFO c) Weighted average d) None 48. Closing stock from above adopted method is a) Units 200 amount Rs. 2300 b) Units 200 amount Rs. 2000 c) Units 200 amount Rs. 2,600 d) None of these 49. When goods sent on approval, buyer become owner of goods when a) When he accepts the goods b) When the time of approval was over c) When he done any act in respect of getting possession of goods d) All of these. 50. ‘A’ sent some goods costing Rs.3500 at a profit of 25% on sale to ‘B’ on sale or return basis. ‘B’ returned goods costing Rs. 800. At the end of accounting period on 31st December 2011 the remaining goods were neither returned nor approved by him. Closing stock on approval basis to be shown in the balance sheet will be a) Rs. 2000 b) Rs. 2700 c) Rs. 2700 less 25% of Rs. 2700 d) Rs. 3500 51. In Income measurement & recognisation of assets & liabilities which of the following concepts goes together? a) Periodicity, Accrual, matching b) Cost, Accrual, matching c) Going concern, cost, Realization d) Going concern, Periodicity, Reliability 52. ____ is root cause for financial accounting? a) Stewardship accounting b) Social accounting c) Management accounting d) Human resource accounting. 53. Gyan received Rs.5,000 in advance but he credited to sale account. Which of the following concept he did not follow? a) Accrual b) Conservatism c) Consistency d) Going concern 54. Change in Accounting estimate means : a) Certain parameters estimate in earlier and re-estimates in the current period b) Certain parameters estimate in earlier and actual results achieved during current year c) Certain parameters re-estimated during the current period and actual result achieved during the previous period d) Both (a) & (b) 55. Interpretation means a) Explanation of meaning and significance of the data in Financial Statements. b) Concerned with preparation and presentation of classified data c) Systematic analysis of recorded data d) Methodical classification of data given in Financial Statements. 56. A trader purchased goods for Rs. 25,00,000, of these 70% of goods were sold during the year. At the end of 31st December 2009, the market value of such goods were Rs.5,00,000. But the trader recorded in his books for Rs.7,50,000. Which of the following concept is violated. a) Money measurement b) Conservatism c) Consistency d) None 57. Matching the following : a) As 26 i) Impairment of assets b) As 10 ii) Discontinued operations c) As 28 iii) Intangible assets d) As 24 iv) Accounting for fixed assets a) a – iii, b-iv, c-ii, d-I b) a-ii, b-iv, c-I, d-iii c) a-ii, b-iii, c-I, d-iv d) a-iii, b-iv, c-I, d-ii 58. A building worth Rs.35 lakhs was purchased and it was dismantled with Rs.1 lakh and it was decided to build as shopping mall. The cost of construction of building was Rs.50,00,000 and other expenses of Rs.50,000. The amount of capital expenditure is a) Rs. 86,00,000 b) Rs. 86,50,000 c) Rs. 85,50,000 d) Rs. 85,00,000 59. Which of the following is not a difference between provision & contingent liability a) A provision meets the recognition criteria where as contingent liability fails to meet the same b) Provision is a present liability of uncertain amount where as contingent liability is possible obligation which arises from past events c) Provision can’t be measured where as contingent liability is absolutely measured d) None of the above 60. Part B – Mercantile Laws 61. A Void Contract is ___ a) An agreement which is not enforceable by law b) A Contract which ceases to be enforceable by law c) An agreement which is voidable at the option of promisee d) An agreement which is voidable at the option of promisor 62. Which of the following is not correct? a) Offer must not be conditional b) Acceptance may be given in any manner c) Acceptance must be absolute d) Communication of offer is an essential element 63. Original offer is rejected when there is ___ a) Standing offer b) Cross offer c) Counter offer d) None of the above 64. A person advertised in newspaper to sell his old car. Then the offer is ____ a) General offer b) Specific offer c) Continuing offer d) None of the above 65. Which of the following is true? a) There can be a stranger to Contract b) There can be a stranger to consideration c) There can be both stranger to consideration and stranger to Contract d) None of the above 66. If in a Contract both legal and illegal part exists, the legal part is separable from illegal part, then the legal part is ____ a) Valid b) Void c) Voidable d) Illegal 67. A promise to pay time barred debt must be _ a) An oral promise b) An implied promise c) In writing and signed by debtor or his authorized agent d) None of the above 68. Maheswari promises to give Raman 1kg of opium if he destroys property of Nikhil. In this case ____ a) There is unlawful consideration b) There is unlawful object c) There is unlawful consideration and object is partly unlawful d) Both consideration and object are unlawful 69. For the necessaries supplied to a minor, the amount can be recovered from___ a) Minor’s personally b) Minor’s estate c) Minor’s Guardian d) Minor is not at all liable 70. Which of the following statements is not correct? a) In matters of fraud, intention to defraud is essential b) Where consent to a Contract is obtained by misrepresentation, Contract is voidable c) A unilateral mistake renders agreement void d) Mistake of foreign law is equal to mistake of fact 71. A told B that he gives Rs. 500 if it rains and B told to give like amount if it does not rain. The agreement is ___ a) Contingent Contract b) Wagering agreement c) Future Contract d) None of the above 72. Quasi Contractual liabilities lead to ____ a) Prevention of unjust enrichment b) Counter Offer c) Cross Offer d) Specific Offer Books for CPT exam preparation: There are no other best reference books other than ICAI’s study material for exam preparation. But if you want to gain more knowledge on subjects or want to do self-preparation of CA CPT then here are suggestions: Section-A : Fundamentals of Accounting – CPT Grewal’s Accountancy by M.P Gupta & B.M Aggarwal Section-B : Mercantile Laws – P. P. S. Gogna or P C Tulsian Section-C : General Economics – S.K. Agarwal or Deepashree Section-D : Quantitative Aptitude – P. N. Arora CA CPT Eligibility: For appearing at the CA CPT main examination Appearance at the Senior secondary (10 + 2/intermediate) examination conducted by an examining body constituted by law in India or an examination recognized by the central government as equivalent thereto.
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |
 |
| |