|
#1
| |||
| |||
|
Can you please provide the syllabus of the CA CPT Exam ?
|
|
#2
| ||||
| ||||
|
The CPT is the first level of Chartered Accountancy examinations in India. CA CPT June 2014 Syllabus: Session – I : Section A : Fundamentals of Accounting ( 60 Marks ) Contents 1. Theoretical Framework Meaning and the Scope of accounting Accounting Concepts, Principles and the Conventions Accounting as measurement discipline – valuation principles, accounting estimates Accounting Standards – concepts, objectives, benefits Accounting Policies 2. Accounting Process Books of Accounts leading to preparation of Trial Balance, Capital and revenue expenditures, Capital and revenue receipts, Contingent assets and contingent liabilities, Fundamental errors including the rectifications thereof. 3. Bank Reconciliation Statement 4. Inventories Basis of inventory valuation and record keeping. 5. Depreciation accounting Methods, computation and accounting treatment of depreciation, Change in depreciationmethods. 6. Preparation of Final Accounts for Sole Proprietors 7. Accounting for Special Transactions Consignments Sale of goods on approval or return basis. Joint Ventures Bills of exchange and promissory notes 8. Partnership Accounts Final accounts of partnership firms – Basic concepts of admission, retirement and death of partner including treatment of goodwill. 9. Introduction to Company Accounts Issue of shares and debentures, forfeiture of shares, re-issue of forfeited shares, redemption of preference shares. Section B: Mercantile Laws ( 40 Marks ) Contents The Indian Contract Act , 1872 : An overview of Sections 1 to 75 covering general nature of contract , consideration , other essential elements of valid contract , performance of contract and breach of contract. The Sale of Goods Act, 1930 : Formation of contract of sale – Conditions and Warranties – Transfer of ownership and delivery of goods – Unpaid seller and his rights. The India Partnership Act, 1932 : General Nature of Partnership – Rights and duties of partners – Registration and dissolution of firm. Session – II Section C: General Economics ( 50 Marks ) Contents ( I ) Micro Economics 1. Introduction to Micro Economics Definition, scope and nature of Economics Methods of economic study Central problems of economy and Production possibilities curve 2. Theory of Demand and Supply Meaning and determinants of demand, Law of demand and Elasticity of demand ─ Price, income and cross elasticity Theory of consumer ’s behaviour – Marshallian approach and Indifference curve approach Meaning and determinants of supply, Law of supply and Elasticity of supply 3. Theory of Production and Cost Meaning and Factors of production Laws of Production – The Law of variable proportions and Laws of returns to scale Concepts of Costs – Short – run and long – run costs, Average and marginal costs, Total, fixed and variable costs. 4. Price Determination in Different Markets Various forms of markets – Perfect Competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Price determination in these markets. ( II ) Indian Economic Development 5. Indian Economy – A Profile Nature of Indian Economy Role of different sectors – Agriculture, Industry and Services in development of the Indian economy, their problems and growth National Income of India – Concepts of national income, Different methods of measuring national income, Growth of national income and per capita income in various plans Basic understanding of tax system of India – Direct and Indirect Taxation 6. Select Aspects of Indian Economy Population – Its size, rate of growth and its implication for growth Poverty – Absolute and relative poverty and main programs for poverty alleviation Unemployment – Types, causes and incidence of unemployment Infrastructure – Energy, Transportation, Communication, Health and Education Inflation Budget and Fiscal deficits Balance of payments External debts 7. Economic Reforms in India Features of economic reforms since 1991 Liberalisation, Privatisation and Disinvestment Globalisation. 8. Money and Banking Money – Meaning and functions Commercial Banks – Role and functions Reserve Bank of India – Role and functions, Monetary policy Section D: Quantitative Aptitude ( 50 Marks ) Contents 1. Ratio and proportion, Indices, Logarithms 2. Equations 3. Inequalities 4. Simple and Compound Interest including annuity ─ Applications 5. Basic concepts of Permutations and Combinations 6. Sequence and Series – Arithmetic and geometric progressions 7. Sets, Functions and Relations 8. Limits and Continuity ─ Intuitive Approach 9. Basic concepts of Differential and Integral Calculus ( excluding trigonometric functions ) 10. Statistical description of data 11. Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion 12. Correlation and Regression 13. Probability and Expected Value by Mathematical Expectation 14. Theoretical Distributions 15. Sampling Theory 16. Index Numbers
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |
|
#3
| |||
| |||
|
CA stands for Chartered Accountancy, it is a professional course The Chartered Accountancy course has three levels : First Stage : CPT or CA Entrance ( Common Proficiency Test ) Second Stage : CA Intermediate / IPCC Third Stage : CA Final Syllabus of CA Course CPT(Common Proficiency Test) CPT – One Paper, Two Sessions ( 200 Marks Total ) Session I: Section A: Fundamentals of Accounting (60 Marks) Section B: Mercantile Laws (40 Marks) Session II: Section C: General Economics (50 Marks) Section D: Quantitative Aptitude (50 Marks) IPCC - Intermediate (Integrated Professional Competence) Course Group I Paper 1: Accounting (100 marks) Paper 2: Business Laws, Ethics and Communication (100 marks) Paper 3: Cost Accounting and Financial Management (100 marks) Paper 4: Taxation (100 marks) Group II Paper 5: Advanced Accounting (100 marks) Paper 6: Auditing and Assurance (100 marks) Paper 7: Information Technology and Strategic Management(100 marks) FINAL Group I Paper 1: Financial Reporting (100 Marks) Paper 2: Strategic Financial Management (100 Marks) Paper 3: Advanced Auditing and Professional Ethics (100 Marks) Paper 4: Corporate and Allied Laws (100 Marks) Group II Paper 5: Advanced Management Accounting (100 Marks) Paper 6: Information Systems Control and Audit (100 Marks) Paper 7: Direct Tax Laws (100 Marks) Paper 8: Indirect Tax Laws (100 Marks) Chartered Accountancy ( CA) – Course structure 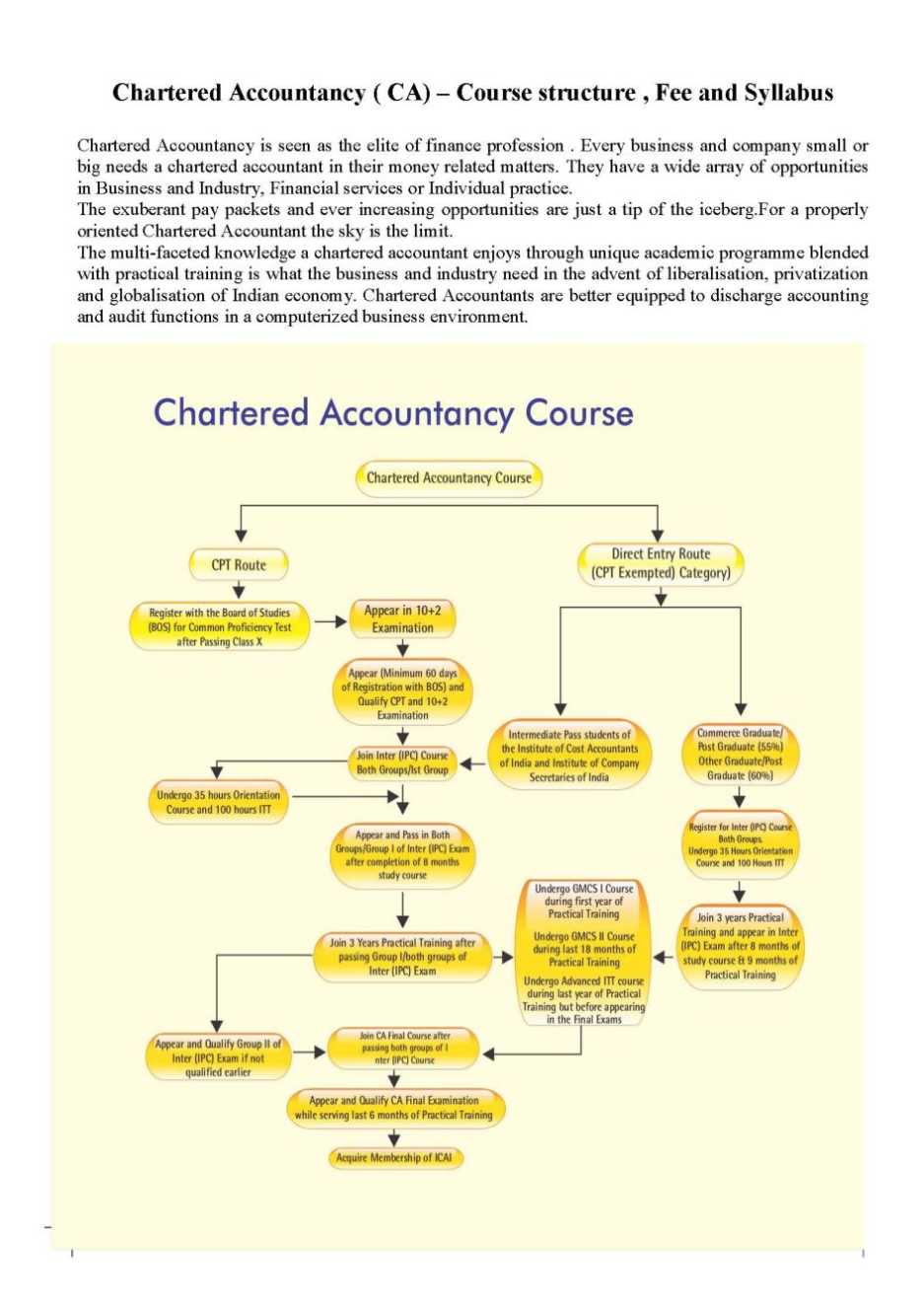  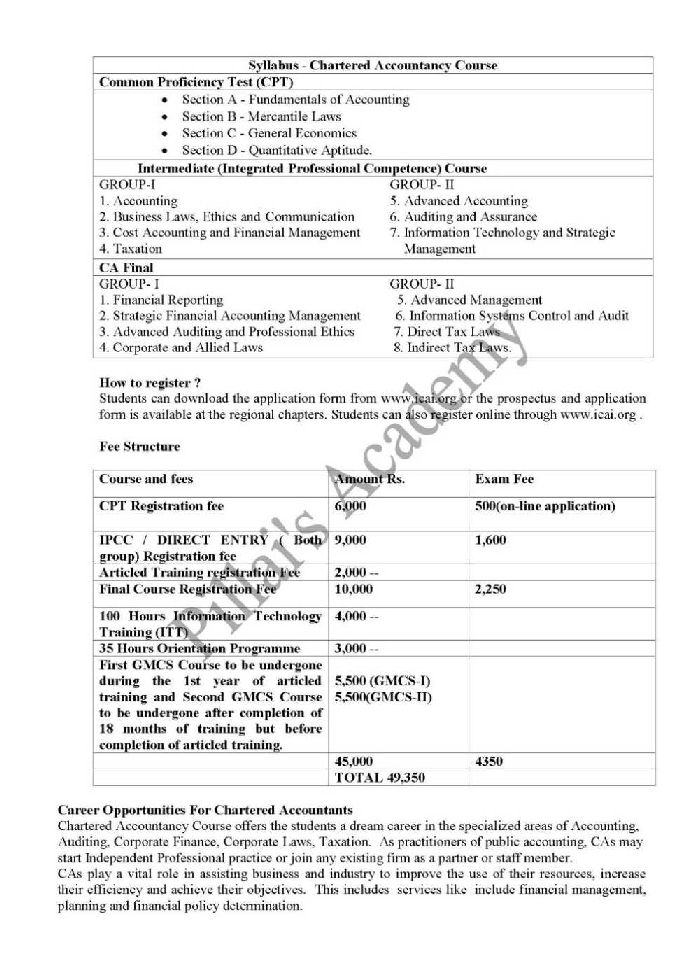
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |