|
#1
| |||
| |||
|
I want to appear in the TANCET MBA Entrance Test. So will you provide some Question Papers of TANCET MBA Exam? As you want to get some Question Papers of TANCET MBA Exam, so here I am providing the following Question Papers; TANCET MBA Exam Question Paper 1 Directions for questions 1 – 20: This section comprises two passages. After each passage questions consisting of items relating to the preceding passage are given. Evaluate each item separately in terms of the respective passage and choose your answer PASSAGE – I (Questions 1 – 10) The Shop-O-shelf Company's supermarkets are situated in Bangalore, Coimbatore and Vellore. The company is dynamic and aggressive having grown from 8 stores ten years ago to 26 today. Kanchipuram is a town 60 miles from Vellore. It has not shown the spectacular growth of other suburbs, but its population has increased from around 56,000 to 1, 30,000 in the past decade. With no other Shop-O-Self supermarket within 20 miles of the area, Shop-O-Self Company is considering opening a store in Kanchipuram. The Arguments against: some Shop-O-Self executives oppose the project as a poor risk. They point to the proposed site, which is in a shopping centre three miles from Kanchipuram business district. Two other food chains have failed on this site because they claim; most new residences are on the other side of the community. Moreover, the shopping centre owners demand a five year lease. Shop-O-Self would have to try to find another business to take over the lease should its own store fail before the end of that time. If a Shop-O-Self market must be opened in Kanchipuram, it would be far better, these executives argue, to build it in the heart of the community. But they point out, another supermarket is already there. The Arguments for: The Majority of the executives maintain that the site has great potential. A new east-west highway is being built which will pass Kanchipuram to the north and force the car commuters to Kanchipuram to pass by the shopping centre. A housing project of 3, 000 units is going to be constructed nearby. The average household is expected to consist of five people with over Rs. 30,000 of income to dispose of annually. They also argue that the centre of Kanchipuram is now congested with traffic and has extremely poor parking facilities, while there is excellent parking in the shopping centre. Investment in a new building in Kanchipuram, proper than a five year lease should the store fail. They are not too concerned about the other supermarket in Kanchipuram. There is enough business for both. Besides, the competitor's prices are higher than shop-o-self. They also discount past supermarket failures in the shopping certre. They claim these were caused more by poor management than by the shopping centre's being slightly off the beaten path. The Decision: The board of directors listens to both sides and then votes to open a Shop- o-self store at the Kanchipuram shopping centre. 1. The residents at the projected residential development will shop in the Kanchipuram store (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 2. Poor management causing past supermarket failures. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 3. New east-west highway. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 4. Expansion of dynamic company. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 5. Failure of two supermarkets due to poor site selection. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 6. Establishing a new store (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 7. New housing development. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 8. Car commuters will shop at Kanchipuram supermarket. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 9. High disposable income of expected new residents. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 10. Kanchipuram's prices are lower than those of competitors. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. PASSAGE II (Questions 11 – 20) In 1997 Mr. Deepak, a chemical engineer, began experimenting in his spare time with a new method for processing fresh orange juice. By 2000, he had perfected the process to such an extent that he was ready to begin production in a small way. His process enabled him to extract 18 percent more juice from oranges than was typically extracted by a pressure juicer of the type currently used in cafes. His process also removed some of the bitterness, which got into the juice from the peelings when oranges were squeezed without peeling them. Since many of the better quality restaurants preferred to serve fresh orange juice instead of canned or frozen juice, Mr. Deepak believed he could find a ready market for his product. Another appeal of his product would be that he could maintain more consistent juice flavor than haphazard restaurant juicing usually produced. Mr. Deepak patented the process and then started production. Since his capital was limited, he began production in a small building, which previously had been a woodworking shop. With the help of his brother, Mr. Deepak marketed the juice through local restaurants. The juice was distributed in glass bottles, which proved to be rather expensive because of high breakage. The new product was favourably accepted by the public and the business proved to e a success. Mr. Deepak began to receive larger and more frequent orders from his customers and their business associates. In 2002, he quit his regular job in order to devote full time to his juice business. He soon reached his capacity because of his inability to personally over a larger area with his pickup truck. Advertising was on a small scale because of limited funds. Faced with the problems of glass bottle breakage and limited advertisement and distribution, Mr. Deepak approached a regional food distributor for a solution Mr. Deepak was offered a plan where by the distributor would advertise and distribute the product on the basis of 25 percent of gross sales. The distributor would assist Mr. Deepak in securing a loan from the local bank to expand the production. Before he had an opportunity to contact the bank to borrow money, Mr. Deepak was introduced to Mr. Sunil, a plastics engineer, who produced plastic containers. Mr. Deepak mentioned his own problems in the expansion of his business. Mr. Sunil wanted to finance expended juice production with the understanding that plastic containers would be used for marketing the orange juice. He would lend the money interest free, but he was to receive 40 percent of the net profits for the next ten years. Distribution and advertising agent for 25 percent of gross sales. The principal on Mr. Sunil's invested money was to be repaid by Mr. Deepak on a basis of 10 percent of his share of the profits. Mr. Sunil was to retain an interest in the profits of the firm until the loan was repaid, or at least for ten years. Mr. Deepak's current sales were 10,000 litres of juice a month. If distribution could be expanded, sales could be doubled, given the potential demand. Of the possible total sales of 20,000 a month, about 75 percent would be sold to large restaurants and the reminder to small cafes and canteens. As soon as the juices were bottled in plastic containers, sales could also be made to household consumers. Mr. Deepak was very optimistic that sales to the final consumer through retail shops would succeed. Some initial contacts were made with a local manager of a food chain supermarket. The manager was sure that he could sell 4,000 litres a month through his outlets. Mr. Deepak also calculated his potential profits. His goal was to increased sales while at the same time earning a 10 percent rate of return on his prior capital investment in equipment and other assets. The present value of Mr. Deepak's investment was Rs. 2,50,000. Of this sum, machinery and equipment were valued at Rs. 1,00,000; building was worth Rs. 50,000 and his patent and know-how were valued at Rs. 1,00,000. On the basis of this evaluation, Mr. Deepak desired a return of Rs. 25,000 above salaries and other expenses after the first year of operation. Both the regional distributor and Mr. Sunil believed that Mr. Deepak's sales could be increased to 15,000 litres of juice per month by the end of the first year of expanded operations. However, the extent to which production could be expanded to meet demand depended on the availability of plastic containers (which would be supplied at factory cost under Mr. Sunil's proposal), and additional machinery. Increased market coverage would be obtained both under the regional food distributor and Mr. Sunil's proposals. The critical deciding factor, as Mr. Deepak understood, was which plan would maximize his return on investment beyond the minimum figure of 10 percent. 11. Cost of securing a loan (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) The item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 12. High breakage rate of glass bottles. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 13. Expansion of the business (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 14. Continued demand by the public for Mr. Deepak's orange juice (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 15. Possibility of doubling sales through expanded distribution (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 16. Previous use of Mr. Deepak's building as a woodworking shop (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 17. Ten percent return of investment (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 18. Small scale of current advertising (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 19. Value of patent held by Mr. Deepak. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 20. Mr. Deepak's current level of sales. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. SECTION II READING COMPREHENSION Direction: This section contains two reading passages. You have to read each carefully. Each passage is followed by questions based on its content. After reading each passage, choose the best answer to each question. The questions are based on what is stated or implied in each passage. PASSAGE I (Questions 21 – 30) The concept of "standard of living" is a wide and multifaceted one. In the absence of comprehensive measurement, it is commonly expressed empirically in terms of consumption or in terms of income. One of the most comprehensive expressions of standard of living is total consumption over an extended period, where consumption is defined not only as family purchases but also as (1) consumption of goods and services produced by the family; (2) consumption of public services provided without payment; and (3) consumption of goods and services received as compensation for labor, over and above wages and salary. It may be assumed that total consumption is less subject to incidental fluctuations than income. Moreover, it reflects not only current income but also past income and savings, windfalls, and expectations regarding future income. Current monetary income constitutes the main indictor for the standard of living; however, standard of living is not determined solely by current income, but also by past income, accumulated assets and expectations for future income. Moreover, the standard of living of a family is influenced by the value of the public services from which it benefits and the rate of taxes which it has to pay. In the period under review, the standard of living of families originating from Asia and Africa improved relative to that of all families. This improvement found expression in higher income levels, better housing, higher ownership rate of consumer durables and an increase in the proportion of families in higher income brackets. However, even after the improvement in their relative position during the past decade, their average income is still only 70% of the overall average for all families. One of the important factors behind the income differential between families of African and Asian originals and the rest of the populations is the level of education. In rent years the gap between these two groups has narrowed among the younger generation, but it is still substantial. Unless the education gap is significantly reduced between these two groups, other means employed in an attempt to produce more income equality will be thwarted. More resources must be immediately put to the task of improving educational opportunities for families of African and Asian origin, without of course, reducing the education facilities and opportunities open to the rest of the population. 21. The author defines 'standard of living' in terms of (a) Total goods and services produced (b) Consumption of goods and services (c) Real income (d) Per capita income (e) Discretionary income. 22. Which income period (s) would be included in the author's definition of 'standard of living;? I. Past income II. Current Income III. Future income (a) I only (b) II only (c) I and II only (d) I, II and III (e) Neither I, II and III 23. Consumption is defined as (a) Total family purchases (b) Total family purchases plus goods and services produced by the family (c) Public services provided by the state. (d) Income minus expenditure on necessities (e) Total family purchases plus other goods and services consumed 24. Between 1994 and 2000, average real income (a) Remained stable (b) Increased by about 5% annually (c) Decreased slightly (d) Decreased during the recession (e) Decreased by 5% annually 25. According to the passage, between 1997 and 2000, income equality (a) Declined among all strata (b) Declined most significantly among lower income groups (C) Widened between the rich and the poor strata (d) Did not change appreciably (e) Declined among older groups in the population. 26. The author believes that inequality of income might be narrowed if (A) The tax structure was reformed (b) The educational gap between different population groups was reduced (c) More jobs could be found for people of Asian-African origin (d) Real income increased (e) A system of price controls was implemented 27. The standard of living of Asian - African immigrants has improved as measured by all of the following factors except (a) Higher income levels (b) Better housing (c) Increased ownership of consumer durables (d) A shift in population centres (e) An increased proportion of Asian - African families in higher income brackets. 28. It may be inferred that the author of the passage is an (a) Engineer (b) Food specialist (c) Economist (d) Bank president (e) Efficiency expert 29. Even though the income level of families of Asian - Africa origin increased relatively, their average income is still (a) Only about equal to that of other groups (b) About 70 percent of the overall national average (c) Close to the national average, but slightly below (d) About 50 percent of the national average (e) About 25 percent of the national average 30. Between 1997 and 2000, the standard of living of the urban population (a) Declined (b) Increased (c) Stagnated (D) Remained constant (e) Doubled PASSAGE II (Questions 31 – 40) Much has been written about the need for increasing our knowledge of marketing in other countries and how different marketing systems operate in delivering goods and services to consumers. Indian businessmen have long been interested in foreign markets for the purpose of stimulating trade. Analysis of the mechanisms of the given country's internal trade and the structural and environmental factors of its marketing system are necessary to the success of an Indian firm's marketing efforts aboard. Knowledge of a country's marketing system is of equal importance to the potential investor. Information pertaining to channels of distribution, promotional facilities, and the marketing experience of management should have weight in the investment decision equal to factors such as financing the possibility of expropriation and plant location. Moreover, Indian businessmen are certainly not limited to investment in manufacturing industry aboard; there may be profitable opportunities for the introduction of Indian marketing institutions and techniques in other countries. The extent to which Indian rupees should be channeled into the introduction of Indian marketing innovations depend upon the answers to the following questions: (1) to what extent is it possible to " transplant" Indian marketing operations or institutions to foreign countries, and (2) would such transplantations, if successful, contribute to the economic development of the recipient country? In light of the above, research is needed to determine the factors responsible for the acceptance and growth of marketing innovations so that an understanding of the adoption process can aid Indian businessmen contemplating the introduction of similar marketing techniques in other developing countries. Take the case of the marketing innovation: self- service. Whether self -service shops can be successful outside India depends upon sufficient population density, consumer income and the availability of suitable store locations and manpower. But even when these environmental forces are positive, cultural constraints may still serve as a barrier to the development of self-server. For example, a packaged food industry cannot develop unless culturally developed habits of buying only "fresh" foods and produce can be overcome. Moreover, consumers must be sufficiently literate to select products from store shelves without the help of sales clerks. The traditional pattern of shopping (in many countries) at different locations for each category of goods -e.g. dairy products, vegetables, meat, etc. is a custom that has been learned and reinforced over many years. It does not break down easily. Daily shopping trips may be re of a social Endeavour, provided the housewife can have contract with her friends at the local market or grocery, although hand-to-mouth buying may also result from low incomes and lack of refrigerating and storage facilities. In Israel, the first supermarket was successful in changing the shopping patterns of many housewives who traditionally shopped at different stores for meat, dairy products, vegetables and fruit, and baked goods. Housewives preferred the self-service shop because it refaced total shopping time and offered quality food at lower prices. Working women switched to the self-service shop because it is open during their lunch hour, unlike the small shops that close at midday for several hours. Besides introducing a wider assortment of products at lower prices, standardized packaging, pricing, and quality was offered to the Israeli consumer. Although prepackaged meats and produce were not accepted by many consumers at first, there are indications that buying habits have changed. For example, packaged meat now accounts for about 25 percent of total sales of Israel's two major self-service food chains. 31. According to the author, knowledge of foreign marketing systems is essential because it (a) Cements relation between countries (b) Helps us to know about other people (c) Can help to stimulate foreign trade (d) Improves channel of distribution (e) Teaches us something about our marketing system. 32. The passage implies that marketing can contribute to (a) Improving goods and services (b) Economic development (c) More efficient promotion and advertising (d) Full employment (e) Growth of economic institutions 33. Successful introduction of Indian marketing techniques abroad depends upon the (a) Educational level in the host country (b) Amount of investment capital available (c) Use of efficient channels of distribution (d) Extent to which the techniques can be 'transplanted' (e) Adaptability of Indian methods to 'foreign cultural conditions' 34. A most important constraint on the introduction of self service shops seems to be (a) Cultural barriers (b) Income (c) Education (d) Capital formation (e) Population dispersion 35. In Israel, daily shopping trips to the food market occur because of (a) A lack of supermarkets (b) Social reasons as much as economic ones (c) Low per-capita income (d) Poor transportation facilities (e) Fluctuating food supplies. 36. Working women in Israel prefer self - service shops owing to their (a) Lower food prices (b) Better quality food products (c) More convenient shopping hours (d) Wider choice of commodities (e) Pre-packaged meats and vegetables. 37. Concerning the transfer of Indian marketing techniques abroad, the author concludes that (a) Most countries can accept these techniques (b) They are not operable in most countries (c) More research is needed into this subject (d) The transfer depends upon capital availability (e) In general, only developed countries can use Indian marketing techniques 38. The author states that adoption of self-service is a function of I. Household income II. Cultural and structural constraints III. Population destiny (a) I only (b) III only (c) I and II only (d) II and III only (e) I, II and III 39. The article from which this passage was extracted probably appeared in an (a) Academic journal (b) Accounting journal (c) Consumer newsletter (d) Popular magazine (e) Newspaper editorial 40. Based on the Israeli experience, we can conclude that the adoption of self-service by developing countries. (a) Is hopeless (b) Shows some promise (C) Is likely to proceed with great rapidity (d) Hinders upon a large population of working women (e) Depends upon a large population of working women SECTION III PROBLEM SOLVING (QUESTIONS 41 - 60) Directions: For each of the following questions, select the choice which best answers the questions or completes the statement 41. If m, n, o and p are real numbers, each of the following expressions equals m(nop) EXCEPT (a) (op)(mn) (b) ponm (c) p(onm) (d) (mp)(no) (e) (mn) (mo)(mp) 42. If the area of the triangle BCE is 8, what is the area of the square ABCD? (a) 16 (b) 82 (c) 8 (d) 4 (e) 22 43. The diagonal of the floor of a rectangle closet is 7.5 m. The shorter side of the closet is 4.5 m. What is the area of the closet in square meter? (a) 37 (b) 27 (c) 54/4 (d) 21/4 (e) 5 44. John has more money than Sam but less than Bill. If the amount held by John, Sam and Bill are x, y and z respectively, which of the following is true? (a) z < x < y (b) x < z < y (c) y < x < z (d) y < z < x (e) x < y < z 45. If mx + ny = 12my and my ≠ 0, then x/y + n/m = (a) 12 (b) 12 mn (c) 12m + 12y (d) 0 (e) mx + ny 46. Some students planned a picnic. The budget for food was Rs 500. But, 5 of them failed to go and thus the cost of food for each member increased by Rs 5. How many students attended the picnic? (a) 15 (b) 25 (c) 20 (d) 30 (e) 45 47. Which of the following must be true? I. Any two lines which are parallel to a third line are also parallel to each other II. Any two planes which are parallel to a third plane are parallel to each other III. Any two lines which are parallel to the same plane are parallel to each other. (a) I only (b) II only (c) I and II only (d) II and III only (e) I, II and III 48. The co-ordinates of the vertices A, B of square ABCD is (2, 0) and (0, 2) respectively. What is the area of the square ABCD? (a) 2 (b) 4 (c) 4√2 (d) 8 (e) 8√2 49. A figure that can be folded over along a straight line so that the result is two equal halves which are then lying on top of one another with no overlap is said to have a line of symmetry. Which of the following figures has only one line of symmetry? (a) Square (b) Circle (c) Equilateral Triangle (d) Isosceles triangle (e) Rectangle 50. A labourer is paid Rs. 8 per hour for an 8 hour day and 1.5 times that rate for each hour in excess of 8 hours in a single day. If the labourer received Rs. 80 for a single day's work, how long did he work on that day? (a) 6 hrs 40 min (b) 9 hrs 20 min (c) 9 hrs 30 min (d) 9 hrs 40 min (e) 10 hrs Last edited by Aakashd; February 14th, 2020 at 05:52 PM. |
|
#2
| |||
| |||
|
Below I am providing you some questions of from question paper of TANCET: 83. The descriptor table registers are used for implementing 1. task switches 2. interrupt transfers 3. virtual memory 4. control transfers 84. Call gates are used for Accessing 1. higher privileged code 2. interrupt service routines 3. subroutines 4. control segments 85. Which of the following cannot be used to The instructions for which equivalent object code are not generated during assembling are 1. machine operations 2. pseudo operationsconnect external devices? 2. SCSI 3. binary operations 4. macro operations 80. The tool Yacc in UNIX generates 1. lexer 2. parser 3. code generator 86. Masking of an interrupt 1. enables the interrupt 2. disables the interrupt permanently 3. changes the priority of the interrupt 4. code optimizer 4. hides the interrupt fromthe processor TANCET Exam Question Paper    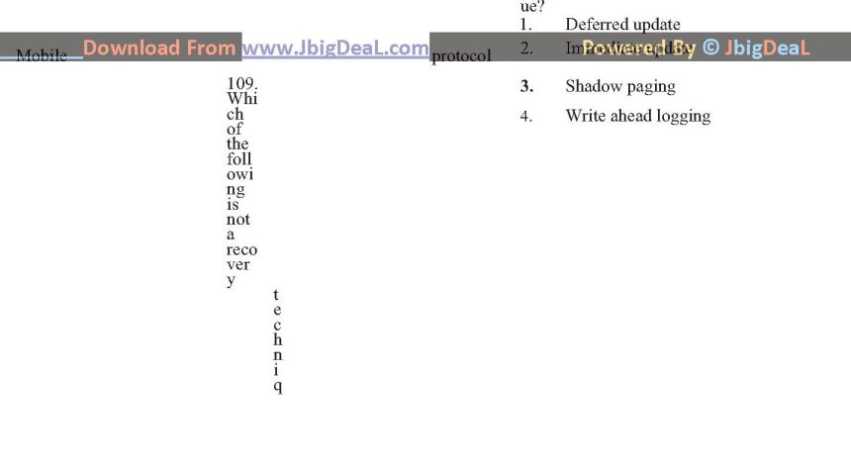 
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |
|
#3
| |||
| |||
|
51. The vertex of the square MNOP is located at the centre of circle O. If arc NP is 4π units long, then the perimeter of the square MNOP is (a) 32 (b) 32π (c) 64 (d) 64π (e) cannot be determined 52. How many minutes will it take to completely fill a water tank with a capacity of 3750 litres if the water is being pumped into the tank at the rate of 800 litres per minute and is being drained out of the tank at the rate of 300 litres per minute? (a) 3 min 36 sec (b) 6 minutes (c) 7 min 30 sec (d) 8 minutes (e) 1875 minutes 53. Triangle ABC is inscribed in a semicircle. What is the area of the shaded region above? (a) 32π – 4 (b) 2π – 4 (c) 12π - 4 (d) 6π - 4 (e) Cannot be determined from the information given 54. Two fences in a field meet at an angle of 120º , A cow is tethered at their intersection with a 15 meter rope. Over how many square meters can the cow graze? (a) 50π (b) 75π (c) 80π (d)85π (e) 90π 55. In the same amount of time a new production assembly robot can assemble 8 times as many transmissions as an old assembly line. If the new robot can assemble 'x' transmissions per hour, how many transmissions can the new robot and the old assembly line produce together in five days of round the clock production. (a) 45x/8 (b) 15x (c) 135x/8 (d) 135x (e) 1080x 56. A computer is available for Rs 39,000 cash or Rs 17,000 as cash down payment followed by five monthly installments of Rs 4,800 each. What is the rate of interest under the installment plan? (a) 35.71% p.a (b) 37.71% p.a (c) 36.71% p.a (d) 38.71% p.a (e) 45.71% p.a 57. If Sasi has Rs. 5 more than Tarun and if Tarun has Rs. 2 more than Eswar, which of the following exchanges will ensure that each of the three has an equal amount of money? (a) Sasi must give Eswar Rs. 3 and Tarun Rs. 1 (b) Tarun must give Sasi Rs. 4 and Sasi must give Eswar Rs. 5 (c) Eswar must give Sasi Rs. 1 and Sasi must give Tarun Ra. 1. ` (d) Sasi must give Eswar Rs. 4 and Tarun must give Eswar Rs. 5 (e) Either Sasi or Eswar must give Tarun Rs. 7. 58. A train with 90 km/h crosses a bridge in 36 seconds. Another train 100 metres shorter, crosses the same bridge at 45 km/h. What is the time taken by the second train to cross the bridge? (a) 61 seconds (b) 63 seconds (c) 62 seconds (d) 64 seconds (e) 68 seconds 59. For which of the following figures can the perimeter of the figure be determined if the area is known? I. a trapezoid II. a square III. an equilateral triangle IV. a parallelogram (a) I only (b) II only (c) III only (d) II and III only (e) I and III only 60. Two crystal spheres of diameter x/2 are being packed in a cubic box with a side of x. If the crystal spheres are in the box and the rest of the box is completely filled with packing powder, approximately what proportion of the box is filled with packing powder? (The volume of a sphere of radius r is 4/3πr³) (a) 11/10 (b) 1/8 (c) ½ (d) ¾ (e) 7/8 SECTION - IV DATA SUFFICIENCY (QUESTIONS 61 - 80) Directions: Each question below is followed by two statements numbered as (a) and (b). You have to determine whether the data given in the statements is sufficient for answering the question. Use the data given, plus your knowledge of mathematics and every day facts, to mark your answer as 1. If statement (a) alone is sufficient to answer the question, but statement (b) alone is not sufficient. 2. If statement (b) alone is sufficient to answer the question, but statement (a) alone is not sufficient. 3. If both statements together are needed to answer the questions, but neither statement alone is sufficient 4. If either statement (a) or (b) by itself is sufficient to answer the question. 5. If not enough facts are given to answer the question. Directions: Each of the following problems has a question and two statements which are labeled (1) and (2) in which certain data are given. You have to decide whether the data given in the statements are sufficient for answering the questions. Using the data given in the problems plus your knowledge of mathematics and every day facts, choose: 1. If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone 2. If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. 3. If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone 4. If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. 5. If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data 61. Find the value of the smaller acute angle of a right angled triangle. 1. The hypotenuse is twice the length of the shorter arm 2. The larger acute angle is 60º (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data. 62. What is the volume of soil required to fill a flower box? 1. The box is 80 cm wide 2. The box is 1 metre long (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data 63. How long will it take for two pipes to empty or fill a tank that is 3/4 full? 1. Pipe A can fill the tank in 12 minutes 2. Pipe B can empty it in 8 minutes. (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data 64. How much did a man earn in 2002? 1. He earned Rs. 6,500 in 2003 which is 12.5 % more than he earned in 2002. 2. His wife (who earned half the amount he earned) and he earned Rs. 8666.67 together in 2002 (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data 65. How long is a bridge that crosses a river which is 250 metres wide? 1. One bank of the river holds 1/5 of the bridge. 2. The other bank holds 1/6 of he bridge. (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data 66. What is the average age of the children in a class? 1. The age of the teacher is as many years as the number of children. 2. The average age increases by 1 year if the teacher’s age is also included. (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data 67. A rectangular field is 40 metres long. Find the area of the field. 1. A fence around the entire boundary of the field is 140 meters long 2. The field is more than 20 metres wide. (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data 68. A man, 2 metres tall is standing near a light on the top of a pole. What is the length of the shadow of by the man? 1. The pole is 6 metres high 2. The man is 4 metres from the pole. (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data. 69. Working at a constant rate, it takes worker U, 3 hours to fill up a ditch with sand. How long would it take for worker V to fill up the same ditch working alone? 1. Working together U and V can fill the ditch in 1 hour 52.5 minutes 2. In any length of time worker V" fills in only 60% as much as worker U does in the same time. (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you an get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data. 70. Mohan is 6 years older than Sohan. What will be the sum of their present ages? 1. After 6 years the ratio of their ages will be 6: 5 2. The ratio of their present ages is 5: 4 (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data. 71. Train T leaves town 'A' for town 'B' and travels at a constant speed. at the same time train 'S' leaves town 'B' for town 'A' and also travels at a steady speed. Town 'C' is between A and B. Which train is traveling faster? Towns A, C and B lie on a straight line 1. Train S arrives at town C before train T 2. C is closer to A than to B. (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data. 72. AB and CD are both chords of the circle with centre O. Which is longer AB or CD? 1. Arc AEB is smaller than arc CFD. 2. The area of the circular segment CAEBD is larger than the area of circular segment ACFDB (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data. 73. Did the XYZ Corporation have higher sales in 1998 than in 1999? 1. In 1998 the sales were twice the average (arithmetic mean) of the sales in 1998, 1999 and 1970. 2. In 1970, the sales were three times those in 1999. (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data. 74. A sequence of numbers a1, a2 , a3 , ................ is given by the rule an 2 = an+1. Does 3 appear in the sequence? 1. a1 = 2 2. a4 = 256. (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data. 75. What is the value of x + y? 1. x – y = 4, 2. 3x + 3y = 4 (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data. 76. x and y are integers that are both less than 10. Is x greater than y? 1. x is a multiple of 3 2. y is a multiple of 2 (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data. 77. Are two triangles congruent? 1. Both triangles are right triangles. 2. Both triangles have the same perimeter. (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data 78. If both conveyer belt A and conveyer belt B are used, they can fill a hopper with coal in one hour. How long will it take for conveyer belt A to fill the hopper without conveyer belt B? 1. Conveyer belt A moves twice as much coal as conveyer belt B. 2. Conveyer belt B would take 3 hours to fill the hopper without belt A. (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data. 79. A fly crawls around the outside of a circle once. A second fly crawls around the outside of a square once. Which fly travels farther? 1. The diagonal of the square is equal to the diameter of the circle. 2. The fly crawling around the circle took more time to complete his journey than the fly crawling around the square. (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data. 80. What is the difference between the shares of profits of Rekha and Nutan out of a profit of Rs 6,000 at the end of the year? 1. Rekha invested Rs.50,000 and withdrew Rs 1,000 after4 months. 2. For the last 8 months, Nutan’s capital was 125% of Rekha’s. (a) If you can get the answer from (1) ALONE but not from (2) alone (b) If you can get the answer from (2) ALONE but not from (1) alone. (c) If you can get the answer from BOTH (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but not from (1) alone or (2) alone (d) If EITHER statement (1) ALONE OR statement (2) ALONE is sufficient. (e) If you CANNOT get the answer from statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER, but need even more data. Directions: (Questions 81 – 100) In each of the following sentences four words or phrases have been underlined. Only one underlined part in each sentence is not acceptable in Standard English. Pick up that part - (1) or (2) or (3) or (4). If there is no error, mark (5). 81. Many scientists are alarmed over the interest in such pseudo-scientific topics as ESP, flying saucers and the occult, fearing that it may herald a new dark age of gullibility, ignorance, and thinking in superstitious ways. No Error. (a) Many scientists are alarmed (b) Fearing that (c) It may herald (d) Thinking in superstitious ways (e) No Error 82. Although the theory of continental drift was not widely accepted until the mid- twentieth century, the basic concept has been described as early as 1620. No Error. (a) Was not widely (b) Accepted until (c) Has been (d) As early (e) No Error 83. In the diagnosis of psychiatric ailments, it is essential that the practitioner approach each subject without pre-judgments as relates to the nature or causes of the disorder. No Error. (a) Diagnosis (b) It is essential that (c) Approach (d) As relates (e) No Error 84. Adaptive radiation is the process whereby a given species, through gradual adaptation in several locations to a variety of different habitats , eventually become separate species with distinct characteristics and behaviors. No error (a) The process whereby (b) Through gradual adaptation (c) Of different habitats (d) Eventually become (e) No Error 85. Foreign auto makers have not only made major inroads into the Indian market: manufacturers of other consumer goods have challenged the dominance of Indian Industry as well. No Error. (a) Have not only made (b) Inroads into (c) Of other (d) As well (e) No Error 86. After six months of study, the commission announced that some of the money previously allocated for water supply projects be spent instead on pollution control measures. No Error (a) Six months of study (b) Some of the money (c) Previously allocated (d) Be spent (e) No Error 87. Jo is the one who seems convinced that we are trying to harm her irregardless of how much we have done for her benefit. No Error (a) Who (b) Are (c) Irregardless (d) How much (e) No Error 88. The advice we had gotten had come just at the right time in our dealings in this most unfortunate matter. No Error (a) Advice (b) Gotten (c) Just (d) In (e) No Error 89. His conclusions are different from the ones that you and I am prepared to accept, even under the present circumstances. No Error (a) From (b) Ones (c) Am (d) Accept, even (e) No Error 90. If anyone in a position of genuine managerial responsibility approved the project, they are largely to blame for it subsequent failure. No Error (a) A position (b) Approved (c) They are (d) For its (e) No Error 91. The three advantages of his plan are : its simplicity, It can be applied immediately, and its probablepopularity among the local population. No Error (a) Of his plan are (b) It can be (c) Immediately, and (d) Among (e) No Error 92. There was scarcely no time given to think about the problem before the bell rang for the end of class. No Error (a) Was (b) No (c) Given (d) Before (e) No Error 93. Everyone in the family looks well in this family portrait except uncle Sam and me. No Error (a) Looks (b) well (c) Except (d) Me (e) No Error 94. Realizing how much had been expected of me, my confidence grew until I was able to face my adversaries boldly. No Error (A) Had been (b) Of Me (c) My Confidence (d) boldly (e) NO Error 95. The situation would have been far different than it is today had Ram listened to the good advice given him by his tutor. No Error (a) Would have been (b) Far different than (c) Had (d) given Him (e) No Error 96. If you would have come earlier, as I had advised, you would never have been missed by that crude trick. No Error (a) Would have (b) Had (c) Would (d) Missed (e) No Error 97. Send it back to whomever you think should receive it; I no longer care whose it is. No Error (a) Whomever (b) Should receive it (c) No longer (d) Whose (e) No Error 98. I am sure that it would be all right if no one but him was allowed to tender their resignation. No Error (a) It would (b) But him (c) Was allowed (d) Their (e) No Error 99. Having been delayed by unfavorable weather, it was not possible for our plane to arrive in time for the connecting flight. No Error (a) Been delayed (b) Unfavorable (c) Was (d) In time (e) No Error 100. The workers were enthused over the prospects for a wage increase. No Error (a) Were (b) Enthused (c) Over (d) Wage (e) No Error TANCET (MBA) Answer Key 1. (d) 2. (e) 3. (c) 4. (a) 5. (c) 6. (a) 7. (b) 8. (d) 9. (b) 10. (b) 11. (b) 12. (b) 13. (a) 14. (d) 15. (b) 16. (e) 17. (a) 18. (c) 19. (c) 20. (d) 21. (b) 22. (c) 23. (e) 24. (b) 25. (b) 26. (b) 27. (d) 28. (c) 29. (b) 30. (b) 31. (c) 32. (b) 33. (d) 34. (a) 35. (b) 36. (c) 37. (c) 38. (e) 39. (c) 40. (b) 41. (e) 42. (a) 43. (b) 44. (c) 45. (a) 46. (b) 47. (c) 48. (d) 49. (d) 50. (b) 51. (c) 52. (c) 53. (b) 54. (b) 55. (d) 56. (c) 57. (a) 58. (b) 59. (d) 60. (e) 61. (d) 62. (e) 63. (c) 64. (d) 65. (e) 66. (a) 67. (a) 68. (c) 69. (d) 70. (d) 71. (c) 72. (d) 73. (e) 74. (d) 75. (b) 76. (e) 77. (e) 78. (d) 79. (e) 80. (d) 81. (e) 82. (c) 83. (d) 84. (d) 85. (b) 86. (c) 87. (c) 88. (a) 89. (c) 90. (c) 91. (b) 92. (b) 93. (d) 94. (a) 95. (d) 96. (b) 97. (d) 98. (d) 99. (d) 100. (a)
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |