|
#1
| |||
| |||
|
Will you please tell me the Topic wise weight age in GATE??? As you want to know the Topic wise weight age in GATE, here I am telling you the same: Subject 1 Mark Questions 2 Mark Questions Engineering Mathematics 0 – 4 5 – 8 Electric Circuits 1 – 4 6 – 7 Electromagnetic Fields 0 – 2 0 – 4 Signals & Systems 0 – 3 0 – 7 Electrical Machines 3 – 6 8 – 12 Power Systems 3 – 6 8 – 11 Control Systems 1 – 3 3 – 7 Electrical & Electronic Measurements 1 – 3 1 – 8 Analog & Digital Electronics 1 – 5 4 – 10 Power Electronics & Drives 2 – 4 5 – 8 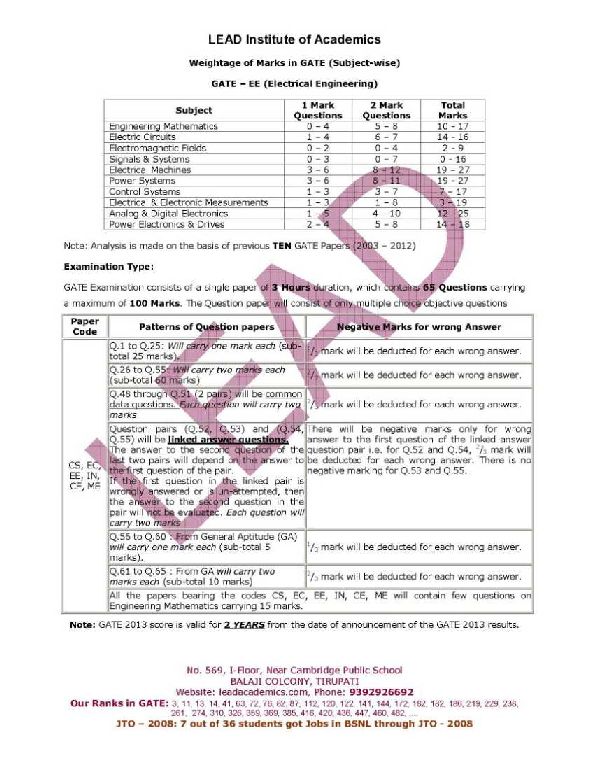 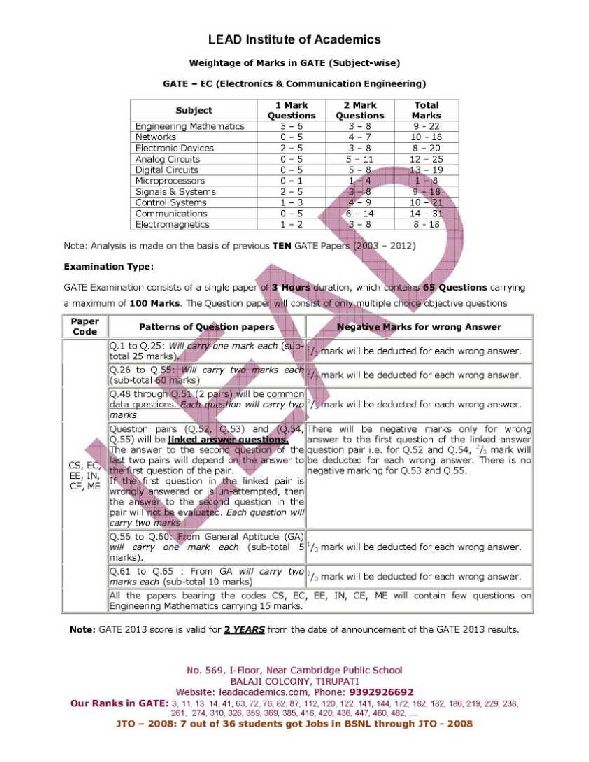 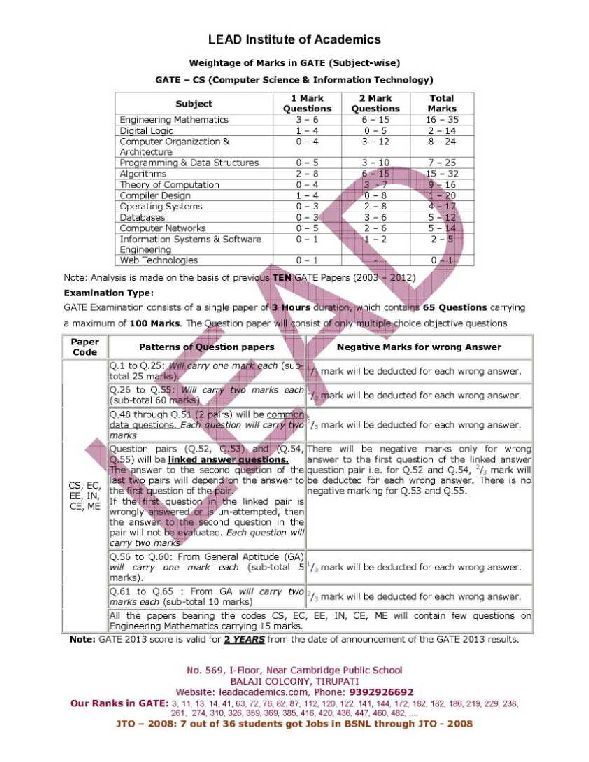 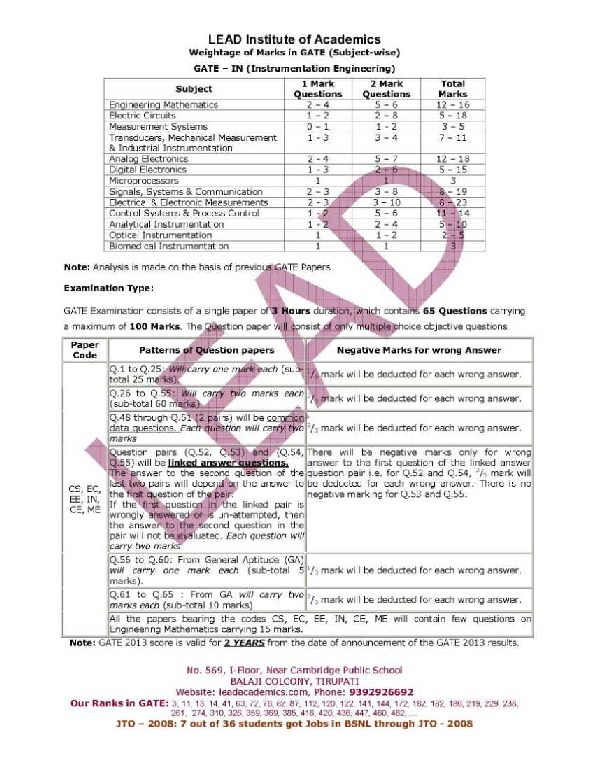 Last edited by Aakashd; May 24th, 2019 at 03:39 PM. |
|
#3
| |||
| |||
|
Here I am giving you topic wise weight age in GATE (Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering) CSE and Syllabus of GATE CSE. GATE CS: Subject Wise Weight Age of Marks: Mathematics 1 Mark Questions: 3-6 2 Mark Question: 6-15 Total Marks: 16-35 Digital Logic 1 Mark Questions: 1-4 2 Mark Question: 0-5 Total Marks: 2-14 Computer Organization & Architect 1 Mark Questions: 1-4 2 Mark Question: 3-12 Total Marks: 8-24 C Programming & Data Structure 1 Mark Questions: 1-5 2 Mark Question: 3-10 Total Marks: 7-25 Algorithm Design & Analysis 1 Mark Questions: 2 – 8 2 Mark Question: 6 – 15 Total Marks: 15 – 32 Theory of Computation 1 Mark Questions: 1-4 2 Mark Question: 3-7 Total Marks: 9-16 Compiler Design 1 Mark Questions: 1-4 0-8 Total Marks: 1-20 Operating System 1 Mark Questions: 1-3 2 Mark Question: 2-8 Total Marks: 4-17 DBMS 1 Mark Questions: 0-3 3-6 Total Marks: 5-12 Computer Network 1 Mark Questions: 1-5 2 Mark Question: 2-6 Total Marks: 5-14 Software Engineering 1 Mark Questions: 0-1 2 Mark Question: 1-2 Total Marks: 2-5 Web Technology 1 Mark Questions: 0-1 2 Mark Question: 0 Total Marks: 0-1 GATE Syllabus for Computer Science - CSE & IT: Engineering Mathematics Mathematical Logic: Propositional Logic; First Order Logic. Probability: Conditional Probability; Mean, Median, Mode and Standard Deviation; Random Variables; Distributions; uniform, normal, exponential, Poisson, Binomial. Set Theory & Algebra: Sets; Relations; Functions; Groups; Partial Orders; Lattice; Boolean Algebra. Combinatorics: Permutations; Combinations; Counting; Summation; generating functions; recurrence relations; asymptotics. Graph Theory: Connectivity; spanning trees; Cut vertices & edges; covering; matching; independent sets; Colouring; Planarity; Isomorphism. Linear Algebra: Algebra of matrices, determinants, systems of linear equations, Eigen values and Eigen vectors. Numerical Methods: LU decomposition for systems of linear equations; numerical solutions of non-linear algebraic equations by Secant, Bisection and Newton-Raphson Methods; Numerical integration by trapezoidal and Simpson's rules. Calculus: Limit, Continuity & differentiability, Mean value Theorems, Theorems of integral calculus, evaluation of definite & improper integrals, Partial derivatives, Total derivatives, maxima & minima. GENERAL APTITUDE(GA): Verbal Ability: English grammar, sentence completion, verbal analogies, word groups, instructions, critical reasoning and verbal deduction. Computer Science and Information Technology Digital Logic: Logic functions, Minimization, Design and synthesis of combinational and sequential circuits; Number representation and computer arithmetic (fixed and floating point). Computer Organization and Architecture: Machine instructions and addressing modes, ALU and data-path, CPU control design, Memory interface, I/O interface (Interrupt and DMA mode), Instruction pipelining, Cache and main memory, Secondary storage. Programming and Data Structures: Programming in C; Functions, Recursion, Parameter passing, Scope, Binding; Abstract data types, Arrays, Stacks, Queues, Linked Lists, Trees, Binary search trees, Binary heaps. Algorithms: Analysis, Asymptotic notation, Notions of space and time complexity, Worst and average case analysis; Design: Greedy approach, Dynamic programming, Divide-and-conquer; Tree and graph traversals, Connected components, Spanning trees, Shortest paths; Hashing, Sorting, Searching. Asymptotic analysis (best, worst, average cases) of time and space, upper and lower bounds, Basic concepts of complexity classes P, NP, NP-hard, NP-complete. Theory of Computation: Regular languages and finite automata, Context free languages and Push-down automata, Recursively enumerable sets and Turing machines, Undecidability. Compiler Design: Lexical analysis, Parsing, Syntax directed translation, Runtime environments, Intermediate and target code generation, Basics of code optimization. Operating System: Processes, Threads, Inter-process communication, Concurrency, Synchronization, Deadlock, CPU scheduling, Memory management and virtual memory, File systems, I/O systems, Protection and security. Databases: ER-model, Relational model (relational algebra, tuple calculus), Database design (integrity constraints, normal forms), Query languages (SQL), File structures (sequential files, indexing, B and B+ trees), Transactions and concurrency control. Information Systems and Software Engineering: information gathering, requirement and feasibility analysis, data flow diagrams, process specifications, input/output design, process life cycle, planning and managing the project, design, coding, testing, implementation, maintenance. Computer Networks: ISO/OSI stack, LAN technologies (Ethernet, Token ring), Flow and error control techniques, Routing algorithms, Congestion control, TCP/UDP and sockets, IP(v4), Application layer protocols (icmp, dns, smtp, pop, ftp, http); Basic concepts of hubs, switches, gateways, and routers. Network security basic concepts of public key and private key cryptography, digital signature, firewalls. Web technologies: HTML, XML, basic concepts of client-server computing.
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |
 |
| |