|
#11
| |||
| |||
|
Yes sure, here I am providing you the TANCET MBA Solved question papers: PASSAGE – I (Questions 1 – 10) The Shop-O-shelf Company's supermarkets are situated in Bangalore, Coimbatore and Vellore. The company is dynamic and aggressive having grown from 8 stores ten years ago to 26 today. Kanchipuram is a town 60 miles from Vellore. It has not shown the spectacular growth of other suburbs, but its population has increased from around 56,000 to 1, 30,000 in the past decade. With no other Shop-O-Self supermarket within 20 miles of the area, Shop-O-Self Company is considering opening a store in Kanchipuram. The Arguments against: some Shop-O-Self executives oppose the project as a poor risk. They point to the proposed site, which is in a shopping centre three miles from Kanchipuram business district. Two other food chains have failed on this site because they claim; most new residences are on the other side of the community. Moreover, the shopping centre owners demand a five year lease. Shop-O-Self would have to try to find another business to take over the lease should its own store fail before the end of that time. If a Shop-O-Self market must be opened in Kanchipuram, it would be far better, these executives argue, to build it in the heart of the community. But they point out, another supermarket is already there. The Arguments for: The Majority of the executives maintain that the site has great potential. A new east-west highway is being built which will pass Kanchipuram to the north and force the car commuters to Kanchipuram to pass by the shopping centre. A housing project of 3, 000 units is going to be constructed nearby. The average household is expected to consist of five people with over Rs. 30,000 of income to dispose of annually. They also argue that the centre of Kanchipuram is now congested with traffic and has extremely poor parking facilities, while there is excellent parking in the shopping centre. Investment in a new building in Kanchipuram, proper than a five year lease should the store fail. They are not too concerned about the other supermarket in Kanchipuram. There is enough business for both. Besides, the competitor's prices are higher than shop-o-self. They also discount past supermarket failures in the shopping certre. They claim these were caused more by poor management than by the shopping centre's being slightly off the beaten path. The Decision: The board of directors listens to both sides and then votes to open a Shop-o-self store at the Kanchipuram shopping centre. 1. The residents at the projected residential development will shop in the Kanchipuram store (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 2. Poor management causing past supermarket failures. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 3. New east-west highway. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 4. Expansion of dynamic company. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 5. Failure of two supermarkets due to poor site selection. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 6. Establishing a new store (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 7. New housing development. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 8. Car commuters will shop at Kanchipuram supermarket. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 9. High disposable income of expected new residents. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 10. Kanchipuram's prices are lower than those of competitors. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. PASSAGE II (Questions 11 – 20) In 1997 Mr. Deepak, a chemical engineer, began experimenting in his spare time with a new method for processing fresh orange juice. By 2000, he had perfected the process to such an extent that he was ready to begin production in a small way. His process enabled him to extract 18 percent more juice from oranges than was typically extracted by a pressure juicer of the type currently used in cafes. His process also removed some of the bitterness, which got into the juice from the peelings when oranges were squeezed without peeling them. Since many of the better quality restaurants preferred to serve fresh orange juice instead of canned or frozen juice, Mr. Deepak believed he could find a ready market for his product. Another appeal of his product would be that he could maintain more consistent juice flavor than haphazard restaurant juicing usually produced. Mr. Deepak patented the process and then started production. Since his capital was limited, he began production in a small building, which previously had been a woodworking shop. With the help of his brother, Mr. Deepak marketed the juice through local restaurants. The juice was distributed in glass bottles, which proved to be rather expensive because of high breakage. The new product was favourably accepted by the public and the business proved to e a success. Mr. Deepak began to receive larger and more frequent orders from his customers and their business associates. In 2002, he quit his regular job in order to devote full time to his juice business. He soon reached his capacity because of his inability to personally over a larger area with his pickup truck. Advertising was on a small scale because of limited funds. Faced with the problems of glass bottle breakage and limited advertisement and distribution, Mr. Deepak approached a regional food distributor for a solution Mr. Deepak was offered a plan where by the distributor would advertise and distribute the product on the basis of 25 percent of gross sales. The distributor would assist Mr. Deepak in securing a loan from the local bank to expand the production. Before he had an opportunity to contact the bank to borrow money, Mr. Deepak was introduced to Mr. Sunil, a plastics engineer, who produced plastic containers. Mr. Deepak mentioned his own problems in the expansion of his business. Mr. Sunil wanted to finance expended juice production with the understanding that plastic containers would be used for marketing the orange juice. He would lend the money interest free, but he was to receive 40 percent of the net profits for the next ten years. Distribution and advertising agent for 25 percent of gross sales. The principal on Mr. Sunil's invested money was to be repaid by Mr. Deepak on a basis of 10 percent of his share of the profits. Mr. Sunil was to retain an interest in the profits of the firm until the loan was repaid, or at least for ten years. Mr. Deepak's current sales were 10,000 litres of juice a month. If distribution could be expanded, sales could be doubled, given the potential demand. Of the possible total sales of 20,000 a month, about 75 percent would be sold to large restaurants and the reminder to small cafes and canteens. As soon as the juices were bottled in plastic containers, sales could also be made to household consumers. Mr. Deepak was very optimistic that sales to the final consumer through retail shops would succeed. Some initial contacts were made with a local manager of a food chain supermarket. The manager was sure that he could sell 4,000 litres a month through his outlets. Mr. Deepak also calculated his potential profits. His goal was to increased sales while at the same time earning a 10 percent rate of return on his prior capital investment in equipment and other assets. The present value of Mr. Deepak's investment was Rs. 2,50,000. Of this sum, machinery and equipment were valued at Rs. 1,00,000; building was worth Rs. 50,000 and his patent and know-how were valued at Rs. 1,00,000. On the basis of this evaluation, Mr. Deepak desired a return of Rs. 25,000 above salaries and other expenses after the first year of operation. Both the regional distributor and Mr. Sunil believed that Mr. Deepak's sales could be increased to 15,000 litres of juice per month by the end of the first year of expanded operations. However, the extent to which production could be expanded to meet demand depended on the availability of plastic containers (which would be supplied at factory cost under Mr. Sunil's proposal), and additional machinery. Increased market coverage would be obtained both under the regional food distributor and Mr. Sunil's proposals. The critical deciding factor, as Mr. Deepak understood, was which plan would maximize his return on investment beyond the minimum figure of 10 percent. 11. Cost of securing a loan (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) The item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 12. High breakage rate of glass bottles. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 13. Expansion of the business (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 14. Continued demand by the public for Mr. Deepak's orange juice (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 15. Possibility of doubling sales through expanded distribution (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 16. Previous use of Mr. Deepak's building as a woodworking shop (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 17. Ten percent return of investment (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 18. Small scale of current advertising (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is, the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 19. Value of patent held by Mr. Deepak. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. 20. Mr. Deepak's current level of sales. (a) If the item is a Major Objective in making the decision: that is , the outcome or result sought by the decision maker. (b) If the item is a Major Factor in arriving at the decision; that is consideration, explicity mentioned in the passage that is basic in determining the decision. (c) If the item is a Minor Factor in making the decision: a less important element bearing on or affecting a Major Factor, rather than a Major Objective directly. (d) If the item is a Major Assumption made deliberately; that is a supposition or projection made by the decision maker before considering the factors and alternatives. (e) If the item is an unimportant issue in getting to the point; that is a factor that is insignificant or not immediately relevant to the situation. SECTION II READING COMPREHENSION Direction: This section contains two reading passages. You have to read each carefully. Each passage is followed by questions based on its content. After reading each passage, choose the best answer to each question. The questions are based on what is stated or implied in each passage. PASSAGE I (Questions 21 – 30) The concept of "standard of living" is a wide and multifaceted one. In the absence of comprehensive measurement, it is commonly expressed empirically in terms of consumption or in terms of income. One of the most comprehensive expressions of standard of living is total consumption over an extended period, where consumption is defined not only as family purchases but also as (1) consumption of goods and services produced by the family; (2) consumption of public services provided without payment; and (3) consumption of goods and services received as compensation for labor, over and above wages and salary. It may be assumed that total consumption is less subject to incidental fluctuations than income. Moreover, it reflects not only current income but also past income and savings, windfalls, and expectations regarding future income. Current monetary income constitutes the main indictor for the standard of living; however, standard of living is not determined solely by current income, but also by past income, accumulated assets and expectations for future income. Moreover, the standard of living of a family is influenced by the value of the public services from which it benefits and the rate of taxes which it has to pay. In the period under review, the standard of living of families originating from Asia and Africa improved relative to that of all families. This improvement found expression in higher income levels, better housing, higher ownership rate of consumer durables and an increase in the proportion of families in higher income brackets. However, even after the improvement in their relative position during the past decade, their average income is still only 70% of the overall average for all families. One of the important factors behind the income differential between families of African and Asian originals and the rest of the populations is the level of education. In rent years the gap between these two groups has narrowed among the younger generation, but it is still substantial. Unless the education gap is significantly reduced between these two groups, other means employed in an attempt to produce more income equality will be thwarted. More resources must be immediately put to the task of improving educational opportunities for families of African and Asian origin, without of course, reducing the education facilities and opportunities open to the rest of the population. 21. The author defines 'standard of living' in terms of (a) Total goods and services produced (b) Consumption of goods and services (c) Real income (d) Per capita income (e) Discretionary income. 22. Which income period (s) would be included in the author's definition of 'standard of living;? I. Past income II. Current Income III. Future income (a) I only (b) II only (c) I and II only (d) I, II and III (e) Neither I, II and III 23. Consumption is defined as (a) Total family purchases (b) Total family purchases plus goods and services produced by the family (c) Public services provided by the state. (d) Income minus expenditure on necessities (e) Total family purchases plus other goods and services consumed 24. Between 1994 and 2000, average real income (a) Remained stable (b) Increased by about 5% annually (c) Decreased slightly (d) Decreased during the recession (e) Decreased by 5% annually 25. According to the passage, between 1997 and 2000, income equality (a) Declined among all strata (b) Declined most significantly among lower income groups (C) Widened between the rich and the poor strata (d) Did not change appreciably (e) Declined among older groups in the population. 26. The author believes that inequality of income might be narrowed if (A) The tax structure was reformed (b) The educational gap between different population groups was reduced (c) More jobs could be found for people of Asian-African origin (d) Real income increased (e) A system of price controls was implemented 27. The standard of living of Asian - African immigrants has improved as measured by all of the following factors except (a) Higher income levels (b) Better housing (c) Increased ownership of consumer durables (d) A shift in population centres (e) An increased proportion of Asian - African families in higher income brackets. 28. It may be inferred that the author of the passage is an (a) Engineer (b) Food specialist (c) Economist (d) Bank president (e) Efficiency expert 29. Even though the income level of families of Asian - Africa origin increased relatively, their average income is still (a) Only about equal to that of other groups (b) About 70 percent of the overall national average (c) Close to the national average, but slightly below (d) About 50 percent of the national average (e) About 25 percent of the national average 30. Between 1997 and 2000, the standard of living of the urban population (a) Declined (b) Increased (c) Stagnated (D) Remained constant (e) Doubled Complete question paper is in the attachment, please click on it……….
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |
|
#15
| ||||
| ||||
|
As you want to get the previous year question papers of exam of TANCET 2014 which is conducted by Anna University so here is the information of the same for you: Some content of the file has been given here: 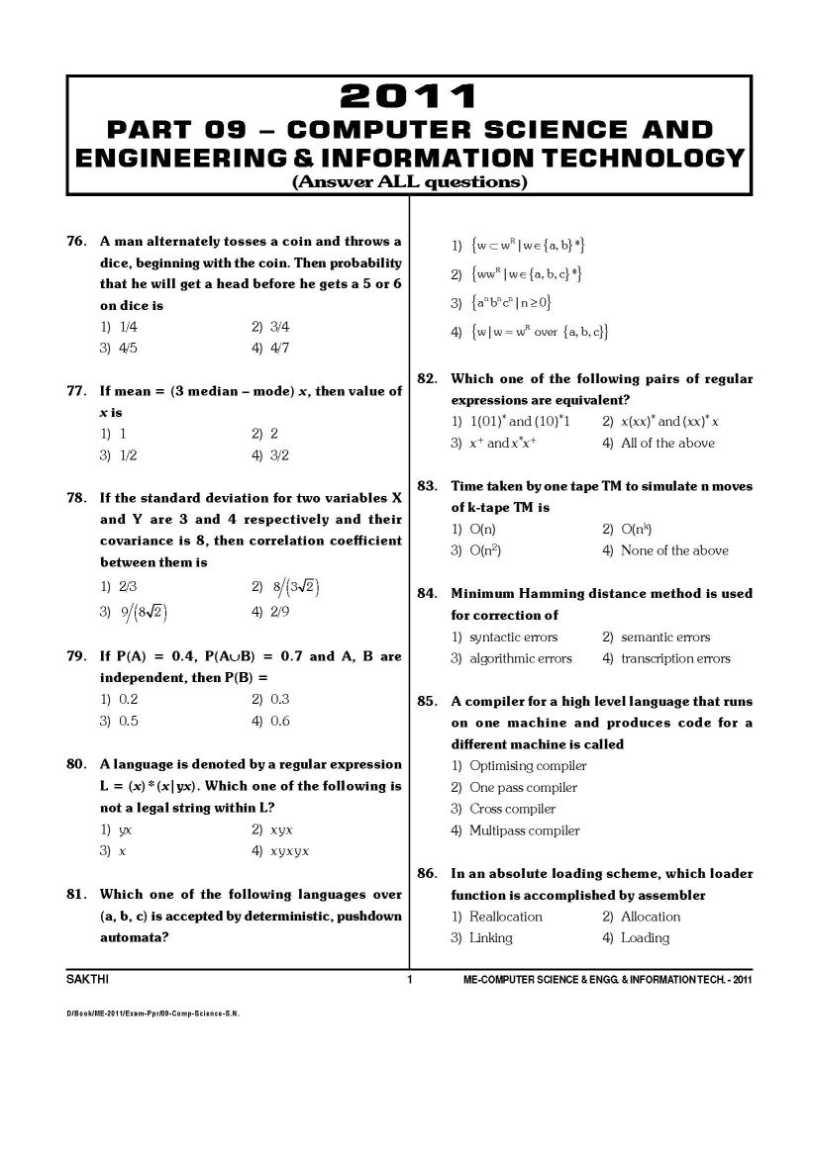   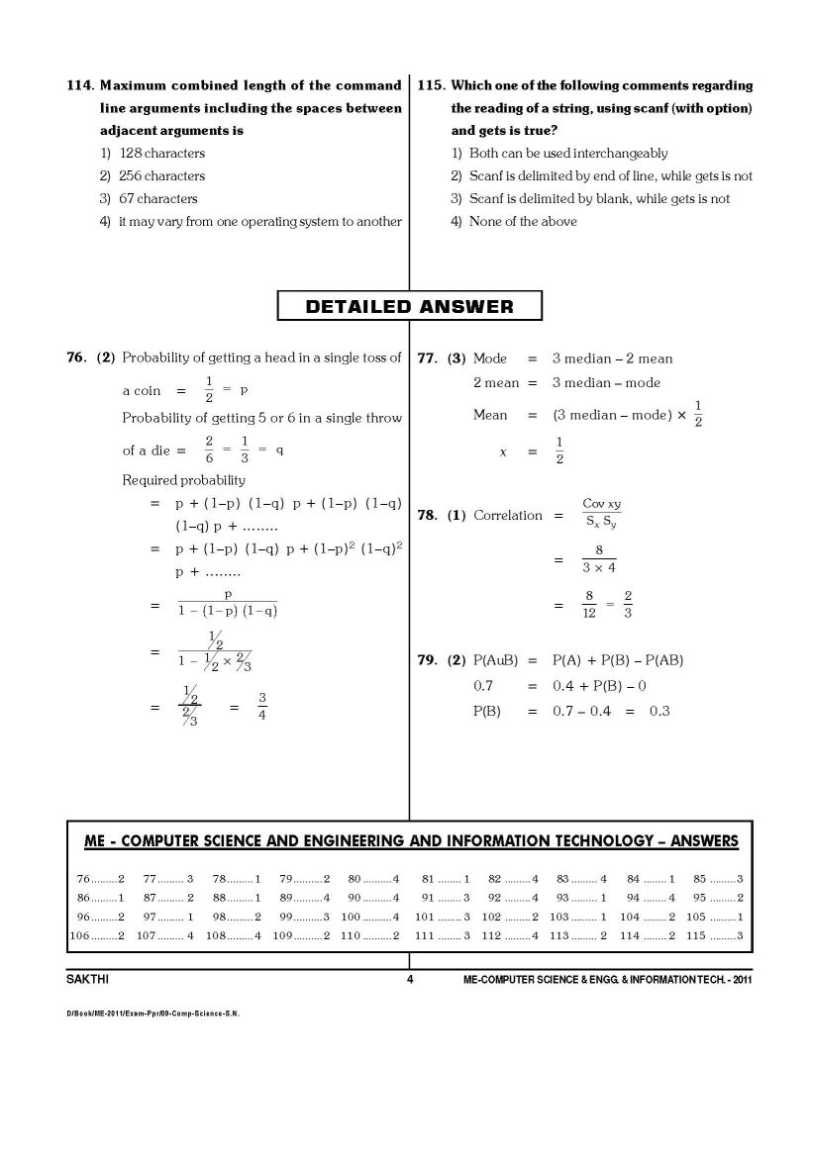 For more detailed information I am uploading a PDF files which are free to download: Contact Details: Anna University Sardar Patel Road, Guindy, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, 600 025 044 2235 7080 India Map Location:
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |
|
#17
| ||||
| ||||
|
Here I am giving you question paper for Tamilnadu Common Entrance Test in PDF file attached with it so you can get it easily.. 1. A sequence of odd numbers is formed as follows: 1, 3, 3, 3, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7 ..... What is the number in the 251st place? 1) 27 2) 28 3) 29 4) 30 2. Out of 50 hockey and football players, the number of players who play only hockey is the same as that who play only football. The number of those playing only hockey is twice that of those playing both games. How many players play both games? 1) 5 2) 20 3) 10 4) 25 3. A, B, C and D are four numbers. Two of them are 0; one is positive and one is negative. AB is not equal to CD, Which of the following can be negative? 1) C+D 2) AD+BC 3) AC 4) BCD 4. A motorist knows four different routes from Bristol to Birmingham. From Birmingham to Sheffield he knows three different routes and from Sheffield to Carlisle he knows two different routes. How many routes does he know from Bristol to Carlisle? 1) 4 2) 8 3) 12 4) 24 5. In a group of 15 people, 7 read French, 8 read English while 3 of them read none of these two. How many of them read French and English both? 1) 0 2) 3 3) 4 4) 5 6. The ratio of milk and water in 150 litres of a solution of milk is 4:1. How much water must be added to this 150 litres of milk so that the ratio of milk to water becomes 4:3? 1) 100 litre 2) 60 litre 3) 50 litre 4) 55 litre 7. A magician called the following to the stage - Beena, Dileep, Farookh and Harish. Whom will he call next? 1) Pradeep 2) Maneesh 3) Jameel 4) Meenal 8. If SEEMA WANTS WATER is 1 2 3, WATER IS BLUE is 1 4 5, SEEMA HAS BLUE DRESSES is 2 4 6 7, SANGEETA HAS WATER is 7 1 8, then SANGEETA WANTS BLUE DRESSES will have the numbers: 1) 8 3 4 6 2) 8 2 5 6 3) 7 2 4 6 4) 8 5 4 6 9. Mohini bought an article. She sold it for Rs.31.25 making a percentage profit equal to the cost price of the article. What is the cost price of the article? 1) 30 2) 25 3) 24 4) 20 Directions for questions (10–14) : There are four nurses – Anita, Beena, Chaiya and Dimple working at the private nursing home, which is open from Monday through Friday. Each nurse works according to the following rules: On Mondays, only Anita or Beena works. On Tuesdays, Beena works alone or with one of the other nurses, but not Anita. On Wednesdays, Chaiya works alone or with one of the other nurses. On Thursdays, two nurses work together, but Beena is not one of them. On Fridays, three nurses work together. 10. Beena must work on which of the following days? 1) Monday 2) Tuesday 3) Wednesday 4) Thursday 11. If only Beena and Dimple are working on a certain day, which day must it be? 1) Monday 2) Tuesday 3) Wednesday 4) Thursday 12. If only one nurse is working on a particular day, which one of the following must be true? 1) Monday or Tuesday 2) Monday or Tuesday or Wednesday 3) Tuesday or Wednesday or Thursday 4) Tuesday or Thursday or Friday 13. If we know that Dimple is working on a par ticular day but don’t know whether anyone else is working, that day could be all of the following EXCEPT 1) Monday 2) Tuesday 3) Wednesday 4) Thursday 14. If two nurses are working on a particular day, and neither of them is Chaiya, which one of the following must be true? 1) Monday or Tuesday 2) Tuesday or Wednesday 3) Tuesday or Thursday 4) Wednesday or Thursday Directions for questions (15–17) : Read carefully the passage given below and answer the questions that follow. The seizures of cocaine laboratories in Colombia, South America, underscore a little noted but crucial fact of life in the $130 billion cocaine business. The drug trade is a two-way street. The cocaine flows from mostly third world producers to the United States or other industrialised nations, but the chemicals and other materials needed to turn coca leaves into cocaine flow comes from the industrialised nations to the third world. By participat ing in this Faust ian technology transfer, the drug consumers are in effect providing raw ingredients for the scourge that bedevils them and that they often blame exclusively on cokeproducing countries. “Look at all this equipment”, said a Colombian police commander, surveying the ruins of a coke lab, “It is almost all from the United States, and the chemicals from all over the world. All Latin American supplies are the coca-leaves and the labour.” 15. The passage seeks to 1) blame U.S.A. for supplying equipment for processing cocaine. 2) preclude the Latin American countries from blame. 3) show how deeply the drug problem has affected Pan American relations. 4) bring out the international nature of this curse that faces “mankind”. 16. By “Faustian technology transfer” the author means 1) transfer of technology involving a deal with the devil. 2) transferring technology in order to taste greater power. 3) technology that is transferred, ends in a fatal experience. 4) exchanging technology for a raw material that asks for a very high price. 17. The two way street indicates 1) all men are greedy 2) to eradicate drugs, the world has to cooperate. 3) the growing distance between the haves and the have-nots. 4) men from all nations are attracted to the high returns in a substance known to be harmful. Directions for questions (18 and 19) : Pick out the most effective word from the given words to fill in the blank to make the sentence meaningfully complete. 18. The ant icipated higher income growth following the second ———— bumper harvest claimed this year is hoped to ease the demand constraint. 1) continuous 2) consecutive 3) successive 4) gradual 19. We live in an interdependent world and cannot therefore afford to ––––––– our neighbour. 1) insult 2) offend 3) annoy 4) irritate 20. The sum of 10000.101 and 1100.001 is 1) 28.75 2) 24.54 3) 28.625 4) 24.375 21. A cricketer has an average of 24 runs in 24 innings. How many runs must he score in the 25th innings to make the average equal to 25 runs? 1) 25 2) 49 3) 50 4) 100 22. From two ornaments weighing 18 gm and 24 gm, containing gold and silver in the ratio of 2:1 and 5:1 respectively, a new ornament is casted. What is the amount of gold in the new ornament in gms? 1) 10 2) 12 3) 32 4) 28 23. The ratio of milk and water in a 48 litre mixture is 7:5. How much of milk is required to be added to this mixture, so that the ratio becomes 3:2? 1) 3 litres 2) 4 litres 3) 1 litre 4) 2 litres 24. 10 litres solution of water and salt contains 150 gm sal t . I f 25% of solut ion gets evaporated, what percent of salt would the remaining solution have? 1) 1.5% 2) 2.0% 3) 1.75% 4) 2.5% 25. Which one of the following numbers would fit into the series: 2, 9, 16, 23, 30, 37 ? 1) 1253 2) 1255 3) 1257 4) 125935 26. Amit wants to distribute either type A or type B or type C of the chocolates to his friends at the birthday party. If he has 225, 250 and 260 nos. of types A, B and C respectively and he wishes to give equal no. of either of these to his friends, how many minimum no. of packets would he have to prepare? 1) 97 2) 735 3) 51 4) 147 27. For painting of the house, it is estimated that 480 kg of paint is needed. Accounting for was tage @ 20% and that the paint is available in tins of 25 kg only, what is the cost of painting if each tin is costing Rs.250? 1) 5,000 2) 6,400 3) 5,600 4) 6,000 Directions : Refer to the data below and answer the questions from 28 to 30 : Col. Singh wants to select instructors at the Indian Army’s Commando Training School. The instructors should meet the following criteria: a) The candidate should be a serving army officer. b) The candidate should be a graduate of the Natioinal Defence Academy (NDA). c) The candidate should be below 40 years of age. d) The candidate should have passed through a commando course in the past 2 years. The only possible exceptions to these rules are: i) If not a graduate of the NDA, should have passed out of the Indian Military Academy (IMA), and been in the top of his/her class of IMA – give a leadership exam. ii) If not an officer, must have won at least 2 glallantry awards – meet Gen. C. iii) If between 40 and 45 – meet Gen. J. iv) If the commando course is taken before two years – go through a fitness test. Col. Singh has received the following applications: – The 25 years old Captain T, stood second in his class in IMA, and completed commando training 2 weeks ago. – Jawan E, winner of 3 gallantry awards, passed out of NDA at the age of 22, 15 years ago. He completed a commando course 6 months ago. – Major W(retired), a 39-year-old is a former NDA graduate and passed a commando course 3 months ago. – Col. P, a 42 year old is an NDA and has passed a commando course 1 year back. – Captain Y, a 24-year-old passed out of NDA and has never been to do a commando course. 28. What should be done with Jawan E? 1) Accept 2) Reject 3) Fitness test 4) Meet Gen. C 29. What should be done with Captain Y? 1) Meet Gen. C 2) Reject 3) Accept 4) Meet Gen. J 30. What should be done with Captain T? 1) Meet Gen. J 2) Meet Gen. C 3) Leadership Exam. 4) Reject 31. If “CODES” is coded as “DQGIX”, then what is the code for “LOGIC”? 1) MPHJD 2) MQJMH 3) MQJMI 4) MQHKE 32. In a class of 80 students, 20% dislike teacher A and 30% dislike teacher B. 50% of the students do not dislike any teacher. How many students dislike both teachers A and B? 1) 40 2) 20 3) 30 4) None of these Directions : Refer to the data below and answer the question (33 to 35) : There are five books A, B, C, D and E from five different subjects, that are, Geology, Maths, Physics, Chemistry and Zoology. a) A is not a Geology or Maths book. b) B is not a Maths, Physics or Chemistry book. c) C is not a Geology, Physics or Zoology book. d) D is a Chemistry book. e) If C is a Maths book, then E must be a Zoology book. 33. Which is the Maths book? 1) A 2) B 3) C 4) A or C 34. Which is the Zoology book? 1) A 2) B 3) E 4) A or E 35. Which is the Physics book? 1) A 2) E 3) C 4) E or C Directions : Refer to the data below and answer the Questions (36 and 37) : R * 2 7 5 E ! $ A S O 3 = 4 # N I N @ 8 !N 6 $ G 36. What is the difference between the sum of the numbers and the number of symbols in the given series? 1) 27 2) 28 3) 29 4) 26 37. How many letters are immediately followed by a symbol in the above series? 1) 2 2) 4 3) 5 4) 3 Directions : Refer to the data below and answer the Questions (38 to 41) : Six lectures are to be organised in a day and six dif ferent persons, A, B, C, D, E and F will deliver these lectures. The arrangement of lectures follow few conditions given below : a) A wakes up late so he cannot give the first or the second lecture. b) B should give a lecture just after D’s lecture. c) Between E and F there will be two lectures and F’s lecture should be held fourth. 38. The fifth lecture can be delivered by all of the following except : 1) A 2) D 3) C 4) B 39. Who can deliver lecture just after E’s lecture? 1) Only A 2) Only D 3) D or C 4) Only C 40. If C’s lecture is the second one, then whose lecture must follow F’s lecture? 1) E 2) D 3) B 4) A 41. If A’s lecture will be held fifth, then who will deliver the 6th lecture? 1) C 2) B 3) D 4) E 42. The most technologically advanced societies have been responsible for the greatest ––––– indeed savagery seems to be indirect proposition to –––––––– 1) inventions - know-how 2) wars - viciousness 3) triumphs - civilisations 4) attrocities - development 43. The ––––––– tones of the flute succeeded in ________ his tense nerves. 1) blatant - enhancing 2) hovendous - calming 3) vibrant - portraying 4) mellifluous - soothing 44. It would be difficult for one so –––––– to be led to believe that all men are equal and that we must disregard race, colour and creed. 1) intolerant 2) democratic 3) emotional 4) patient 45. Unlike the Shakespearean plays, The “closet dramas” of the nineteenth century were meant to be –––––– rather than –––––– 1. seen - acted 2) read - acted 3. produced - acted 4) quiet - loud 46. We never believed that he would resort to ––––––– in order to achieve his goal ; we always regarded him as a ––––––– 1) subterfuge - honest 2) charm - insincere 3) necromancy - pietistic 4) logic - honorable 47. Yellow fever, the disease that killed 4,000 Phi ladelphians in 1793, and so ––– –– Memphis, Tennessee, that the city lost its charter, has reappeared after nearly two de cade s in – – – – – – in the we s te r n hemisphere. 1) disabled - quarantine 2) decimated - abeyance 3) terrorised - contention 4) ravaged - secret Use the following passage to answer questions (48 to 50) : A clear answer to whether the languages of the ancient American people were made use of for expressing abstract universal concepts can be sought in the case of Nahuat l, which like Greek and German, i s a language that allows the format ion of extensive compounds. By combining radicals or semant ic elements, single compound words can express complex conceptual relations, often of an abstract universal character. The tlamatinime (“those who know”) were able to use this rich stock of abstract terms to express the nuances of their thought. They also availed themselves of other forms of expression with metaphorical meaning, some probably original, some derived from Toltec coinages. Of these forms the most characteristic in Nahuatl is the juxtaposition of two words that, because they are synonyms, associated terms, or even cont rar ies, complement each other to evoke one single idea. The juxtaposed terms, used as metaphor, suggest specific or essential traits of the being they refer to, introducing a mode of poetry as an almost habi tual form of expression. 48. The main purpose of the passage is to 1) argue against a theory of poetic expression by citing evidence about the Nahuatl. 2) delineate the function of the tlamatinime in Nahuatl society 3) explore the rich metaphorical heritage the Nahuatl received from the toltecs 4) descr ibe some conceptual and aesthet ic resources of the Nahuatl language. 49. It can be inferred solely from the information in the passage that 1) Metaphors are always used in Nahuatl to express abstract conceptual relationships. 2) There are many languages that, like Greek or German, allow extensive compounding. 3) The abstract terms of the Nahuatl language are habitually used in poetry 4) Some record or evidence of the thought of the tlamatinime exists 50. According to the passage, some abstract universal ideas can be expressed in Nahuatl by 1) putting various meaningful elements together in one word 2) taking away from a word any reference to particular instances 3) turning each word of a phrase into a poetic metaphor 4) giving a word a new and opposite meaning. 51. Water is cont inuous ly poured f rom a reservoir to a locality at a steady rate of 10,000 litres per hour. When delivery exceeds demand the excess water is stored in a tank. If the demand for 8 consecutive three-hour periods is 10000, 10000, 45000, 25000, 40000, 15000, 60000 and 35000 l itres respectively, the minimum capacity required of the water tank (in 1000 litres) to meet the demand is 1) 10 2) 30 3) 40 4) 50 52. Jhaveri invested in Upendra & Upendra, Celco and Winger shares at Rs.300, Rs.200 and Rs.5 per share respectively. He bought 100 shares for Rs.1,000. The number of Upendra & Upendra and Celco shares he bought are respectively. 1) 23, 17 2) 17, 23 3) 17, 60 4) 15, 25 53. A certain organisation has three committees. Only two persons are member s of al l committees, but every pair of committees have three members in common. What is the least possible no. of members on any one committee? 1) 4 2) 5 3) 6 4) None of the above 54. One bottle is half-full of oil and another bottle with twice the capacity is one quarter full of oil. If water is added so that both the bottles are full and the contents of both are then poured into a third bottle that is empty and large enough to hold the contents of both, what fractions of the contents in the third bottle is oil? 1) 1/4 2) 1/3 3) 3/8 4) 2/3 55. Don and his wife each receive an 8 percent annual raise. If Don receives a raise Rs.800 and his wife receives a raise of Rs.840, what is the di fference between their annual income after their raises? 1) 40 2) 460 3) 500 4) 540 56. If 5 tomatoes are worth 8 oranges, 5 oranges are worth 4 apples, 7 apples are worth 3 pineapples and 7 pineapples cost Rs.203, then the approx. price of each tomato is 1) 16 2) 5 3) 19 4) None of the above 57. 1 Kbyte is 1) 1000 bytes 2) 1016 bytes 3) 1008 bytes 4) 1024 bytes 58. The heart of the Computer is 1) Input devices 2) Output devices 3) Central processing unit 4) Peripheral devices 59. DOS in MS-DOS stands for 1) Disk open system 2) Disk operating system 3) Disk open standards 4) Device operating system 60. Pressing the following keys simultaneously will reboot your computer automatically 1) Ctrl – Alt – Del 2) Shift – Alt – Del 3) Shift – Tab – Del 4) Ctrl – Tab – Del 61. Which helps you to build documents from ver y s imple let ters to comprehensive manuscripts? 1) MS-Excell 2) MS-Word 3) MS-Access 4) MS-Powerpoint 62. The basic operat ions per formed by a computer are 1) Arithmetic 2) Logical 3) Storage and Retrieval 4) All of the above 63. The earliest calculating devices are 1) Abacus 2) Clock 3) Different engine 4) None of the above 64. The man who built the first mechanical calculator was 1) Joseph Marie Jacquard 2) John Mauchly 3) Blaise Pascal 4) Harward Aliken 65. Punched cards were first introduced by 1) Powers 2) Pascal 3) Jacquard 4) Herman Hollerith 66. The event A is independent of itself if and only if 1) P(A) = 1 2) P(A) = 1/2 3) P(A) = 1/3 4) None of the above 67. If the sum of two numbers is 200, then the largest value of their product is 1) 9000 2) 10000 3) 100000 4) 1900 68. The equation of the curve which passes through the point (1, –1) and has slope 3x2 is 1) y = 3x3–2 2) y = 3x2 3) y = 3x3 4) None of the above 69. Which one of the following is true? 1) A semi-group with more than one idempotent element cannot be a group. 2) If G is a group, then it may not be a monoid. 3) G is a group if and only if it is a semi-group. 4) None of the above 70. The points of maximum and minimum curvature on the curve y=log x, x and y are real and –xare 1) ±2) 0, ±/4 respectively 3) ±/2, ±respectively 4) None of the above 71. The area of the circle whose center is at (0, 0) is 25. The circle passes through all the points except. 1) (–5, 0) 2) (5, 0) 3) (5, 5) 4) (0, 5) 72. A class room has r rows of desks with d desks in each row. On a particular day when all pupils are present 3 seats are left vacant (one student per desk). The number of pupils in the class is 1) dr–3 2) d+r+3 3) dr+3 4) r/d+3 73. The length of a rectangle is increased by 50%. By what percent the width has to be decreased to maintain the same area? 1) 33.33 2) 50 3) 66.67 4) 150 74. If the radius of a circle is 0.5m, how many revolut ions does the wheel make per kilometer? 1) 1000 2) 2000 3) 1000/4) 2000/ 75. The average of 5, 10, 15, and X is 20. What is X? 1) 20 2) 25 3) 45 4) 50 76. What is the largest prime factor of 255? 1) 15 2) 5 3) 51 4) 17 77. A and B are in the ratio 5:4. B and C are in the ratio 6:7 then A:B:C is 1) 30 : 24 : 28 2) 5 : 10 : 7 3) 5 : 4 : 7 4) 15 : 12 : 14 78. “Idle brain is a devils workshop”. Which of the following has the same logic? 1) Hardwork is the basis of success. 2) Dissatisfied person is rebellious. 3) Educated are cultured people. 4) Players are physically healthy. 79. “The ground is wet because it has rained” which of the following is based on the same logic? 1) Leaves are green because they have chlorophyll 2) Iron is unbreakable because it is logical 3) The lawyer is convincing because he is logical 4) The soldier is bleeding because he is injured. 80. Pick the odd one out. 1) Counting sort 2) Bucket sort 3) Shell sort 4) Radix sort 81. The complexity of merge operation on two sorted arrays of size m and n (given m>n) 1) O (mn) 2) O (m+n) 3) O (m/n) 4) O (m) 82. Pick the odd one out. 1) Random value 2) Return address 3) Local variable space 4) Global variable space 83. The function for which among the following will not be linear recursion 1) Factorial 2) Fibonacci series 3) ab 4) Sum of the natural numbers 84. How many stack will be needed for the evaluation of a prefix expression? 1) 1 2) 2 3) 0 4) 3 85. Which one of the following may be true for a quadratic equation (is real)? 1) If is a root, 1/is also a root. 2) If is a root, –is also a root. 3) If is a root, iis also a root. 4) If iis a root, –iis also root. 86. I f a and a re the root s of |x2+x+5|+6x+1=0 then is 1) 7 2) –7 3) 5 4) –5 87. If a+b+c=0, then one root of the equation ax2–bx+c=0 is 1) –b/a 2) –c/a 3) (a+c)/a 4) (a+b)/a 88. If a and b are positive integers such that a3–b3 is a prime number, then a3-b3 is 1) a2+ab+b2 2) a2–ab+b2 3) a+b 4) a–b 89. The smallest angle in degrees between the hour and minute needles of a clock when the time is 12 hr 30 min is 1) 180o 2) 165o 3) 196o 4) 150o 90. The collating sequence of five alphabets is W, P, Z, A and E. Which one will be the first string of the above collating sequence? 1) AZPWW 2) APAEP 3) ZPAPA 4) ZAPWE 91. How many numbers between 100 and 300 (inclusive) is divisible by 3? 1) 100 2) 66 3) 76 4) None of the above 92. Which one of the following figures has the largest area for the given circumference? 1) Square 2) Triangle 3) Circle 4) Ellipse 93. If 2 1) 1 and answer the questions given below the passage. A family consisting of six members AA, BB, CC, DD, EE, and FF is travelling together. We have _ BB is the son of CC but CC is not the mother of BB. _ FF is the brother of BB. _ EE is the brother of CC. _ DD is the daughter of AA. _ AA and CC are a married couple. 94. How many male members are there in the family? 1) 1 2) 2 3) 3 4) 4 95. Who is the mother of BB? 1) AA 2) BB 3) CC 4) DD 96. How many children does AA have? 1) 1 2) 2 3) 3 4) 4 97. How many brother-brother pair can be made from the above family? 1) 1 2) 2 3) 3 4) 4 98. How is EE related to DD? 1) Father 2) Brother 3) Uncle 4) Sister-in-law 99. The function f(x)=q+|sinx| is 1) discontinuous everywhere 2) not differentiable at x=0 3) not differentiable at an infinite number of points 4) All of the above 100. The function f(x)=2log(x–2)–x2+4x+1 increases in the interval 1) (1, 2) 2) (2, 3) 3) (2, 4) 4) (1, 5) MCA 2011 – ANSWERS 1 ......... * 2 ......... 3 3 ......... 1 4 ..........4 5 ..........2 6 ........ 2 7 ......... 3 8 ......... 1 9 ......... 2 10..........2 11 ........ 2 12 ......... 2 13 ......... 1 14 ..........3 15 ..........4 16 ........ 4 17 ......... 2 18 ......... 2 19......... 3 20..........1 21 ........ 2 22 ......... 3 23 ......... 4 24 ..........2 25 ..........2 26 ........ 4 27 ......... 4 28 ......... 1 29......... 2 30..........4 31 ........ 2 32 ......... 4 33 ......... 3 34 ..........3 35 ..........1 36 ........ 1 37 ......... 2 38 ......... 2 39......... 3 40..........2 41 ........ 1 42 ......... 4 43 ......... 4 44 ..........1 45 ..........2 46 ........ 1 47 ......... 2 48 ......... 4 49......... 4 50..........1 51 ........ 3 52 .......... * 53 ......... 2 54 ..........2 55 ..........4 56 ........ 1 57 ......... 4 58 ......... 3 59......... 2 60..........1 61 ........ 2 62 ......... 4 63 ......... 1 64 ..........3 65 ..........4 66 ........ 1 67 ......... 2 68 ......... 4 69......... 1 70..........1 71 ........ 3 72 ......... 1 73 ......... 1 74 ..........3 75 ..........4 76 ........ 4 77 ......... 4 78 ......... 1 79......... 4 80..........3 81 ........ 2 82 ......... 4 83 ......... 2 84 ..........3 85 ..........4 86 ........ 2 87 ......... 2 88 ......... 1 89......... 2 90..........3 91 ........ 2 92 ......... 3 93 ......... 2 94 ..........4 95 ..........1 96 ........ 3 97 ......... 2 98 ......... 3 99......... 3 100 ..........2
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |
|
#19
| |||
| |||
|
This is the Previous Question Papers Tancet: The most commonly used chemical for dechlorination of water is 1. sodium thiosulphate 2. sodium bisulphate 3. sodium sulphate 4. all of the above 101. The boundary of water of a still lake, represents a 1. level surface 2. horizontal surface 3. contour line 4. concave surface 102. Removal of parallax may be achieved by 1. refocusing the objective 2. refocusing the eye-piece 3. refocusing the objective and eye piece 4. none of the above 103. International date line is located along 1. Standard meridian 2. Greenwich meridian 3. Equator 4. longitude 104. The position of the sun when its north declination is maximum is known as 1. Vernal equinox 2. Autumnal equinox 3. Summer solstice 4. Winter solstice 105. Triangulation surveys are carried out for providing 1. planimetric control 2. height control 3. both planimetric and height control 4. none of the above Previous Question Papers Tancet    
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |