|
#11
| |||
| |||
|
sir,i am studying 3rd year EEE i want to become an IES officer but i don't have minimum knowledge in technical and all IES syllabus so it possible for me also if it is possible how i prepare my time table and any coaching is necessary, if it is necessary which one is best, which type of book is i prepare
|
|
#13
| |||
| |||
|
Indian Engineering Services (IES) the engineering services that meet the technical and managerial functions of the Government of India. As you are asking for UPSC Indian Engineering Services (IES) exam Preparation Material so on your demand I am providing same : UPSC Indian Engineering Services (IES) exam question paper : 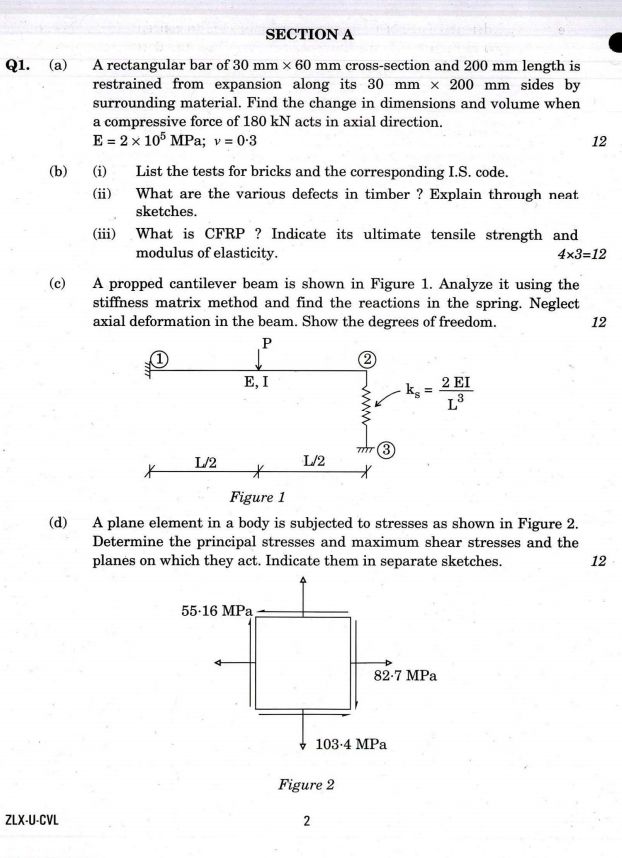 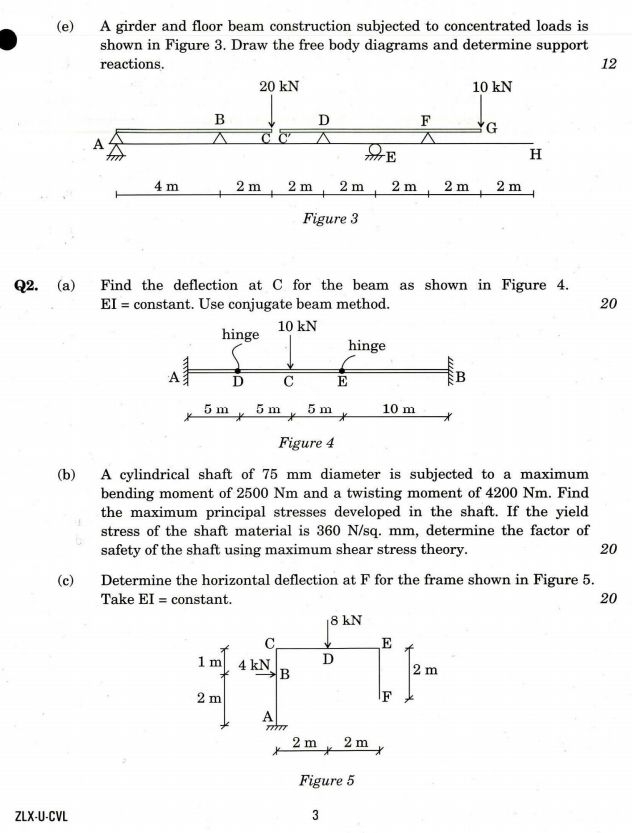 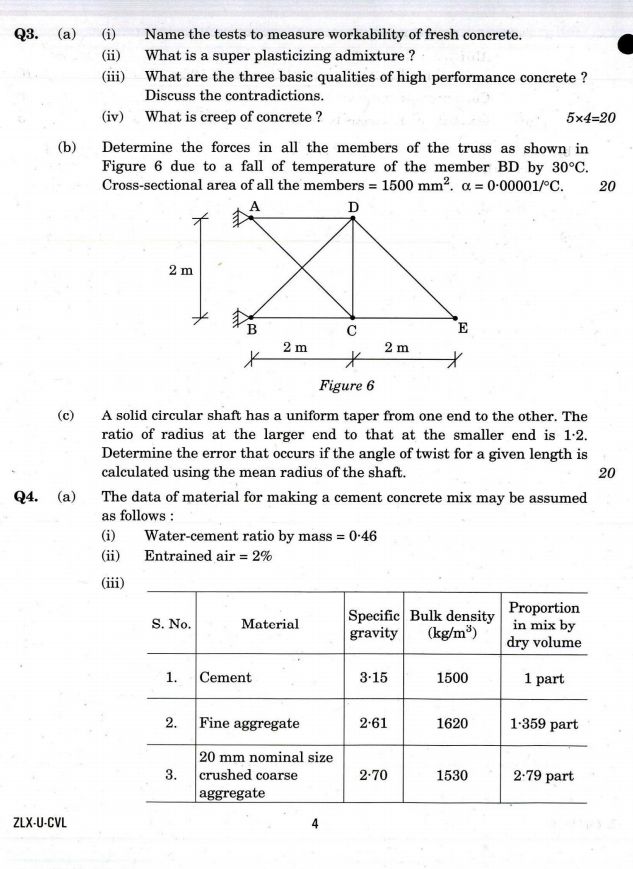  Exam syllabus Branch/Discipline: Civil Engineering (Contents for syllabi of both the Papers together for StageI objective type PaperII and separately for StageII Conventional type PaperI and Paper II) PAPER I 1. Building Materials: Stone Lime Glass Plastics Steel FRP Ceramics Aluminum Fly Ash Basic Admixtures Timber Bricks and Aggregates: Classification properties and selection criteria;Cement: Types Composition Properties Uses Specifications and various Tests; Lime & Cement Mortars and Concrete: Properties and various Tests; Design of Concrete Mixes: Proportioning of aggregates and methods of mix design. 2. Solid Mechanics: Elastic constants Stress plane stress Strains plane strain Mohrs circle of stress and strain Elastic theories of failure Principal Stresses Bending Shear and Torsion. 3. Structural Analysis: Basics of strength of materials Types of stresses and strains Bending moments and shear force concept of bending and shear stresses; Analysis of determinate and indeterminate structures; Trusses beams plane frames; Rolling loads Influence Lines Unit load method & other methods; Free and Forced vibrations of single degree and multi degree freedom system; Suspended Cables; Concepts and use of Computer Aided Design. 4. Design of Steel Structures: Principles of Working Stress methods Design of tension and compression members Design of beams and beam column connections builtup sections Girders Industrial roofs Principles of Ultimate load design. 5. Design of Concrete and Masonry structures: Limit state design for bending shear axial compression and combined forces; Design of beams Slabs Lintels Foundations Retaining walls Tanks Staircases; Principles of prestressed concrete design including materials and methods; Earthquake resistant design of structures; Design of Masonry Structure. 6. Construction Practice Planning and Management: Construction Planning Equipment Site investigation and Management including Estimation with latest project management tools and network analysis for different Types of works; Analysis of Rates of various types of works; Tendering Process and Contract Management Quality Control Productivity Operation Cost; Land acquisition; Labour safety and welfare. PAPER II 1. Flow of Fluids Hydraulic Machines and Hydro Power: (a) Fluid Mechanics Open Channel Flow Pipe Flow: Fluid properties; Dimensional Analysis and Modeling; Fluid dynamics including flow kinematics and measurements; Flow net; Viscosity Boundary layer and control Drag Lift Principles in open channel flow Flow controls. Hydraulic jump; Surges; Pipe networks. (b) Hydraulic Machines and Hydro power Various pumps Air vessels Hydraulic turbines types classifications & performance parameters; Power house classification and layout storage pondage control of supply. 2. Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering: Hydrological cycle Ground water hydrology Well hydrology and related data analysis; Streams and their gauging; River morphology; Flood drought and their management; Capacity of Reservoirs. Water Resources Engineering : Multipurpose uses of Water River basins and their potential; Irrigation systems water demand assessment; Resources storages and their yields; Water logging canal and drainage design Gravity dams falls weirs Energy dissipaters barrage Distribution works Cross drainage works and headworks and their design; Concepts in canal design construction & maintenance; River training measurement and analysis of rainfall. 3. Environmental Engineering: (a) Water Supply Engineering: Sources Estimation quality standards and testing of water and their treatment; Rural Institutional and industrial water supply; Physical chemical and biological characteristics and sources of water Pollutants in water and its effects Estimation of water demand; Drinking water Standards Water Treatment Plants Water distribution networks. (b) Waste Water Engineering: Planning & design of domestic waste water sewage collection and disposal; Plumbing Systems. Components and layout of sewerage system; Planning & design of Domestic Wastewater disposal system; Sludge management including treatment disposal and reuse of treated effluents; Industrial waste waters and Effluent Treatment Plants including institutional and industrial sewage management. (c) Solid Waste Management: Sources & classification of solid wastes along with planning & design of its management system; Disposal system Beneficial aspects of wastes and Utilization by Civil Engineers. (d) Air Noise pollution and Ecology: Concepts & general methodology. 4. Geotechnical Engineering and Foundation Engineering : (a) Geotechnical Engineering : Soil exploration planning & methods Properties of soil classification various tests and interrelationships; Permeability & Seepage Compressibility consolidation and Shearing resistance Earth pressure theories and stress distribution in soil; Properties and uses of geosynthetics. (b) Foundation Engineering: Types of foundations & selection criteria bearing capacity settlement analysis design and testing of shallow & deep foundations; Slope stability analysis Earthen embankments Dams and Earth retaining structures: types analysis and design Principles of ground modifications. 5. Surveying and Geology: (a) Surveying: Classification of surveys various methodologies instruments & analysis of measurement of distances elevation and directions; Field astronomy Global Positioning System; Map preparation; Photogrammetry; Remote sensing concepts; Survey Layout for culverts canals bridges road/railway alignment and buildings Setting out of Curves. (b) Geology : Basic knowledge of Engineering geology & its application in projects. 6. Transportation Engineering: Highways Planning & construction methodology Alignment and geometric design; Traffic Surveys and Controls; Principles of Flexible and Rigid pavements design. Tunneling Alignment methods of construction disposal of muck drainage lighting and ventilation. Railways Systems Terminology Planning designs and maintenance practices; track modernization. Harbours Terminology layouts and planning. Airports Layout planning & design.
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |