|
#1
| |||
| |||
|
Sir here I am searching for the Tata Institute of Social Sciences sample papers with solution so please can you give me the papers and tell me from where can I download the papers with solution?
|
|
#2
| ||||
| ||||
|
I am providing you Tata Institute of Social Sciences sample papers with solution. This question paper is free for you. You can download it whenever you want.    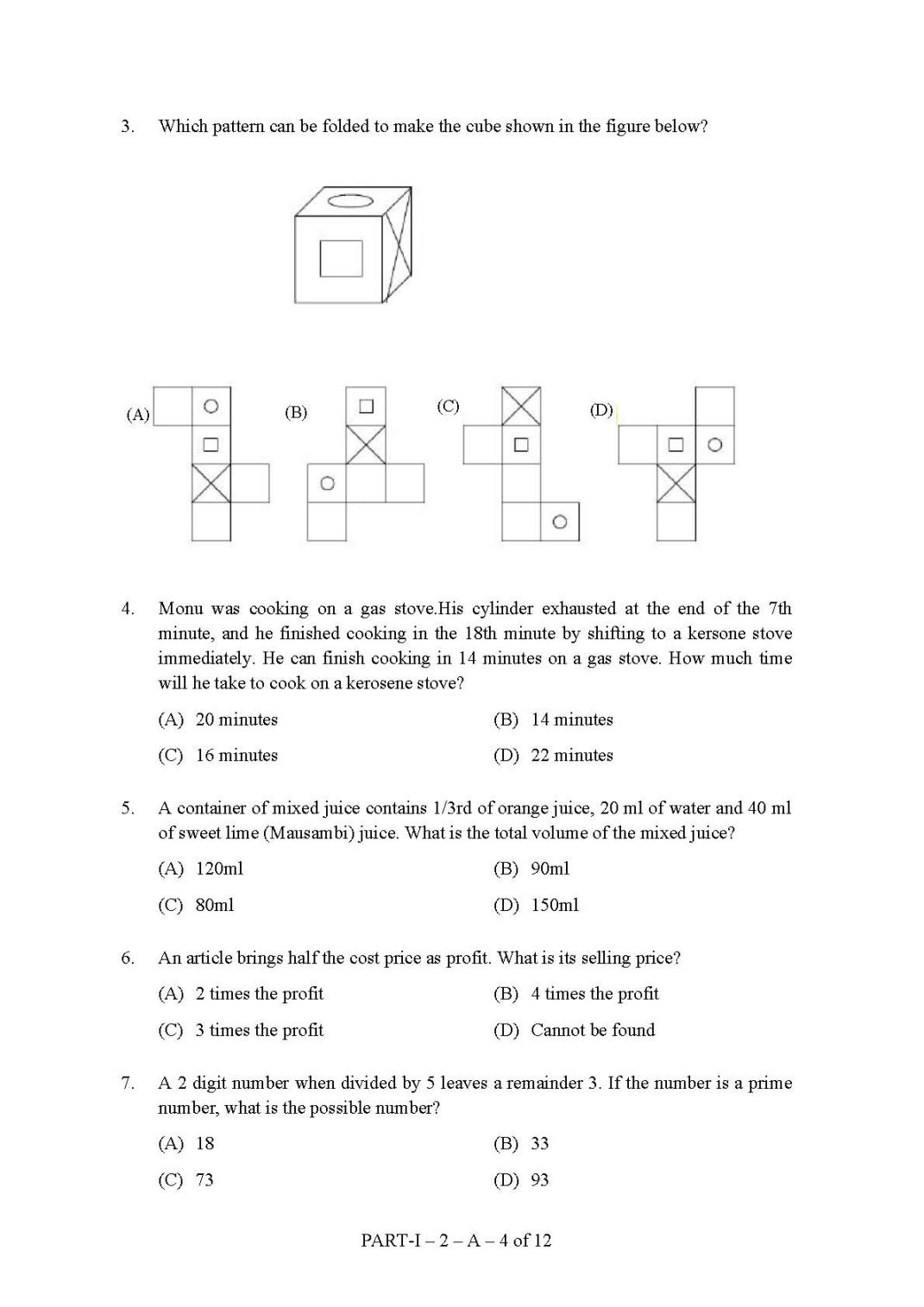
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member Last edited by shabnams; February 17th, 2014 at 05:16 PM. |
|
#5
| ||||
| ||||
|
here I am giving you question paper for Tata Institute of Fundamental Research TIFR entrance examination with it .. Some Questions are given below : Section A (Marks 20) Language abitlity Read the passage provided below and answer the questions that follow: The Teacher Shobha Vajpayee divides her class into groups of five or six children, and soon everyone is engrossed in measuring the length and breath of the classroom to draw a map to scale. She took a moment to share with me her reflections on the episode that had just taken place, and she was quick to acknowledge, “Had it not been for the training I have received, I would certainly have interrupted the girl. The training has helped me learn to respect what the children are saying and be receptive to the why of it.” Shobha was referring to the trainings organised by the NGO as a part of their Social Science Teaching Programme (SSTP). This is an educational innovation that is being tried out in eight schools of Madhya Pradesh. She felt that this exposure had greatly influenced her teaching not just in social science but in other subjects too. “It has changed my entire way of looking at things she exclaimed, saying that now she is able to look beyond rote learning and exams and understand that in every subject there is a scope to discuss the social and attempt the practical.” 1.Who has given training to the teachers? (a) Shobha (b) The NGO (c) The school board (d) Madhya Pradesh government 2. What is the author referring to as an ‘educational innovation’? (a) Children working in groups (b) The teacher (c) The teaching methodology. (d) The social science programme of the NGO. 3. Which of the following sentences is not based upon information given in the passage. (a) Through this programme children achieve more. (b) Through this programme teachers have begun to teach in a different manner. (c) Through this programme social science is being taught differently. (d) Through this programme other subject areas have been influenced. 4. In the sentence ‘It has changed my entire ways of looking at things’ she exclaimed ‘it’ refers to: (a) Children working in groups (b) The training programme (c) The NGO (d) The children 5. In the first sentence of this passage, the word closest in meaning to ‘engrossed’ is: (a) focussed (b) busy (c) working (d) enabled 6. According to the author, in what way has Shobha’s teaching changed? (a) she worked harder (b) she enjoys being with children more (c) she is able to understand ways to handle the subjects better (d) non of the above 7. Which of the following words does not belong to the set: (i) indifferent (ii) involved, (iii) interested (iv) engrossed (a) i (b) iv (c) iii (d) ii 8. The word ‘terminally- ill’ refers to (a) the condition of a person who is very ill. (b) the condition of a person who needs to be hospitalised (c) the condition of a person whose illness will definitely lead to death (c) the condition of a person whose illness has been terminated. 9. .......... all countries in the world, India has the highest level of illiteracy. (a) in (b) of (b) at (d) on 10. “We are all ready to go, but we have not yet received our visas.” This sentence can be rewritten as: (a.) We can go there only if we receive our visa (b) Although we are all ready to go, we are not yet able to as we have not received our visa. (c) Only if we receive our visa we can go. (d) Unless we receive visa we cannot go. Given below is a sentences with a word or phrase underlined. Pick an alternative that can be used in its place, without altering the meaning of the original sentence: 11. On the other hand many parents feel that it is better to begin studying English from Class I. (a) However (b) For this reason (c) Despite this (d) In any case Fill in the appropriate choice to complete the sentence 12. For the first time CIDCO has ...........to implement the green building concept. (a) decides (b) decided (c) decisive (d) decision 13. Which of the following sentences has the same meaning as the sentence provided: In spite of the fact that there has been an increase in the number of schools in rural areas, still many children do not have access. (a)Because there are too many children in rural areas, many of them are not able to access schools. (b)Although there are many more schools now, still there are children who are not able to access schools. (c)Because of the increase in the number of schools, children are not able to get access. (d)The biggest hurdle is giving children access to schools. 14. One of the biggest problem we face in our country is our inability to work in teams. The correct form of this sentence is: (a)One of the big problems we face in our country is our inability to work in teams. (b)One of the biggest problems we face in our country is our inability to work in teams. (c)One of the big problem we face in our country is our inability to work in teams. (d)One of the problem we face in our country is our inability to work in teams. 15. ___ there a better way of getting this thing done? (a) Is (b) Are (c) Of course (d) Which of 16.When she learnt that she had been selected, she was the ................. person in the colony (a) happier (b) happiest (c) happy (d) most happiest Fill in the blanks with the correct word/phrase: The Floor Space Index (FSI)—the permissible built up area on a plot— ___(17) 1.33 for most of Mumbai. The concept of FSI in Mumbai at present is scheme specific ___(18)___ area-specific. 17. (a) were (b) be (c) is (d) being 18. (a) rather than (b) rather (c) instead (d) than instead 19. ‘I am beginning to feel tired’. a) She said she was beginning to feel tired. b) She said I am feeling tired. c) She said she is tired. d) She said she feels tired. 20. “I did not prepare for this examination.’ This sentence is the answer to which of the following questions? a. Did you do this examination? b. Why didn’t you prepare for this examination? c. Did you prepare for this examination? d. Didn’t you prepare for this examination? Section B (Marks 15) Analytical and numerical ability. 21. Study the following figures Which of the following figures is the next in the sequence? 24. After a discount of 11.11%, a trader still makes a gain of 14.28%. At how many percent above the cost price does he mark his goods? (a) 28.56% (b) 35% (c) 22.22% (d) None of these 25. A dealer buys dry fruit at Rs.100, Rs. 80 and Rs. 60 per kg. He mixes them in the ratio 3: 4: 5 by weight, and sells them at a profit of 50%. At what price does he sell the dry fruit? (a) Rs. 80/kg (b) Rs. 100/kg (c) Rs. 95/kg (d) None of these 26. An express train travelling at 80 kmph overtakes a goods train, twice as long and going at 40 kmph on a parallel track, in 54 seconds. How long will the express train take to cross a station 400 m long? (a) 36 sec (b) 45 sec (c) 27 sec (d) None of these 27. The average marks of a student in ten papers are 80. If the highest and the lo west scores are not considered, the average is 81. If his highest score is 92, find the lowest. (a) 55 (b) 60 (c) 62 (d) Cannot be determined. 28. A person starts from a point A and travels 3 km eastwards to B and then turns left and travels thrice that distance to reach C. He again turns left and travels five times the distance he covered between A and B and reaches his destination D. The shortest distance between the starting point and destination is (a) 18 km (b) 16 km (c) 15 km (d) 12 km 29. What is maximum number of pieces of 5 cm x 5 cm x 10 cm cake that can be cut from a big ca ke of 5 cm x30 cm x 30 cm size? (a) 10 (b) 15 (c) 18 (d) 30 30. A rectangular water tank measures 15 m x 6 m at top and is 10 m deep. It is full of water. If water is drawn out lowering the level by 1 meter, how much of water has been drawn out? ? (a) 90,000 litres? (b) 45,000 litres? (c) 4,500 litres? (d) 900 litres 31. The average weight of a class of 24 students is 36 years. When the weight of the teacher is also included, the average weight increases by 1 kg. What is the weight of the teacher? (A) 60 kg (B) 61 kg (C) 37 kg (D) 40 kg Directions (For the next FOUR items): Based on the information given below, answer the four items which follow it : Gopal, Harsh, Inder, Jai and Krishnan live in one of these cities: Ahmedabad, Bhopal, Cuttack, Delhi and Ernakulam (Not necessarily in that order). They' keep only one of the following pets at home: Horse, Rat, Elephant, Dog and cat. (Not necessarily in that order). None of the five children likes the same thing, but each of them likes one of the following: Ice-cream, kebab, Soda, Biryani, Curdrice Further, it is given that: I. Gopal's lives in Ernakulam and likes Ice-cream II. Harsh does not live in Cuttack or Bhopal. . III. The person in Bhopal keeps a rat. IV. Inder's lives in Cuttack. V. Krishnan likes biryani and does not live in Ahmedabad. VI. Jai lives in Delhi and likes curd-rice. VII. There are no dogs or cats in Cuttack, Bhopal or Delhi Based on the information given above answer the next FOUR items: 32. What is Krishnan’s pet? (a) Rat (b) Horse (c) Elephant (d) Cannot be determined 33. Which is in Inder’s pet? (a) Elephant (b) Horse (c) Rat (d) Cannot be determined 34. Who likes Soda? (a) Inder (b) Harsh (c) Harsh or Inder (d) Cannot be determined 35. Which one of the following is the not a possible combination of Person – Hometown - Pet? (a) Gopal - Ernakulam- Dog (b) Jai - Delhi - Elephant (c) Inder - Cuttack - Elephant (d) None of the above Section I: Caselet (5X5=25 marks) The City that Ended Hunger* A city in Brazil did somethin g many cities in the world have yet to do: end hunger. Belo, a city of 2.5 million people, once had 11 percent of its population living in absolute poverty, and almost 20 percent of its children going hungry. Then in 1993, a newly elected administration declared food a right of citizenship. The new mayor, Patrus Ananias began by creating a city agency, which included assembling a 20-member council of citizen, labor, business, and church representatives to advise in the design and implementation of a new food system. The city already involved regular citizens directly in allocating municipal resources through participatory budgeting. During the first six years of Belo’s food-as-aright policy, perhaps in response to the new emphasis on food security, the number of citizens engaging in the city’s participatory budgeting process doubled to more than 31,000. The city of Belo Horizonte puts“Direct From the Country” farmer produce stands throughout busy downtown areas. It offered local family farmers dozens of choice spots of public space on which to sell to urban consumers, essentially redistributing retailer mark-ups on produce—which often reached 100 percent—to consumers and the farmers. Farmers’ profits grew, since there was no wholesaler taking a cut. And poor people got access to fresh, healthy food. In addition to the farmer-run stands, the city makes good food available by offering entrepreneurs the opportunity to bid on the right to use well-trafficked plots of city land for “ABC” markets, where the city determines a set price—about two-thirds of the market price—of about twenty healthy items, mostly from in-state farmers and chosen by store-owners. Everything else they can sell at the market price. Another product of food-as-a-right thinking is three large, airy “People’s Restaurants” (Restaurante Popular), plus a few smaller venues, that daily serve 12,000 or more people using mostly locally grown food for the equivalent of less than 50 cents a meal. “We’re fighting the concept that the state is a terrible, incompetent administrator,” Adriana, a city manager explained. “We’re showing that the state doesn’t have to provide everything, it can facilitate. It can create channels for people to find solutions themselves.” The result of these and other related innovations? In just a decade Belo Horizonte cut its infant death rate—widely used as evidence of hunger—by more than half, and today these initiatives benefit almost 40 percent of the city’s 2.5 million population. One six- month period in 1999 saw infant malnutrition in a sample group reduced by 50 percent. And between 1993 and 2002 Belo Horizonte was the only locality in which consumption of fruits and vegetables went up. The cost of these efforts? Around $10 million annually, or less than 2 percent of the city budget. That’s about a penny a day per Belo resident. Behind this dramatic, life-saving change is what Adriana calls a “new social mentality”—the realization that “everyone in our city benefits if all of us have access to good food, so—like health care or education—quality food for all is a public good.” The Belo experience shows that a right to food does not necessarily mean more public handouts (although in emergencies, of course, it does.) It can mean redefining the “free” in “free market” as the freedom of all to participate. It can mean, as in Belo, building citizen-government partnerships driven by values of inclusion and mutual respect. Based on the above passage, answer the following questions: 1. State the main initiatives of the city government to end hunger. __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ 2. What, according to you are the key factors that brought about this change? __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ 3. What lessons do you draw from this case? __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ 4. Do you subscribe to the need of ‘redefining free in free market’? Why? __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ 5. As a person and as a habitat professional, how do you perceive the widespread existence of hunger and poverty in our cities? __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ __________________________________________________ ______________________ Section II: Language (15X1=15 marks) Identify the suitable set of words that would fit the sentences given below 6. In this context, the __________of the British labor movement is particularly ____. a. Affair, weird b. activity, moving c. experience, significant d. atmosphere, gloomy 7. Since her face was free of _____________ there was no way to _________ if she appreciates what had happened a. Make-up, realize b.Expression, ascertain c.Emotion, diagnose d.Scars, understand 8. The Darwin who ______________is the most remarkable for the way in which he _______the various attributes of the world class thinker and head of the household A Comes, figures b.Arises, adds c Emerges, combines d Appeared, combines 9. Indian intellectuals may boast, if they are so inclined, of being __________to the most elitist among the intellectual ______ of the world a. Subordinate, traditions b. Heirs, cliques c. Ancestors, societies d. Heir, tradition 10. But _____________ are now regularly written to describe well-established practices, organizations and institutions, not all of which seem to be ____________away. a.Reports, withering b.Stories, trading c.Books, dying d.Obituaries, fading Tick the correct answers 11. A democratic school should understand school dropout from the student’s point of view. This sentence is an answer to the question: a) Why should a school take the student’s view point? b) How should a democratic school understand drop out? c) When should a school take a student’s view point? d) Who should understand drop out? 12. Which of the following two sentences mean the same? i) Although he wanted to go home, he kept on working ii) In spite of wanting to go home, he kept on working iii) Even though he wanted to go home, he kept on working a) (i) and (ii) b) (ii) and (iii) c) (iii) and (i) d) All of them mean the same 13. A positive development this time was the _________________number of women candidates who qualified the written examination a) largest b) larger c) largely d) large 14____________ this diary is found, please return it to the owner at the above address a) Whenever b) Whomever c) If d) Supposedly 15.He said: I will come tomorrow a)He said that he will come the next day b)He said that he would come tomorrow c)He said that he would come the next day d)He said that I would come the next day 16. Since the escaping vapors proved to be highly -, measures were at once taken for the - of the experiments. a. Volatile – ratification b. Observable – insulation c. Gaseous – reduction d. Noxious – cessation 17. As man reached the stars, a booming populatio n threatened to destroy the - of life on his home planet and even its chances for – a. Quality – survival b. Basis – growth c. Existence – upliftment d. Chances – improvement 18.Until the current warming trend exceeds the range of normal climatic fluctuations, there will be, among scientists, considerable - the possibility that increasing levels of atmosphere Co2 can cause long term warming effects a. interest in b. uncertainty about c. enthusiasm for d. worry about 19.To meet all __________ a source of _________ electrical power was added to the train's engine. a. Integuments - parallel b. possibilities - incidental c. amenities - diverse d. contingencies – auxiliary 20.Slang is a language that rolls up its sleeves, spits on its hands and - a.goes to work b.stays cool c.embarrasses its user d.communicates Section III: Reasoning and Aptitude (10X1=10marks) 21. The term ‘FDI’ stands for: a. Foreign Directed Investment b. Floor Development Index c. Foreign Direct Investment d. Fundamental Development Index 22. The increase in populatio n of a city includes: a.Natural increase in population b.In- migration to the city c.Increase in population due to reconstitution of boundaries d.All of the above 23. The highest number of SEZ proposals submitted is in the state of a.Maharashtra b.Gujarat c.Andhra Pradesh d.Punjab 24.Trace the commonality in the cities given below and trace the odd one out. a.Ahmedabad b.Bangalore c.Bhubaneshwar d.Delhi 25.Which of the following is not a dimension of sustainability? a.Intergenerational b.Ever increasing productivity and incomes c.Environmental considerations d.Social sustainability 26.Which Constitutional Amendments Act (CAA) provided for 33% reservation for women in local bodies? a.73rd and 74th CAA b.83rd CAA c.64th & 68th CAA d.91st CAA 27.Mumbai accounts for 6.6% of India’s GDP in 2006-07. This means – a.Mumbaikars have 6.6% of country’s income b.Mumbai pays 6.6% of country’s taxes c.6.6% of total production value of Indian goods and services are produced in Mumbai d.6.6% of India’s General Development Fund is spent on Mumbai 28.The biggest difference in a slum and non-slum area is: a.Poor living environment b.Poverty c.Presence of illegal activities d.Lack of safety 29.The Assembly of all adult residents of the village is: a.Area sabha b.Gram sabha c.Election d.Lok adalat 30.Which of the following is a right accorded by the Indian State? a.Education b.Housing c.Health d.Sanitation Contact Details : Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Dr. Homi Bhabha Road, Navy Nagar, Colaba, Mandir Marg, TIFR, Old Navy Nagar, Colaba, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400005 022 2280 4545 •
__________________ Answered By StudyChaCha Member |